Portal:Pan-Africanism
IntroductionWelcome to the Pan-Africanism portal!
Bienvenue sur le portail panafricanisme!  .jpg)  Pan-Africanism is an idea that aims to encourage and strengthen bonds of solidarity between all indigenous peoples and diasporas of African ancestry. Based on a common goal dating back to the Atlantic slave trade, the Trans-Saharan slave trade, the Indian Ocean slave trade, the Red Sea slave trade, slavery in the Cape Colony (now South Africa), along with slavery in Mauritius, the belief extends beyond continental Africans with a substantial support base among the African diaspora in the Americas and Europe. Pan-Africanism is said to have its origins in the struggles of the African people against enslavement and colonization and this struggle may be traced back to the first resistance on slave ships—rebellions and suicides—through the constant plantation and colonial uprisings and the "Back to Africa" movements of the 19th century. Based on the belief that unity is vital to economic, social, and political progress, it aims to unify and uplift people of African ancestry. However, it was in the twentieth century that Pan Africanism emerged as a distinct political movement initially formed and led by people from the Diaspora (people of African heritage living outside of the Continent). In 1900, the Trinindadian barrister – Henry Sylvester Williams – called a conference that took place in Westminster Hall, London to "protest stealing of lands in the colonies, racial discrimination and deal with other issues of interest to Blacks". (Full article...) Selected article The Pan-African flag—also known as the UNIA flag, Afro-American flag, Black Liberation flag and various other names—is a tri-color flag consisting of three equal horizontal bands of (from top down) red, black and green. The Universal Negro Improvement Association and African Communities League (UNIA-ACL) formally adopted it on August 13, 1920 in Article 39 of the Declaration of the Rights of the Negro Peoples of the World, during its month-long convention at Madison Square Garden in New York City. Variations of the flag can and have been used in various countries and territories in the Americas to represent Garveyist ideologies. Selected biography
Edward Wilmot Blyden (3 August 1832 – 7 February 1912) was an educator, writer, diplomat, and politician primarily in Liberia. Born in the West Indies, he joined the free black immigrants from the United States who migrated to the region. He taught for five years in the British West African Colony of Sierra Leone in the early 20th century. His writings on pan-Africanism were influential in both colonies. These were founded during the slavery years for the resettlement of free blacks from Great Britain and the United States. Blyden's writings attracted attention in the sponsoring countries as well. He believed that Zionism was a model for what he called Ethiopianism, and that African Americans could return to Africa and redeem it. He believed political independence to be a prerequisite for economic independence, and argued that Africans must counter the neo-colonial policies of former colonial powers. Selected history
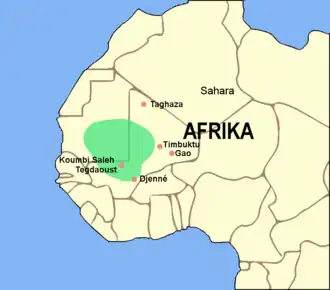
The Ghana Empire (c. 700 until c. 1240), (Ghana or Ga'na being the title of its ruler), was located in the area of present-day southeastern Mauritania and western Mali. Complex societies based on trans-Saharan trade with salt and gold had existed in the region since ancient times, but the introduction of the camel to the western Sahara in the 3rd century A.D. opened the way to great changes in the area that became the Ghana Empire. By the time of the Muslim conquest of North Africa in the 7th century the camel had changed the ancient, more irregular trade routes into a trade network running from Morocco to the Niger river. The Ghana Empire grew rich from this increased trans-Saharan trade in gold and salt, allowing for larger urban centres to develop. The traffic furthermore encouraged territorial expansion to gain control over the different trade-routes. When Ghana's ruling dynasty began remains uncertain; it is mentioned for the first time in written records by Muḥammad ibn Mūsā al-Khwārizmī in 830. In the 11th century the Cordoban scholar Abuof travelled to the region and gave a detailed description of the kingdom. He claimed that the Ghana could "put 200,000 men into the field, more than 40,000 of them archers", and noted they had cavalry forces as well. As the empire declined it finally became a vassal of the rising Mali Empire at some point in the 13th century. When the Gold Coast in 1957 became the first country in sub-Saharan Africa to regain its independence from colonial rule, it renamed itself in honor of the long-gone empire. Selected cultureAfrican-American culture, also known as Black American culture, refers to the contributions of African Americans to the culture of the United States, either as part of or distinct from mainstream American culture. The distinct identity of African-American culture is rooted in the historical experience of the African-American people, including the Middle Passage. The culture is both distinct and enormously influential on American and global worldwide culture as a whole. African-American culture is primarily rooted in West and Central Africa. Understanding its identity within the culture of the United States it is, in the anthropological sense, conscious of its origins as largely a blend of West and Central African cultures. Although slavery greatly restricted the ability of African Americans to practice their original cultural traditions, many practices, values and beliefs survived, and over time have modified and/or blended with European cultures and other cultures such as that of Native Americans. African-American identity was established during the slavery period, producing a dynamic culture that has had and continues to have a profound impact on American culture as a whole, as well as that of the broader world. Elaborate rituals and ceremonies were a significant part of African Americans' ancestral culture. Many West African societies traditionally believed that spirits dwelled in their surrounding nature. From this disposition, they treated their environment with mindful care. They also generally believed that a spiritual life source existed after death, and that ancestors in this spiritual realm could then mediate between the supreme creator and the living. Honor and prayer was displayed to these "ancient ones", the spirit of those past. West Africans also believed in spiritual possession. Selected imagesOrganisationsAll-African People's Revolutionary Party · African Society for Cultural Relations with Independent Africa · African Unification Front · African Union · African Queens and Women Cultural Leaders Network · Conseil de l'Entente · Convention People's Party · East African Community · Economic Freedom Fighters · Global Afrikan Congress · International African Service Bureau · International League for Darker People · Organisation of African Unity · Pan African Association · Pan-African Congress · Pan Africanist Congress of Azania · Rassemblement Démocratique Africain · Pan Africa Chemistry Network · Pan African Federation of Accountants · Pan-African Freedom Movement for East and Central Africa · Sahara and Sahel Observatory · UNIA-ACL · ZANU–PF
See also
Category:Pan-Africanist organizations & Category:Pan-Africanist political parties
Festivals_(cropped)_1.jpg) Photo by Helinä Rautavaara (1977) Publications
Films and TVAudios and videosDid you know ...that on arriving in Cuba in 1920, the SS Yarmouth (crew pictured), flagship of Marcus Garvey's Black Star Line, was hailed as the "Ark of the Covenant of the colored people"?
Selected quotesOn the subject of "Black self-hatred", the African-American scholar and Pan-Africanist Dr. Amos N. Wilson said:
Pan-Africanism topicsCategoriesSelect [►] to view subcategories
Pan-Africanism Pan-Africanism by continent Pan-Africanism by country Pan-Africanists Afrocentrism Kwanzaa Nkrumaism Novels by Ayi Kwei Armah Pan-Africanist organizations Pan-African media companies Pan-Africanism portal Sankarism Things you can do
Other things you can do...
Related portalsAssociated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Discover Wikipedia using portals
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||



.jpg)