Portal:Germany
Welcome to the Germany Portal!
Willkommen im Deutschland-Portal!

|

|
| |
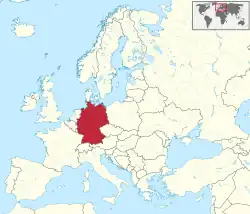
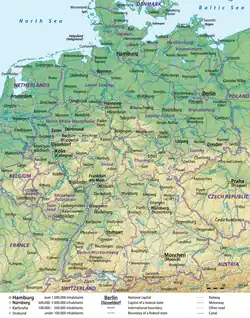
Germany (German: Deutschland), officially the Federal Republic of Germany (German: Bundesrepublik Deutschland), is a country in Central and Western Europe, lying between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. It borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, France to the southwest, and Luxembourg, Belgium and the Netherlands to the west.
Germany includes 16 constituent states, covers an area of 357,596 square kilometres (138,069 sq mi) and has a largely temperate seasonal climate. With nearly 83 million inhabitants, it is the second most populous state of Europe after Russia, the most populous state lying entirely in Europe, as well as the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is a very decentralized country. Its capital and most populous city is Berlin, while Frankfurt serves as its financial capital and has the country's busiest airport.
In 1871, Germany became a nation-state when most of the German states unified into the Prussian-dominated German Empire. After World War I and the Revolution of 1918–19, the empire was replaced by the parliamentary Weimar Republic. The Nazi seizure of power in 1933 led to World War II, and the Holocaust. After the end of World War II in Europe and a period of Allied occupation, two new German states were founded: West Germany, formed from the American, British, and French occupation zones, and East Germany, formed from the western part of the Soviet occupation zone, reduced by the newly established Oder-Neisse line. Following the Revolutions of 1989 that ended communist rule in Central and Eastern Europe, the country was reunified on 3 October 1990.
Germany is a federal parliamentary republic led by a chancellor. It is a great power with a strong economy. As a global leader in several industrial, scientific and technological sectors, it is a major trading nation. The Federal Republic of Germany was a founding member of the European Economic Community in 1957 and the European Union in 1993. Read more...
Selected article

Felix Mendelssohn (3 February 1809 – 4 November 1847) was a German composer, pianist, organist and conductor of the early Romantic period.
A grandson of the philosopher Moses Mendelssohn, Felix Mendelssohn was born into a prominent Jewish family. He was brought up without religion until the age of seven, when he was baptised as a Reformed Christian. Mendelssohn was recognised early as a musical prodigy, but his parents were cautious and did not seek to capitalise on his talent.
Mendelssohn enjoyed early success in Germany, where he also revived interest in the music of Johann Sebastian Bach, and in his travels throughout Europe. He was particularly well received in Britain as a composer, conductor and soloist, and his ten visits there – during which many of his major works were premiered – form an important part of his adult career. His essentially conservative musical tastes, however, set him apart from many of his more adventurous musical contemporaries such as Franz Liszt, Richard Wagner, Charles-Valentin Alkan and Hector Berlioz. The Leipzig Conservatoire (now the University of Music and Theatre Leipzig), which he founded, became a bastion of this anti-radical outlook. More...
Selected picture
Related portals
- Parent portals
- Regional
Rhön
 Baden-Württemberg
Baden-Württemberg Bavaria
Bavaria Berlin
Berlin Brandenburg
Brandenburg Hamburg
Hamburg Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony.svg.png) Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
Mecklenburg-Vorpommern Ore Mountains
Ore Mountains North Rhine-Westphalia
North Rhine-Westphalia Rhineland-Palatinate
Rhineland-Palatinate Saxony
Saxony
- History
 Holy Roman Empire (900–1806)
Holy Roman Empire (900–1806) East Germany (1949–1990)
East Germany (1949–1990)
- Neighbouring countries
Anniversaries for August 20

- 1639 – Death of poet Martin Opitz von Boberfeld
- 1854 – Death of philosopher Friedrich Wilhelm Joseph von Schelling
- 1915 – Death of scientist Paul Ehrlich, recipient of the 1908 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
- 1917 – Death of chemist Adolf von Baeyer, recipient of the 1905 Nobel Prize in Chemistry
Did you know...

- ... that the Munich kitchen was developed because the Stuttgart kitchen (example pictured did not allow a housewife to look after her children?
- ... that Hans Ephraimson-Abt began advocating for better support for families of aviation-accident victims after his daughter's death on Korean Air Lines Flight 007 in 1983?
- ... that some of the interior decoration of the Ernst-Haeckel-Haus is inspired by jellyfish?
- ... that Olympic silver medallist Eduard von Lütcken captured a Russian general before being killed in an early action of the First World War?
- ... that attempted crimes with no chance of success are still punishable by law in Germany?
- ... that German equestrian Hermann Weiland competed for Croatia at the 1992 Summer Olympics, but marched with Guam during the opening ceremony?
- ... that the first volume of Felix Klein's books on the history of mathematics does not mention the three women who originally transcribed his lectures?
- ... that German athlete Leander Wiegand received a scholarship to play American football at an American college that had never seen him play?
Selected cuisines, dishes and foods

Handkäse (pronounced [ˈhantkɛːzə]; literally: "hand cheese") is a German regional sour milk cheese (similar to Harzer) and is a culinary specialty of Frankfurt am Main, Offenbach am Main, Darmstadt, Langen, and other parts of southern Hesse. It gets its name from the traditional way of producing it: forming it with one's own hands.
Handkäse is a small, translucent, yellow cheese. It has a pungent aroma, and a sour taste. (Full article...)Topics
Categories

Things you can do

A list of articles needing cleanup associated with this project is available. See also the tool's wiki page and the index of WikiProjects.
Here are some tasks you can do. Please remove completed tasks from the list.
- Requests: German Archaeological Institute at Rome, Deutsche Familienversicherung, Dietlof von Arnim-Boitzenburg, Rolf von Bargen, Hennes Bender, Eduard Georg von Bethusy-Huc, Rolf Brandt (1886–1953), Jan Philipp Burgard, Rudolf Epp, Lisa Feller, Georg Arbogast von und zu Franckenstein, Georg Gafron, Ferdinand Heribert von Galen, Gundula Gause, Wolfgang von Geldern, Karl-Heinz Hagen, Herbert Helmrich, Nils von der Heyde, Monty Jacobs (1875–1945), Siegfried Kauder, Klimbim Matze Knop, Wolfgang Kryszohn, Claus Larass, Isidor Levy (1852–1929), Markus Löning, Tobias Mann, Mathias Müller von Blumencron ,Günther Nonnenmacher, Nord bei Nordwest, Günter von Nordenskjöld, Anke Plättner, Hans Heinrich X. Fürst von Pless, Günter Prinz, Ulrich Reitz, Hans Sauer (inventor), Franz August Schenk von Stauffenberg, Paul Schlesinger (1878-1928), Hajo Schumacher, Der Seewolf (1971), Otto Theodor von Seydewitz, Christoph Sieber (comedian), Dorothea Siems, Werner Sonne, Udo zu Stolberg-Wernigerode, Christoph Strässer, Joseph von Utzschneider, Hedda von Wedel, Jürgen Wieshoff, Hans Wilhelmi, Dietmar Wischmeyer, Alexandra Würzbach
- Unreferenced: especially Unreferenced BLPs
- Cleanup: 53541 issues in total as of 2024-03-03
- Translate: Articles needing translation from German Wikipedia
- Stubs: the largest stub category is Category:German history stubs; see also 114 articles in Category:German MEP stubs
- Update: Deutsches Wörterbuch
- : Update News, Did you know, announcements and the todo list
- Orphans:
Orphaned articles in Germany

- Photo: Take/Add requested photographs
- Help assess the quality of 907 unassessed articles
WikiProject Germany • German-speaking noticeboard • More resources...
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
-
 List of all portals
List of all portals -

-

-

-

-

-
-

-

-

-
 Random portal
Random portal -
 WikiProject Portals
WikiProject Portals



.jpg)









.jpg)

.jpg)