Portal:Stars
IntroductionA star is a luminous spheroid of plasma held together by self-gravity. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night; their immense distances from Earth make them appear as fixed points of light. The most prominent stars have been categorised into constellations and asterisms, and many of the brightest stars have proper names. Astronomers have assembled star catalogues that identify the known stars and provide standardized stellar designations. The observable universe contains an estimated 1022 to 1024 stars. Only about 4,000 of these stars are visible to the naked eye—all within the Milky Way galaxy. A star's life begins with the gravitational collapse of a gaseous nebula of material largely comprising hydrogen, helium, and traces of heavier elements. Its total mass mainly determines its evolution and eventual fate. A star shines for most of its active life due to the thermonuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium in its core. This process releases energy that traverses the star's interior and radiates into outer space. At the end of a star's lifetime, fusion ceases and its core becomes a stellar remnant: a white dwarf, a neutron star, or—if it is sufficiently massive—a black hole. Stellar nucleosynthesis in stars or their remnants creates almost all naturally occurring chemical elements heavier than lithium. Stellar mass loss or supernova explosions return chemically enriched material to the interstellar medium. These elements are then recycled into new stars. Astronomers can determine stellar properties—including mass, age, metallicity (chemical composition), variability, distance, and motion through space—by carrying out observations of a star's apparent brightness, spectrum, and changes in its position in the sky over time. Stars can form orbital systems with other astronomical objects, as in planetary systems and star systems with two or more stars. When two such stars orbit closely, their gravitational interaction can significantly impact their evolution. Stars can form part of a much larger gravitationally bound structure, such as a star cluster or a galaxy. (Full article...) Selected star - Photo credit: NASA and ESA
Sirius is the brightest star in the night sky. With a visual apparent magnitude of −1.46, it is almost twice as bright as Canopus, the next brightest star. The name "Sirius" is derived from the Ancient Greek Seirios ("scorcher"), possibly because the star's appearance was associated with summer. The star has the Bayer designation α Canis Majoris (α CMa, or Alpha Canis Majoris). What the naked eye perceives as a single star is actually a binary star system, consisting of a white main sequence star of spectral type A1V, termed Sirius A, and a faint white dwarf companion of spectral type DA2, termed Sirius B. Sirius appears bright due to both its intrinsic luminosity and its closeness to the Earth. At a distance of 2.6 parsecs(8.6 ly), the Sirius system is one of our near neighbors. Sirius A is about twice as massive as the Sun and has an absolute visual magnitude of 1.42. It is 25 times more luminous than the Sun but has a significantly lower luminosity than other bright stars such as Canopus or Rigel. The system is between 200 and 300 million years old. It was originally composed of two bright bluish stars. The more massive of these, Sirius B, consumed its resources and became a red giant before shedding its outer layers and collapsing into its current state as a white dwarf around 120 million years ago. Selected article -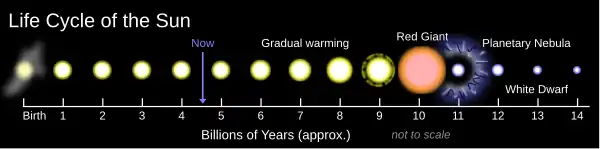 Photo credit: User:Oliverbeatson
All stars are born from collapsing clouds of gas and dust, often called nebulae or molecular clouds. Nuclear fusion powers a star for most of its life. Stars similar to our Sun gradually grow in size until they reach a red giant phase, after which the core collapses into a dense white dwarf and the outer layers are expelled as a planetary nebula. Larger stars can explode in a supernova as their cores collapse into an extremely dense neutron star or black hole. It is not clear how red dwarfs die because of their extremely long life spans, but they probably experience a gradual death in which their outer layers are expelled over time. Stellar evolution is not studied by observing the life of a single star, as most stellar changes occur too slowly to be detected, even over many centuries. Instead, astrophysicists come to understand how stars evolve by observing numerous stars at various points in their lifetime, and by simulating stellar structure using computer models. A stellar evolutionary model is a mathematical model that can be used to compute the evolutionary phases of a star from its formation until it becomes a remnant. The mass and chemical composition of the star are used as the inputs, and the luminosity and surface temperature are the only constraints. The model formulae are based upon the physical understanding of the star, usually under the assumption of hydrostatic equilibrium. Selected image -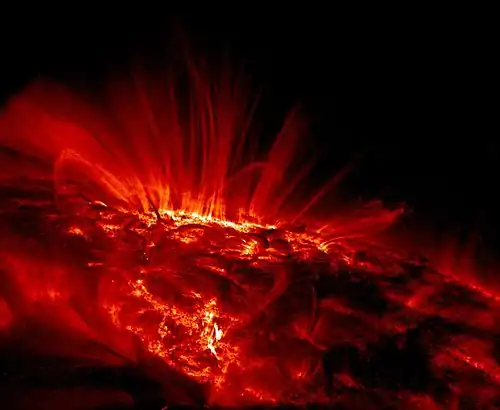 Photo credit: NASA/TRACE
Sunspots are temporary phenomena on the surface of the Sun (the photosphere) that appear visibly as dark spots compared to surrounding regions. They are caused by intense magnetic activity, which inhibits convection, forming areas of reduced surface temperature. Although they are at temperatures of roughly 3,000–4,500 K, the contrast with the surrounding material at about 5,780 K leaves them clearly visible as dark spots, as the intensity of a heated black body (closely approximated by the photosphere) is a function of T (temperature) to the fourth power. If the sunspot were isolated from the surrounding photosphere it would be brighter than an electric arc. Sunspots expand and contract as they move across the surface of the sun and can be as large as 80,000 km (50,000 miles) in diameter, making the larger ones visible from Earth without the aid of a telescope. Did you know?
SubcategoriesTo display all subcategories click on the ►
Stars Stars by luminosity class Stars by metallicity Stars by spectral type Stars by type Stars with proper names Lists of stars Star types Astronomical catalogues of stars Star atlases Coats of arms with stars Flags with stars Star symbols Stars in the Andromeda Galaxy Star clusters Fiction about stars Stellar groupings Hypothetical stars Star images Stellar astronomy Stellar dynamics Sun Star systems Wikipedia categories named after stars Star stubs Sun Atmospheric radiation Solar calendars Coats of arms with sunrays Coats of arms with suns Sun in culture Day Horizontal coordinate system Missions to the Sun Solar observatories Solar phenomena Solar alignment Solar eclipses Solar energy Sun tanning Sundials Sun stubs Galaxies Astronomical catalogues of galaxies Galaxies by year of discovery Galaxies by century of discovery Fiction about galaxies Galaxy clusters Galaxy filaments Galaxy superclusters Lists of galaxies Galaxy morphological types Active galaxies Barred galaxies Dark galaxies Dwarf galaxies Elliptical galaxies Field galaxies Hypothetical galaxies Galaxy images Interacting galaxies Irregular galaxies Lenticular galaxies Low surface brightness galaxies Overlapping galaxies Peculiar galaxies Polar-ring galaxies Protogalaxies Ring galaxies Spiral galaxies Supermassive black holes Galaxy stubs Wikipedia categories named after galaxies Black holes Fiction about black holes Intermediate-mass black holes Stellar black holes Supermassive black holes Tidal disruption events White holes Supernovae Fiction about supernovae Historical supernovae Hypernovae Superbubbles Discoverers of supernovae Supernova remnants Selected biography -Photo credit: Eduard Ender
Tycho Brahe, born Tyge Ottesen Brahe (de Knudstrup) (14 December 1546 – 24 October 1601), was a Danish nobleman known for his accurate and comprehensive astronomical and planetary observations. Coming from Scania, then part of Denmark, now part of modern-day Sweden, Tycho was well known in his lifetime as an astronomer and alchemist. His Danish name "Tyge Ottesen Brahe" is pronounced in Modern Standard Danish as [ˈtsʰyːə ˈʌtəsn̩ ˈpʁɑːə]. He adopted the Latinized name "Tycho Brahe" (usually /ˈtaɪkoʊ ˈbrɑː/ or /ˈbrɑːhiː/ in English) from Tycho (sometimes written Tÿcho) at around age fifteen, and he is now generally referred to as "Tycho", as was common in Scandinavia in his time, rather than by his surname "Brahe". (The incorrect form of his name, Tycho de Brahe, appeared only much later. Tycho Brahe was granted an estate on the island of Hven and the funding to build the Uraniborg, an early research institute, where he built large astronomical instruments and took many careful measurements. After disagreements with the new king in 1597, he was invited by the Bohemian king and Holy Roman emperor Rudolph II to Prague, where he became the official imperial astronomer. He built the new observatory at Benátky nad Jizerou. Here, from 1600 until his death in 1601, he was assisted by Johannes Kepler. Kepler later used Tycho's astronomical information to develop his own theories of astronomy.
TopicsWikiProjects
More science WikiProjects...
Things to do
Related portals
More science portals...
Associated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Discover Wikipedia using portals
|