Portal:Volcanoes
The Volcanoes portal

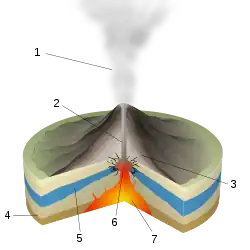
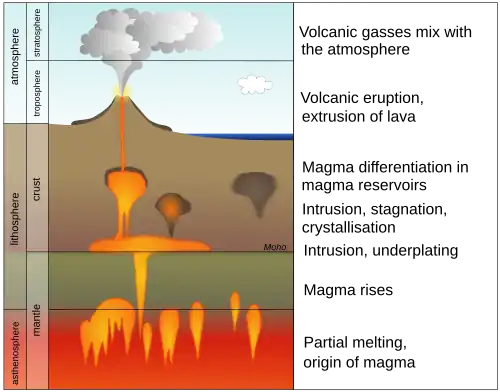
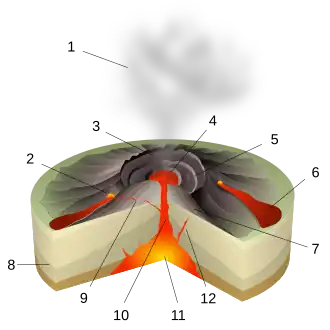
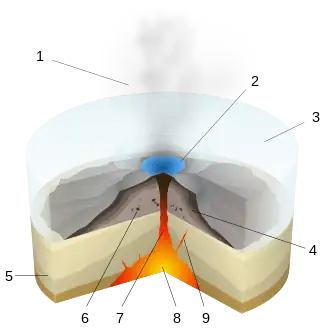
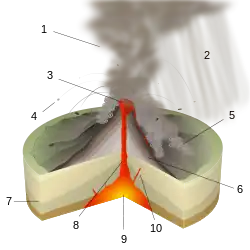
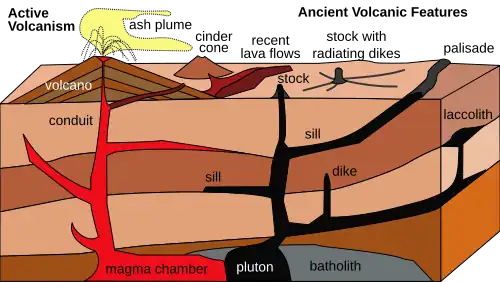
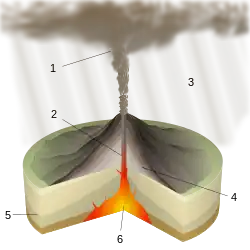
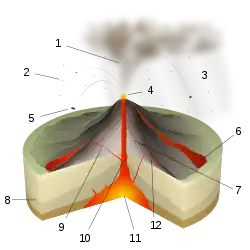
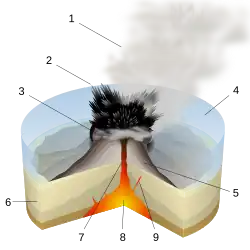
A volcano is commonly defined as a vent or fissure in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
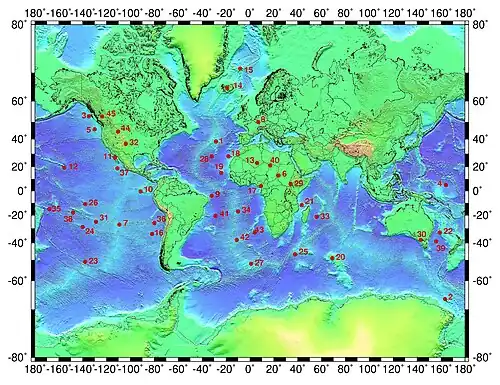
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging, and because most of Earth's plate boundaries are underwater, most volcanoes are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes resulting from divergent tectonic activity are usually non-explosive whereas those resulting from convergent tectonic activity cause violent eruptions. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's plates, such as in the East African Rift, the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field, and the Rio Grande rift in North America. Volcanism away from plate boundaries most likely arises from upwelling diapirs from the core–mantle boundary called mantle plumes, 3,000 kilometres (1,900 mi) deep within Earth. This results in hotspot volcanism or intraplate volcanism, in which the plume may cause thinning of the crust and result in a volcanic island chain due to the continuous movement of the tectonic plate, of which the Hawaiian hotspot is an example. Volcanoes are usually not created at transform tectonic boundaries where two tectonic plates slide past one another.
Volcanoes, based on their frequency of eruption or volcanism, are referred to as either active or extinct. Active volcanoes have a history of volcanism and are likely to erupt again while extinct ones are not capable of eruption at all as they have no magma source. "Dormant" volcanoes have not erupted in a long time- generally accepted as since the start of the Holocene, about 12000 years ago- but may erupt again. These categories aren't entirely uniform; they may overlap for certain examples.
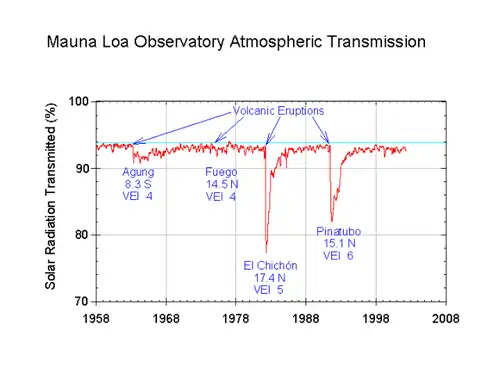
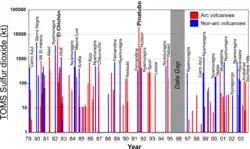
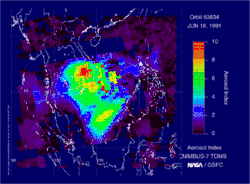
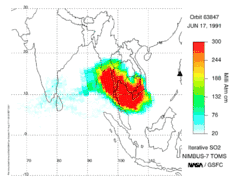
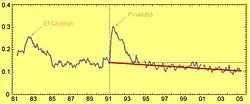
Large eruptions can affect atmospheric temperature as ash and droplets of sulfuric acid obscure the Sun and cool Earth's troposphere. Historically, large volcanic eruptions have been followed by volcanic winters which have caused catastrophic famines.
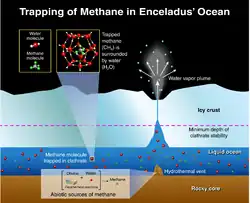
Other planets besides Earth have volcanoes. For example, volcanoes are very numerous on Venus. Mars has significant volcanoes. In 2009, a paper was published suggesting a new definition for the word 'volcano' that includes processes such as cryovolcanism. It suggested that a volcano be defined as 'an opening on a planet or moon's surface from which magma, as defined for that body, and/or magmatic gas is erupted.'
This article mainly covers volcanoes on Earth. See § Volcanoes on other celestial bodies and cryovolcano for more information. (Full article...)
Selected article -
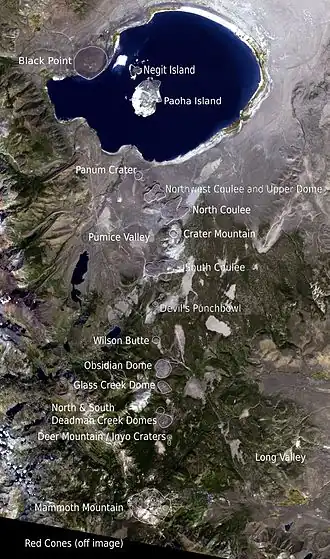
The Mono–Inyo Craters are a volcanic chain of craters, domes and lava flows in Mono County, Eastern California. The chain stretches 25 miles (40 km) from the northwest shore of Mono Lake to the south of Mammoth Mountain. The Mono Lake Volcanic Field forms the northernmost part of the chain and consists of two volcanic islands in the lake and one cinder cone volcano on its northwest shore. Most of the Mono Craters, which make up the bulk of the northern part of the Mono–Inyo chain, are phreatic (steam explosion) volcanoes that have since been either plugged or over-topped by rhyolite domes and lava flows. The Inyo volcanic chain form much of the southern part of the chain and consist of phreatic explosion pits, and rhyolitic lava flows and domes. The southernmost part of the chain consists of fumaroles and explosion pits on Mammoth Mountain and a set of cinder cones south of the mountain; the latter are called the Red Cones.
Eruptions along the narrow fissure system under the chain began in the west moat of Long Valley Caldera 400,000 to 60,000 years ago. Mammoth Mountain was formed during this period. Multiple eruptions from 40,000 to 600 years ago created the Mono Craters and eruptions 5,000 to 500 years ago formed the Inyo volcanic chain. Lava flows 5,000 years ago built the Red Cones, and explosion pits on Mammoth Mountain were excavated in the last 1,000 years. Uplift of Paoha Island in Mono Lake about 250 years ago is the most recent activity. These eruptions most likely originated from small magma bodies rather than from a single, large magma chamber like the one that produced the massive Long Valley Caldera eruption 760,000 years ago. During the past 3,000 years, eruptions have occurred every 250 to 700 years. In 1980, a series of earthquakes and uplift within and south of Long Valley Caldera indicated renewed activity in the area. (Full article...)
Did you know

- ... that the decomposing skeleton of a right whale was found on the submarine volcano Patton Seamount (pictured)?
- ... that Suiyo Seamount, a seamount near Japan, was thought to be extinct until a hydrothermal event in 1991 was brought to light?
- ... that death can be found living on hell's half acre?
- ... that the 27-million-year-old Cobb Seamount is so heavily encrusted in sea life that no bare rock surface has been found in dives?
- ... that parts of the shield volcano Fumarole Butte were once covered by Lake Bonneville?
- ... that the Temagami Greenstone Belt in Ontario was the site of the largest deposit of nearly pure chalcopyrite ever discovered in Canada?
- ... that the Makushin Volcano is one of the most active volcanoes of Alaska?
General images
Selected biography -
William J. McGuire (born 1954) is a volcanologist and Emeritus Professor of Geophysical & Climate Hazards at University College London. His main interests include volcano instability and lateral collapse, the nature and impact of global geophysical events and the effect of climate change on geological hazards. (Full article...)
Selected picture
Wildfire on the island of Hawaiʻi caused by pāhoehoe lava flowing on the coastal plain of Kīlauea. The new lava is moving across the old surface, which is covered with a roughly 1-inch (2.54 cm)-thick layer of moss. The burning moss generates the smoke visible in the image. This kind of fire cannot be easily prevented or suppressed.
Selected quote
Now an extinct volcano is not quite so safe a neighbour as many may suppose. Vesuvius was an extinct volcano from time immemorial till the year 63, when it suddenly broke out again, and soon after destroyed Pompeii and Herculaneum; since which time it has never again subsided into entire inactivity.
— A possible event — dangers of our planet, The National Magazine, November 1854, p. 435
Related portals
WikiProjects

- WikiProject Volcanoes
- WikiProject Seamounts
- WikiProject Mountains
Volcanoes topics
Subcategories
![]()
Featured work and other approved content

Featured articles: 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens • 2007–2008 Nazko earthquakes • Amchitka • Armero tragedy • Craters of the Moon National Monument and Preserve • Cerro Azul (Chile volcano) • David A. Johnston • Enceladus (moon) • Geology of the Lassen volcanic area • Io (moon) • Kamaʻehuakanaloa Seamount • Mauna Kea • Mauna Loa • Metacomet Ridge • Mono-Inyo Craters • Mount Cayley volcanic field • Mount St. Helens • Mount Tambora • Nevado del Ruiz • Surtsey • The Volcano (British Columbia) • Triton (moon) • Upper and Lower Table Rock • Volcanism on Io • Volcano (South Park) • Yellowstone National Park
Featured lists: List of volcanoes in Indonesia • List of volcanoes in the Hawaiian – Emperor seamount chain • List of largest volcanic eruptions
Featured pictures: There are currently 43 volcano-related Featured pictures. A full gallery can be seen here.

Good articles: Abyssal plain • Amak Volcano • Anahim hotspot • Axial Seamount • Ben Nevis • Bowie Seamount • Crater Lake • Davidson Seamount • Ferdinandea • Gareloi Volcano • Geyser • Glacier Peak • Hawaii hotspot • Hualālai • Kohala (mountain) • Lake Toba • Minoan eruption • Mount Adams (Washington) • Mount Bailey • Mount Baker • Mount Cleveland (Alaska) • Mount Edziza volcanic complex • Mount Garibaldi • Mount Hood • Mount Kenya • Mount Rainier • Mount Redoubt • Mount Tehama • Mount Thielsen • Mount Vesuvius • Peter I Island • Roxy Ann Peak • Rùm • Sakurajima • Sangay • Silverthrone Caldera • Staffa • Types of volcanic eruptions • Volcanic ash • Weh Island • Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field • Yamsay Mountain
Valued pictures: A gallery of volcano-related valued pictures can be seen here.
What you can do

- Add the {{WikiProject Volcanoes}} message box to talk pages of articles within the scope of this project, including appropriate assessments, if needed.
- Add appropriate volcano type categories to articles, and verify the accuracy of any existing categories. See the section "Categorization" below.
- Add {{infobox mountain}} to articles if needed and missing, and add volcano-related fields to existing infoboxes if these are missing.
- Expand volcano articles which are stubs, especially by adding photos and (most importantly) proper references.
- Help improve articles related to Hawaiian and Canadian volcanism by joining the Hawaiian and Canadian workgroups.
- Improve some of the project's most visible articles.
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
-
 List of all portals
List of all portals -

-

-

-

-

-
-

-

-

-
 Random portal
Random portal -
 WikiProject Portals
WikiProject Portals



















.jpg)

.jpg)