Nabitan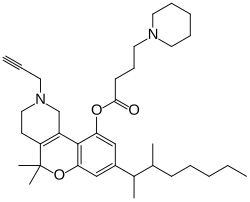 |
|
| Other names | Nabutam, benzopyranoperidine, SP-106, Abbott 40656 |
|---|
| Drug class | Cannabinoid |
|---|
| ATC code | |
|---|
|
5,5-Dimethyl-8-(3-methyloctan-2-yl)-2-(prop-2-yn-1-yl)-1,3,4,5-tetrahydro-2H-[1]benzopyrano[4,3-c]pyridin-10-yl 4-(piperidin-1-yl)butanoate
|
| CAS Number | |
|---|
| PubChem CID | |
|---|
| ChemSpider | |
|---|
| UNII | |
|---|
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
|---|
|
| Formula | C35H52N2O3 |
|---|
| Molar mass | 548.812 g·mol−1 |
|---|
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
|---|
O=C(Oc2cc(cc1OC(C\3=C(/c12)CN(CC/3)CC#C)(C)C)C(C)C(C)CCCCC)CCCN4CCCCC4
|
InChI=1S/C35H52N2O3/c1-7-9-11-15-26(3)27(4)28-23-31(39-33(38)16-14-21-36-19-12-10-13-20-36)34-29-25-37(18-8-2)22-17-30(29)35(5,6)40-32(34)24-28/h2,23-24,26-27H,7,9-22,25H2,1,3-6H3  Y YKey:MCVPMHDADNVRKF-UHFFFAOYSA-N  Y Y
|
| (verify) |
Nabitan (nabutam, benzopyranoperidine, SP-106, Abbott 40656) is a synthetic cannabinoid analog of dronabinol (Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol) and dimethylheptylpyran.[1] It exhibits antiemetic and analgesic effects, most likely by binding to and activating the CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors, and reduced intraocular pressure in animal tests, making it potentially useful in the treatment of glaucoma.[2]
Nabitan has the advantage of being water-soluble, unlike most cannabinoid derivatives, and was researched for potential use as an analgesic or sedative,[3] although it was never developed for clinical use and is not currently used in medicine, as dronabinol or nabilone were felt to be more useful. However, it is sometimes used in research into the potential therapeutic applications of cannabinoids.
See also
References
|
|---|
Phytocannabinoids
(comparison) | | Cannabibutols | |
|---|
| Cannabichromenes | |
|---|
| Cannabicyclols | |
|---|
| Cannabidiols | |
|---|
| Cannabielsoins | |
|---|
| Cannabigerols | |
|---|
| Cannabiphorols | |
|---|
| Cannabinols |
- CBN
- CBNA
- CBN-C1
- CBN-C2
- CBN-C4
- CBNM
- CBND
- CBNP
- CBVD
|
|---|
| Cannabitriols | |
|---|
| Cannabivarins | |
|---|
| Delta-3-tetrahydrocannabinols | |
|---|
| Delta-4-tetrahydrocannabinols | |
|---|
| Delta-7-tetrahydrocannabinols | |
|---|
| Delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinols | |
|---|
| Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinols | |
|---|
| Delta-10-Tetrahydrocannabinols | |
|---|
| Delta-11-Tetrahydrocannabinols | |
|---|
| Miscellaneous cannabinoids | |
|---|
| Active metabolites | |
|---|
|
|---|
| Endocannabinoids | |
|---|
Synthetic
cannabinoid
receptor
agonists /
neocannabinoids | Classical cannabinoids
(dibenzopyrans) | |
|---|
Non-classical
cannabinoids | |
|---|
| Adamantoylindoles | |
|---|
| Benzimidazoles | |
|---|
| Benzoylindoles | |
|---|
| Cyclohexylphenols | |
|---|
| Eicosanoids | |
|---|
Indazole-3-
carboxamides | |
|---|
| Indole-3-carboxamides | |
|---|
| Indole-3-carboxylates | |
|---|
| Naphthoylindazoles | |
|---|
| Naphthoylindoles | |
|---|
| Naphthoylpyrroles | |
|---|
| Naphthylmethylindenes | |
|---|
| Naphthylmethylindoles | |
|---|
| Phenylacetylindoles | |
|---|
| Pyrazolecarboxamides | |
|---|
Tetramethylcyclo-
propanoylindazoles | |
|---|
Tetramethylcyclo-
propanoylindoles | |
|---|
| Others | |
|---|
|
|---|
| Allosteric CBRTooltip Cannabinoid receptor ligands | |
|---|
Endocannabinoid
enhancers
(inactivation inhibitors) | |
|---|
Anticannabinoids
(antagonists/inverse
agonists/antibodies) | |
|---|
|
|
|---|
Psychedelics
(5-HT2AR agonists) |
- Tryptamines (e.g., DMT, psilocin, psilocybin, bufotenin, 5-MeO-DMT, AMT)
- Phenethylamines (e.g., mescaline, 2C-B, DOM, MDA, TMA, 2C-B-FLY, 25I-NBOMe)
- Lysergamides (e.g., LSD, ergine, isoergine)
- Others (e.g., quipazine, efavirenz)
- For a full list of serotonergic psychedelics, see the navbox here and the list here instead.
|
|---|
Dissociatives
(NMDAR antagonists) | |
|---|
Deliriants
(mAChR antagonists) | |
|---|
Cannabinoids
(CB1R agonists) | |
|---|
| κOR agonists | |
|---|
| GABAAR agonists | |
|---|
Inhalants
(mixed MoATooltip mechanism of action) | |
|---|
| Others |
- Aminochromes (e.g., adrenochrome, adrenolutin)
- Carbogen
- Certain GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators (nonbenzodiazepines/Z-drugs) (e.g., eszopiclone, zaleplon, zolpidem, zopiclone)
- CI-966
- Cryogenine
- Glaucine
- Hallucinogenic bolete mushrooms (e.g., Lanmaoa asiatica)
- Harmala alkaloids/β-carbolines (e.g., harmaline, 6-methoxyharmalan)
- Iboga alkaloids/azepinoindoles (e.g., ibogaine)
- Isoaminile
- Noscapine
- Nutmeg (e.g., myristicin, elemicin)
- Oneirogens (e.g., Calea zacatechichi, galantamine, nicotine, Silene capensis)
- Prenoxdiazine
- Pukateine
|
|---|
|
|
|---|
Receptor
(ligands) | | CB1Tooltip Cannabinoid receptor type 1 | Agonists
(abridged,
full list) | |
|---|
| Inverse agonists | |
|---|
| Antagonists | |
|---|
|
|---|
| CB2Tooltip Cannabinoid receptor type 2 | | Agonists |
- 2-AG
- 2-AGE (noladin ether)
- 3,3'-Diindolylmethane
- 4-O-Methylhonokiol
- α-Amyrin · β-Amyrin
- A-796,260
- A-834,735
- A-836,339
- AM-1172
- AM-1221
- AM-1235
- AM-1241
- AM-2232
- Anandamide
- AZ-11713908
- Cannabinol
- Caryophyllene
- CB-13
- CBS-0550
- CP 55,940
- GW-405,833 (L-768,242)
- GW-842,166X
- HU-308
- JTE 7-31
- JWH-007
- JWH-015
- JWH-018
- JWH-73
- JWH-133
- L-759,633
- L-759,656
- Lenabasum (anabasum)
- Magnolol
- MDA-19
- NADA
- Olorinab (APD-371)
- PF-03550096
- S-444,823
- SER-601
- Serinolamide A
- UR-144
- Tedalinab
- THC (dronabinol)
- THCV
- Tetrahydromagnolol
- Virodhamine
|
|---|
| Antagonists | |
|---|
|
|---|
NAGly
(GPR18) | |
|---|
| GPR55 | |
|---|
| GPR119 | |
|---|
|
|---|
Transporter
(modulators) | | eCBTsTooltip Endocannabinoid transporter | |
|---|
|
|---|
Enzyme
(modulators) | | FAAHTooltip Fatty acid amide hydrolase | |
|---|
| MAGL | |
|---|
| ABHD6 |
- Inhibitors: JZP-169
- JZP-430
- KT182
- KT185
- KT195
- KT203
- LEI-106
- ML294
- ML295
- ML296
- UCM710
- WWL-70
|
|---|
| ABHD12 | |
|---|
|
|---|
| Others |
- Others: 2-PG (directly potentiates activity of 2-AG at CB1 receptor)
- ARN-272 (FAAH-like anandamide transporter inhibitor)
|
|---|
- See also
- Receptor/signaling modulators
- Cannabinoids (cannabinoids by structure)
|
