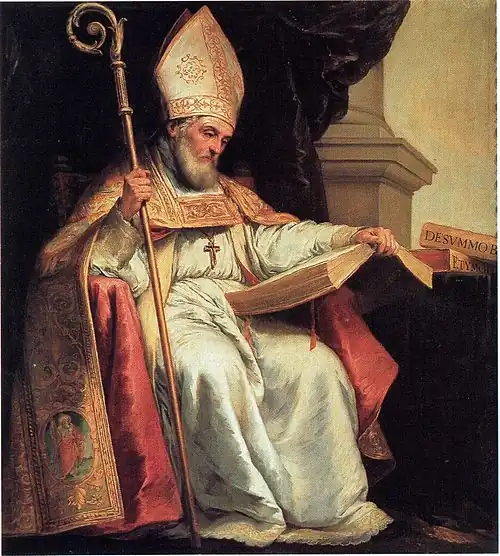
Portal:Catholic Church
Introduction The Catholic Church (Latin: Ecclesia Catholica), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization. The Church consists of 24 sui iuris (autonomous) churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and eparchies around the world, each overseen by one or more bishops. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the chief pastor of the church. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The Catholic Church teaches that it is the one, holy, catholic and apostolic church founded by Jesus Christ in his Great Commission, that its bishops are the successors of Christ's apostles, and that the pope is the successor of Saint Peter, upon whom primacy was conferred by Jesus Christ. It maintains that it practises the original Christian faith taught by the apostles, preserving the faith infallibly through scripture and sacred tradition as authentically interpreted through the magisterium or teaching office of the church. The Roman Rite and others of the Latin Church, the Eastern Catholic liturgies, and communities and societies such as mendicant orders, enclosed monastic orders, third orders and voluntary charitable lay associations reflect a variety of theological and spiritual emphases in the church. Of its seven sacraments, the Eucharist is the principal one, celebrated liturgically in the Mass. The church teaches that through consecration by a priest, the sacramental bread and wine become the body and blood of Christ. The Virgin Mary is venerated as the Mother of God, and Queen of Heaven; she is honoured in dogmas, such as that of her Immaculate Conception, perpetual virginity and assumption into heaven, and devotions. Catholic social teaching emphasizes voluntary support for the sick, the poor and the afflicted through the corporal and spiritual works of mercy. The Catholic Church operates tens of thousands of Catholic schools, universities and colleges, hospitals and orphanages around the world, and is the largest non-governmental provider of education and health care in the world. Among its other social services are numerous charitable and humanitarian organizations. (Full article...) Selected article
 The Tomb of Antipope John XXIII is the marble tomb monument of Antipope John XXIII (Baldassare Cossa, c. 1360–1419), created by Donatello and Michelozzo for the Florence Baptistery adjacent to the Duomo. It was commissioned by the executors of Cossa's will after his death on December 22, 1419 and completed during the 1420s, establishing it as one of the early landmarks of Renaissance Florence. According to Ferdinand Gregorovius, the tomb is "at once the sepulchre of the Great Schism in the church and the last Papal tomb which is outside Rome itself".Cossa had a long history of cooperation with Florence, which had viewed him as the legitimate pontiff for a time during the Western Schism. The tomb monument is often interpreted as an attempt to strengthen the legitimacy of Cossa's pontificate by linking him to the spiritually powerful site of the Baptistry.The evocation of papal symbolism on the tomb and the linkage between Cossa and Florence have been interpreted as a snub to Cossa's successor Pope Martin V or vicarious "Medici self-promotion", as such a tomb would have been deemed unacceptable for a Florentine citizen.
Selected image
 Credit: LivioAndronico The Trevi Fountain is the largest — standing 25.9 meters (85 feet) high and 19.8 meters (65 feet) wide — and most ambitious of the Baroque fountains of Rome. Competitions had become the rage during the Baroque era to design buildings, fountains, and even the Spanish Steps. In 1730 Pope Clement XII organized a contest in which Nicola Salvi initially lost to Alessandro Galilei — but due to the outcry in Rome over the fact that a Florentine won, Salvi was awarded the commission anyway. Work began in 1732, and the fountain was completed in 1762, long after Clement's death, when Pietro Bracci's 'Neptune' was set in the central niche. Selected biography
 Blaise Pascal (French pronunciation: [blɛz paskal]), (June 19, 1623 – August 19, 1662) was a French mathematician, physicist, and religious philosopher. He was a child prodigy who was educated by his father. Pascal's earliest work was in the natural and applied sciences where he made important contributions to the construction of mechanical calculators, the study of fluids, and clarified the concepts of pressure and vacuum by generalizing the work of Evangelista Torricelli. Pascal also wrote in defense of the scientific method. Pascal was a mathematician of the first order. He helped create two major new areas of research. He wrote a significant treatise on the subject of projective geometry at the age of sixteen, and later corresponded with Pierre de Fermat on probability theory, strongly influencing the development of modern economics and social science. Following a mystical experience in late 1654, he abandoned his scientific work and devoted himself to philosophy and theology. His two most famous works date from this period: the Lettres provinciales and the Pensées. Pascal suffered from ill health throughout his life and died two months after his 39th birthday.
Did you know...

Related portalsFeast Day of August 18
.jpg)
Hurtado was canonized on October 23, 2005, by Pope Benedict XVI, becoming his country's second saint. (Full article...)
Selected quote

News
Subcategories Catholic Church Catholic Church by city Catholic Church by continent Catholic Church by country Catholic Church-related lists Catholic particular churches sui iuris Latin Church Eastern Catholic Churches Catholic bibles Buildings and structures of the Catholic Church Catholic Church portals Catholics Catholic charities Catholic culture Catholic dioceses Ecclesiastical polity of the Catholic Church Catholic ecumenical and interfaith relations History of the Catholic Church Catholic liturgy Catholic missions Catholic orders and societies Catholic Church organisation Outlines of the Catholic Church Popes Catholic Church in popular culture Roman Catholic saints Catholic spirituality Catholic studies Catholic theology and doctrine Venerated Catholics Catholic Church stubs Topics
The Holy Bible:
Particular churches (grouped by liturgical rite):
Things you can do
External resourcesWikiProjects
Associated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Discover Wikipedia using portals
|
.jpg)

.svg.png)
.svg.png)