Velnacrine
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
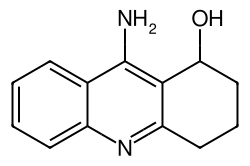
| IUPAC name
9-amino-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroacridin-1-ol
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H14N2O | |
| Molar mass | 214.268 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
Velnacrine, also known as 1-hydroxytacrine[1], is an inhibitor of cholinesterase enzymes. It is also a metabolite of tacrine.[2]
Pharmacology
Velnacrine is able to inhibit acetylcholinesterase (AChE)[3], this results in elevated levels of acetylcholine, as AChE is the enzyme that hydrolyzes acetylcholine.[4] It is also able to inhibit butyrylcholinesterase.[5]
Therapeutic potential
Velnacrine, as many other cholinergics, has been described as possibly useful to help manage symptoms of Alzheimer's disease. Some research has described the drug as having benefits over placebo[6] and an acceptable safety profile.[7] However, a review described available data as not proving efficacy and showing evidence of toxicity.[8] Additionally, the FDA voted against recommending approval of velnacrine.[8]
References
- ^ PubChem. "Velnacrine". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2025-07-31.
- ^ Viau, C. J.; Curren, R. D.; Wallace, K. (1993). "Cytotoxicity of tacrine and velnacrine metabolites in cultured rat, dog and human hepatocytes". Drug and Chemical Toxicology. 16 (3): 227–239. doi:10.3109/01480549309081817. ISSN 0148-0545. PMID 8404544.
- ^ "AID 31170 - Inhibition of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) of human red blood cell (type XIII) by modified radiometric AChE assay - PubChem". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2025-07-31.
- ^ Trang, Amy; Khandhar, Paras B. (2025), "Physiology, Acetylcholinesterase", StatPearls, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, PMID 30969557, retrieved 2025-07-31
- ^ "AID 44453 - Inhibition of (BChE) Butyrylcholinesterase of horse serum - PubChem". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2025-07-31.
- ^ Antuono, P. G. (1995-09-11). "Effectiveness and safety of velnacrine for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. A double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Mentane Study Group". Archives of Internal Medicine. 155 (16): 1766–1772. doi:10.1001/archinte.1995.00430160102010. ISSN 0003-9926. PMID 7654110.
- ^ Puri, S. K.; Ho, I.; Hsu, R.; Lassman, H. B. (October 1990). "Multiple dose pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerance of velnacrine (HP 029) in healthy elderly subjects: a potential therapeutic agent for Alzheimer's disease". Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 30 (10): 948–955. doi:10.1002/j.1552-4604.1990.tb03576.x. ISSN 0091-2700. PMID 2229455.
- ^ a b Birks, J.; Wilcock, G. G. W. (2004). "Velnacrine for Alzheimer's disease". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (2): CD004748. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004748. ISSN 1469-493X. PMID 15106259.