Portal:East Germany
|
Subject area: East Germany: | Project pages | Contact | Our best | Category
"Gruß" and welcome!
The East Germany portal offers an overview of the most important and newest articles on the subject of East Germany, the former Communist state officially known as the German Democratic Republic or GDR The portal contains links to a cross-section of articles from the areas of history and politics, geography and economy, art and culture, and some of the important personalities from the region.
Introduction
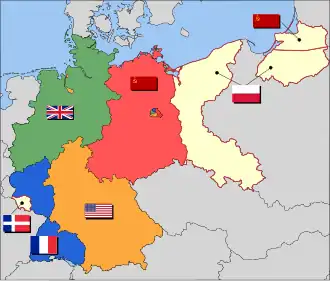
East Germany, officially known as the German Democratic Republic (GDR), was a country in Central Europe from its formation on 7 October 1949 until its reunification with West Germany (FRG) on 3 October 1990. Until 1989, it was generally viewed as a communist state and described itself as a socialist "workers' and peasants' state". The economy of the country was centrally planned and state-owned. Although the GDR had to pay substantial war reparations to the Soviets, its economy became the most successful in the Eastern Bloc. Before its establishment, the country's territory was administered and occupied by Soviet forces following the Berlin Declaration abolishing German sovereignty in World War II. The Potsdam Agreement established the Soviet-occupied zone, bounded on the east by the Oder–Neiße line. The GDR was dominated by the Socialist Unity Party of Germany (SED), a communist party, before being democratized and liberalized in 1989 as a result of the pressure against communist governments brought by the revolutions of 1989. This paved the way for East Germany's reunification with West Germany. Unlike the government of West Germany, the SED did not see its state as the successor to the German Reich (1871–1945). In 1974, it abolished the goal of unification in the constitution. The SED-ruled GDR was often described as a Soviet satellite state; historians described it as an authoritarian regime. (Full article...) | ||||
|
Selected article -
Margot Honecker (née Feist; 17 April 1927 – 6 May 2016) was an East German politician and influential member of the country's Communist government until 1989. From 1963 until 1989, she was Minister of National Education (Ministerin für Volksbildung) of the German Democratic Republic (GDR). She was married to Erich Honecker, leader of East Germany's ruling Socialist Unity Party from 1971 to 1989 and concurrently from 1976 to 1989 the country's head of state. Margot Honecker was widely referred to as the "Purple Witch" ("Lila Hexe" in German) for her tinted hair and hardline Stalinist views. She was responsible for the enactment of the "Uniform Socialist Education System" in 1965 and mandatory military training in schools to prepare pupils for a future war with the west. She was alleged to have been responsible for the regime's forced adoption of children of jailed dissidents or people who attempted to flee the GDR, and is considered to have "left a cruel legacy of separated families." Honecker also established prison-like institutions for children, including a camp at Torgau known as "Margot's concentration camp." She was one of the few spouses of a ruling Communist Party leader who held significant power in her own right, as her prominence in the regime predated her husband's ascension to the leadership of the SED. Following the downfall of the communist regime in 1990, Honecker fled to the Soviet Union with her husband to avoid criminal charges from the government of reunified Germany. Their asylum pleas were never acted upon in light of similar problems befalling the Soviet government. Fearing extradition to Germany, they took refuge in the Chilean embassy in Moscow in 1991, but the following year her husband was extradited to Germany by Yeltsin's Russian government to face criminal trial, and detained in the Moabit prison. Margot Honecker then fled from Moscow to Chile to avoid a similar fate. At the time of her death, she lived in Chile with her daughter Sonja. (Full article...) Geography and nature
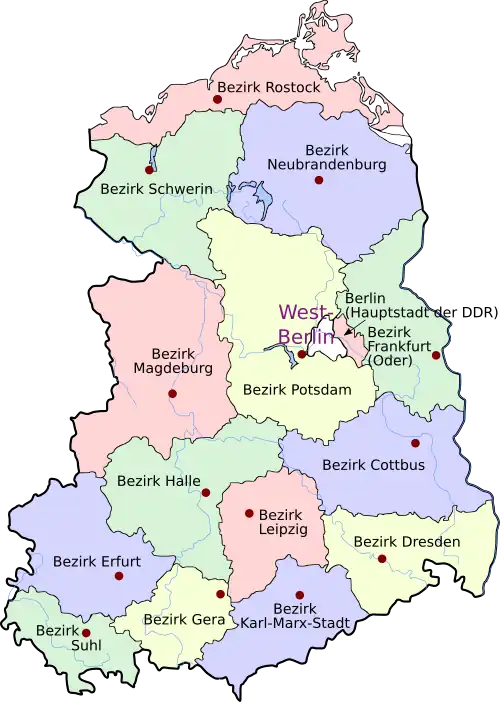 The German Democratic Republic, which consisted geographically of what is now eastern Germany, had an area of 107,771 km2 (41,610 mi2), bordering Czechoslovakia in the south, West Germany in the south and west, the Baltic Sea to the north, and Poland in the east. Much of the territory of the former East Germany lay on the North German Plain and was largely flat and agricultural apart from low morainic hills left by the ice age. However in the south the land rose to the Ore Mountains and Elbe Sandstone Mountains that formed the border with its Communist neighbour, Czechoslovakia. Administration divisions (Bezirke): Berlin – Cottbus – Dresden – Erfurt – Frankfurt (Oder) – Gera – Halle – Karl-Marx-Stadt – Leipzig – Magdeburg – Neubrandenburg – Potsdam – Rostock – Schwerin – Suhl Cities and towns: Altenburg – Apolda – Bautzen – Brandenburg/Havel – Cottbus – Dessau – Dresden – Eberswalde – Eisenach – Stalinstadt/Eisenhüttenstadt – Erfurt – Frankfurt (Oder) – Freiberg – Gera – Görlitz – Gotha – Greifswald – Halberstadt – Halle – Halle-Neustadt – Hoyerswerda – Jena – Chemnitz/Karl-Marx-Stadt – Leipzig – Magdeburg – Merseburg – Neubrandenburg – Plauen – Potsdam – Rostock – Schwedt – Schwerin – Stralsund – Suhl – Weimar – Wismar – Wittenberg – Zittau – Zwickau Rivers and canals: Elbe – Gera - Havel – Neiße – Oder – Saale – Spree – Unstrut – White Elster – Black Elster – Mittelland Canal – Werra Waterbodies: Müritz – Schweriner See – Plauer See – Kummerower See – Scharmützelsee – Werbellinsee – Großer Müggelsee – Bay of Greifswald – Oderhaff Islands: Rügen – Poel – Usedom – Hiddensee – Greifswalder Oie Mountain and hill ranges: Ore Mountains – Harz – Elbe Sandstone Mountains – Thuringian Forest – Thuringian Highland – Vogtland – Kyffhäuser – Rhön – Zittau Mountains Regions: Dresden Elbe Valley – Lusatia – Spreewald – Mecklenburg Lake District – Barnim – Fläming – Magdeburg Börde – Altmark – Saxon Switzerland – Eichsfeld History, politics and religion
History: 1953 Uprising – Dacha – Four Power Agreement on Berlin – Basic Treaty, 1972 – Permanent representative – Palace of the Republic – Begrüßungsgeld GDR border: Treaty of Zgorzelec – Berlin Wall – Inner German border – Border crossings – Berlin Friedrichstraße station – Checkpoint Charlie – Marienborn border crossing – Spring-gun – Republikflucht – Mindestumtausch Die Wende: Monday demonstrations – Social Democratic Party – 1990 General Election – Treuhand – Two Plus Four Agreement – Reunification (Einigungsvertrag) – Stasi Records Agency – Ostalgie  Politics: State flag – National Emblem – National hymn – Constitution – Volkskammer (People's Chamber) – State Council – Council of Ministers – National Front – Socialist Unity Party – Bloc party – Christian Democratic Union – Liberal Democratic Party – Democratic Farmers' Party – National Democratic Party – Administrative divisions (Bezirke) "Mass organisations": Free German Youth – Free German Trade Union Federation – Cultural Association of the GDR – Democratic Women's League of Germany – People's Solidarity – Society for German–Soviet Friendship – Ernst Thälmann Pioneer Organisation Armed bodies: National People's Army – Border Troops – Schießbefehl – Stasi – Hauptverwaltung Aufklärung (Main Directorate for Reconnaissance) – Volkspolizei – Combat Groups – Volksmarine – Armeegeneral – Marshal – Warsaw Pact – Construction soldier Other orders: Orders, decorations, and medals of East Germany – Banner of Labour – Order of Karl Marx – National Prize of the German Democratic Republic – Scharnhorst Order – Star of People's Friendship – Blücher Order .jpg) Religion: Evangelical Church in Berlin, Brandenburg and Silesian Upper Lusatia – Evangelical Lutheran Church of Mecklenburg – Pomeranian Evangelical Church – Evangelical Church of the Church Province of Saxony– Evangelical Lutheran Church in Thuringia – Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Berlin – Roman Catholic Diocese of Dresden-Meissen – Roman Catholic Diocese of Erfurt – Roman Catholic Diocese of Görlitz – Roman Catholic Diocese of Magdeburg
Education, culture and sport
 Education and science: Education in East Germany – Academy of Sciences of the German Democratic Republic– Charité – Humboldt University of Berlin – Erweiterte Oberschule – Polytechnic Secondary School – Tierpark Berlin – Muttiheft Language: German – Berlinerisch – Sorbian Culture: Culture of East Germany – Classical Weimar Art: Theater am Schiffbauerdamm – Semperoper Architecture: Bauhaus World Heritage Site - Fernsehturm Berlin - Krämerbrücke - Plattenbau - Prora Music: List of classical composers – Ostrock Film: DEFA – DEFA Film Library - Kino International - List of films set in Berlin Places of interest: Dresden Castle – Sanssouci – Dessau-Wörlitz Garden Realm Cathedrals and churches: Berlin Cathedral – Erfurt Cathedral – Naumburg Cathedral Museums and collections: DDR Museum - German Hygiene Museum - Memorial and Education Centre Andreasstrasse - Museum Island – Old Synagogue (Erfurt) - Pergamon Museum - Stasi Museum - Tränenpalast Sport: List of football clubs – GDR Football Association – DDR-Oberliga – FDGB-Pokal – 1. FC Union Berlin – Berliner FC Dynamo – Dynamo Dresden – FC Carl Zeiss Jena – Red Bull Arena East German people
 Politicians: Benjamin – Bergmann-Pohl – Böhme – Dertinger – Dieckmann – Fechner – Gerlach – Götting – G. Gysi – Hager – H. Hoffmann – Th. Hoffmann – E. Honecker – M. Honecker – Keßler – Krack – Krenz – de Maizière – Maleuda – Mielke – Mittag – Modrow – Neumann – Norden – Schabowski – Schalck-Golodkowski – Sindermann – Stoph – Tisch – Ulbricht – Verner – M. Wolf – Wollweber – Zaisser Opposition and resistance: Bahro – Biermann – M. Birthler – Bohley – Brüsewitz – Eppelmann – Fuchs – Führer – Gauck – Havemann – Ullmann Scientists: von Ardenne Artists, playwrights, poets, writers: Andersen Nexø – Baierl – Brecht – Busch – Esche – Hacks – Heym – Kant – H. Müller – Noll – Plenzdorf – Anna Seghers – Strittmatter – Tübke – Weigel – Chr. Wolf – Womacka Athletes: Cierpinski – Emmrich – Geyer – Hoppe – Langhammer – Laser – Recknagel – Sammer – Täve Schur – Siegl – Sparwasser – Streich – Weißflog – Witt |
General images
The following are images from various East Germany-related articles on Wikipedia.
Quick start
Wikimedia Commons has media related to East Germany.
Wikipedia in the local dialects
Category tree
Did you know?
... that Ostalgie is a German term referring to nostalgia for aspects of the old life in East Germany?
Image of the month
Related portals
Wanted articles
The following are wanted articles, related to East Germany, that exist on German Wikipedia, or are otherwise wanted.
| |||
|
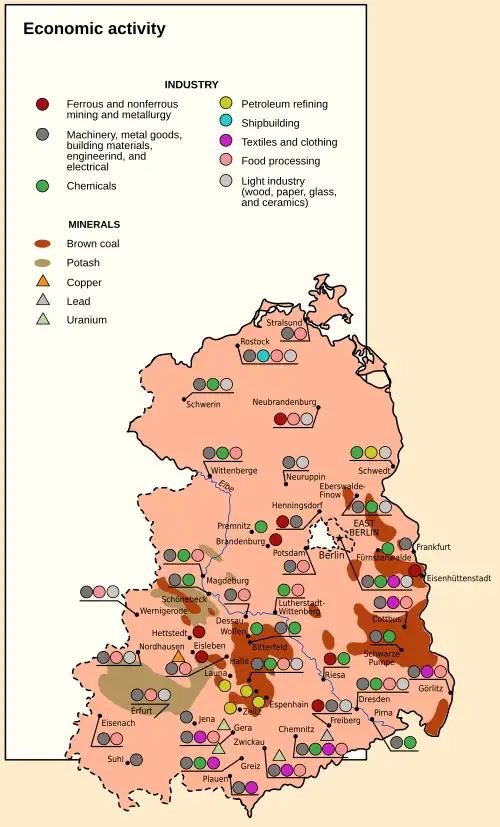
Economy and transport
 Finance: Mindestumtausch – Forum check – East German mark – Staatsbank Cuisine: Broiler – Ketwurst – Soljanka Media: Censorship in East Germany Newspapers and magazines: Berliner Zeitung – Neues Deutschland – Junge Welt – Der Morgen – Sputnik – Mosaik – FRÖSI Radio: Rundfunk der DDR – Berliner Rundfunk – Radio DDR 1 – Radio DDR 2 – Deutschlandsender – Radio Berlin International – DT64 Television: Fernsehen der DDR – Aktuelle Kamera – Sandmännchen – Der schwarze Kanal Cinema and films: DEFA – Solo Sunny – Die Legende von Paul und Paula – Traces of Stones – Bear Ye One Another's Burden Postal: Deutsche Post of the GDR Justice: Brandenburg-Görden Prison Transport: Alexanderplatz – Karl-Marx-Allee – Barkas – Interflug – Reichsbahn – Robur – Trabant – Wartburg Economy: Genex - Industrieverband Fahrzeugbau (IFA) – Intershop – Combine – Leipzig Trade Fair – Landwirtschaftliche Produktionsgenossenschaft (LPG) – Minol – ORWO – Pentacon – Planned economy - Praktica – Comecon – VEB Robotron – Kombinat Mikroelektronik Erfurt - SDAG Wismut – Treuhand – Volkseigener Betrieb (VEB) – Public property New and expanded articles
The following are articles, related to East Germany, added in the last six months.
All articles on East Germany are here;
Articles on East German people are here.
|
Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Discover Wikipedia using portals
| ||||