Thiopurine
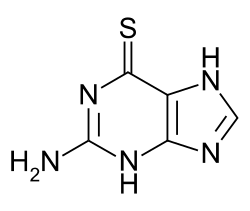
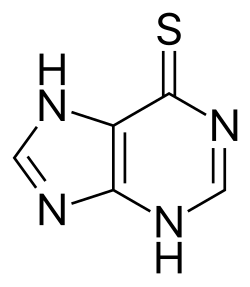
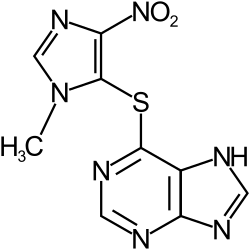
Thiopurine is an analogue of a purine wherein a C=O/C-OH group has been replaced by a C=S/C-SH group. These organosulfur compounds are bioactive in beneficial and complicating manner. They interfere with purine biosynthesis. Thiopurine drugs antimetabolites widely used in the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia, autoimmune disorders (e.g., Crohn's disease, rheumatoid arthritis), and organ transplant recipients. Azathioprine is a prodrug. 6-Mercaptopurine is substrate for three enzyme]]s: thiopurine methyltransferase (to give 6-methylmercaptopurine), xanthine oxidase (to give 6-thiouric acid], and hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase (to give 6-thioisonine 5'-monphosphate).[1] They are also substrates for nudix hydrolase 15 (NUDT15).[2]
Controversy
Litigation over patents covering diagnostic kits to monitor the dosing of these drugs led to a US Supreme Court case, Mayo Collaborative Services v. Prometheus Laboratories, Inc. that dramatically changed the nature of patent law in the United States.[3][4]
See also
- 6-Mercaptopurine (6-MP)
- 6-Thioguanine (6-TG)
- Azathioprine (AZA)
References
- ^ Dubinsky, Marla C.; Lamothe, Stéphanie; Yang, Hui Ying; Targan, Stephan R.; Sinnett, Daniel; Théorêt, Yves; Seidman, Ernest G. (2000). "Pharmacogenomics and metabolite measurement for 6-mercaptopurine therapy in inflammatory bowel disease". Gastroenterology. 118 (4): 705–713. doi:10.1016/s0016-5085(00)70140-5. PMID 10734022.
- ^ Sahasranaman S, Howard D, Roy S (August 2008). "Clinical pharmacology and pharmacogenetics of thiopurines". Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 64 (8): 753–67. doi:10.1007/s00228-008-0478-6. PMID 18506437.
- ^ Supreme Court Decision. Mayo Collaborative Services v. Prometheus Laboratories, Inc., No. 10-1150, Slip Op. at 16. Decision
- ^ Gene Quinn, Killing Industry: The Supreme Court Blows Mayo v. Prometheus IP Watchdog (March 20, 2012).
External links