Portal:Energy
| New articles & Tasks |
 The Energy Portal Welcome to Wikipedia's Energy portal, your gateway to energy. This portal is aimed at giving you access to all energy related topics in all of its forms.
|
Page contents: Selected article • Selected image • Selected biography • Did you know? • General images • Quotations • Related portals • Wikiprojects • Major topics • Categories • Help • Associated Wikimedia |
Introduction
Energy (from Ancient Greek ἐνέργεια (enérgeia) 'activity') is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat and light. Energy is a conserved quantity—the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed. The unit of measurement for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (J).
Forms of energy include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the potential energy stored by an object (for instance due to its position in a field), the elastic energy stored in a solid object, chemical energy associated with chemical reactions, the radiant energy carried by electromagnetic radiation, the internal energy contained within a thermodynamic system, and rest energy associated with an object's rest mass. These are not mutually exclusive.
All living organisms constantly take in and release energy. The Earth's climate and ecosystems processes are driven primarily by radiant energy from the sun. (Full article...)
Selected article

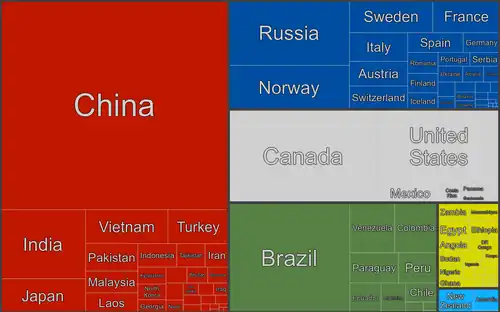
The use of coal dates back to the Bronze Age, but it was the Industrial Revolution that led to its large-scale use, as the steam engine took over from the water wheel. Today world coal consumption is about 5.3 billion tonnes annually, of which about 75% is used to produce electricity. The region including the China and India uses about 1.7 billion tonnes annually, forecast to exceed 2.7 billion tonnes by 2025. The United States consumes about 1.0 billion tons annually. Almost one-third of all coal used was supplied by China in 2005.
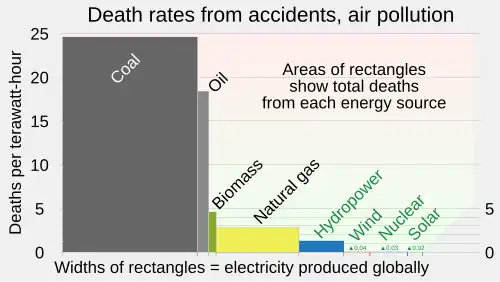
Coal mining causes a number of harmful effects, including the pollution of water sources by sulfuric acid caused by a chemical reaction between water and iron sulfide in the coal. In common with other fossil fuels, the burning coal produces carbon dioxide and nitrogen oxides. It also produces sulfur dioxide, the cause of acid rain. Coal contains traces of uranium, thorium, and other naturally-occurring radioactive isotopes which, due to the vast quantities of coal used, cause more radioactive contamination than nuclear power plants. To eliminate CO2 emissions from coal plants, carbon capture and storage technology has been proposed but has yet to be commercially used.
Selected image

Photo credit: Charliebrown7034
Skyglow over New York City, one form of light pollution.
Did you know?
- According to research by the IPCC, government funding for most energy research programmes has been flat or declining for nearly 20 years, and is now about half the 1980 level?
- Renewable energy in Iceland provides over 70% of the country's primary energy needs, and 99.9% of Iceland's electricity?
- The Rance tidal power plant in France was the world's 1st electrical generating station powered by tidal energy?
- A tropical cyclone (example pictured) can release heat energy at the rate of 50 to 200 trillion joules per day, roughly 200 times the world-wide electrical generating capacity?
- Ordinary fossil fuel power plants convert between 36% and 48% of the fuel's energy into electricity, with the remainder being lost as waste heat, about half of which is unavoidable due to the second law of thermodynamics?
- Burning biomass indoors leads to between 1.5 and 2 million deaths each year from indoor air pollution in developing nations?
- Over 50% of world small hydroelectricity generating capacity is in China?
- Charles Fritts developed the first solar cell in 1884, although its efficiency was less than 1%?
Selected biography

Edison invented the first commercially practical electric light bulb which, by 1879 would burn for hundreds of hours. He was able to sell the concept to homes and businesses by mass-producing them and creating a complete system for the generation and distribution of electricity.
Edison patented an electric distribution system in 1880, and in January 1882 he switched on the first steam generating power station at Holborn Viaduct in London, UK. The direct current (DC) supply system provided electricity supplies to street lamps and a number of private dwellings within a short distance of the station. The first investor-owned electric utility, Pearl Street Station, New York City, started generating on September 4, 1882, providing 110 volts direct current to 59 customers in lower Manhattan.
Life magazine (USA), in a special double issue, placed Edison first in the list of the "100 Most Important People in the Last 1000 Years," noting that the light bulb he promoted "lit up the world." He was ranked thirty-fifth on Michael H. Hart's list of the most influential figures in history.
In the news
- 27 July 2025 – Tariffs in the second Trump administration
- U.S. president Donald Trump and European Commission president Ursula von der Leyen announce a trade deal that would set a reciprocal 15% tariff on all exports and promise to boost European Union investment into the U.S. by $600 billion. The EU also promises to purchase $750 billion in American energy products over an unspecified period of time. (BBC News)
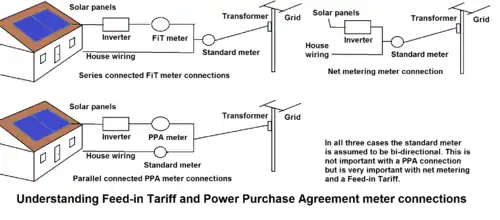
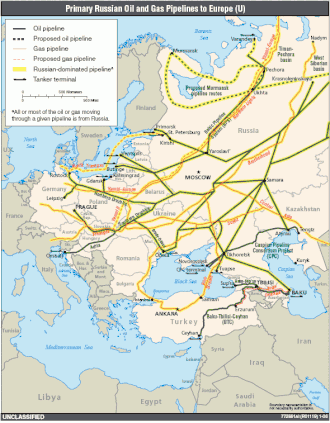
General images
Quotations
- "Breaking the dependence on oil is, in my view, a matter of political will. A consistent policy will turn obstacles into opportunities. To hide behind excuses of ignorance or economic considerations is not leading us to a sustainable future." – Mona Sahlin, 2006
- "America is addicted to oil, which is often imported from unstable parts of the world. The best way to break this addiction is through technology." – George W. Bush, 2006
- "Energy independence [for India] has to be our nation's first and highest priority. We must be determined to achieve this within the next 25 years i.e. by the year 2030." – Abdul Kalam, 2005
- "Energy security is assuming a strategic significance once reserved for territorial security, and the global environmental challenges from energy production and use are amongst our most pressing." – John Howard, 2006
Related portals
WikiProjects
WikiProjects connected with energy:
- WikiProject Energy
- Oil megaprojects task force
Other WikiProjects that may be of interest:
- WikiProject Environment
- WikiProject Technology
- WikiProject Biography
Major topics
Major categories
National energy supply, use & conservation
- Energy by country
National electricity sector
- Electric power by country
Politics, economics, environment
- Climate change
- Energy conservation
- Energy economics
- Energy crises
- Energy development
- Energy policy
- Peak oil
Energy sources
- Fuels
- Biofuels
- Fossil fuels
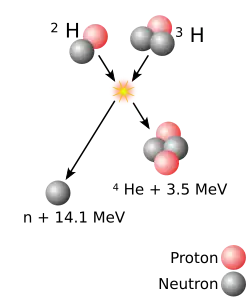
- Fusion power
- Nuclear technology
- Renewable energy
- Energy conversion
- Electric power
- Energy storage
Energy-related design
- Electric vehicles
- Hybrid vehicles
- Low-energy building
- Solar design
Scientific usage
- Heat transfer
- Thermodynamics
- Units of energy
Category browser

Help

Puzzled by energy?
Can't answer your question?
Don't understand the answer?
- Ask at the reference desk
- Read the Wikipedia help pages
For further ideas, to leave a comment, or to learn how you can help improve and update this portal, see the talk page.
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
-
 List of all portals
List of all portals -

-

-

-

-

-
-

-

-

-
 Random portal
Random portal -
 WikiProject Portals
WikiProject Portals















.jpg)






.jpg)








.svg.png)







.jpg)




.jpg)










































.svg.png)