Portal:Ecology
| |
|
|
Ecology
|
|
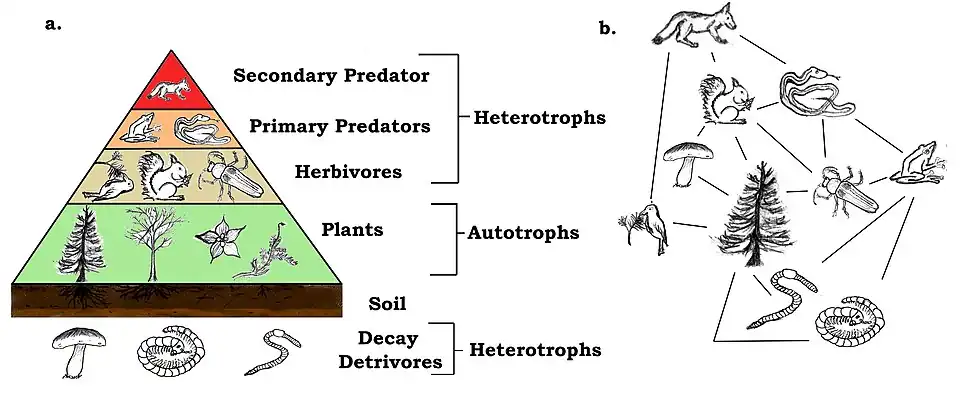
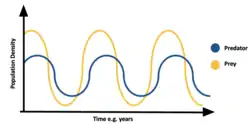
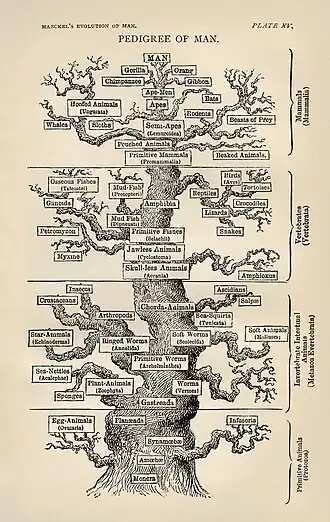
Ecology (from Ancient Greek οἶκος (oîkos) 'house' and -λογία (-logía) 'study of') is the natural science of the relationships among living organisms and their environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere levels. Ecology overlaps with the closely related sciences of biogeography, evolutionary biology, genetics, ethology, and natural history. Ecology is a branch of biology, and is the study of abundance, biomass, and distribution of organisms in the context of the environment. It encompasses life processes, interactions, and adaptations; movement of materials and energy through living communities; successional development of ecosystems; cooperation, competition, and predation within and between species; and patterns of biodiversity and its effect on ecosystem processes. Ecology has practical applications in fields such as conservation biology, wetland management, natural resource management, and human ecology. The term ecology (German: Ökologie) was coined in 1866 by the German scientist Ernst Haeckel. The science of ecology as we know it today began with a group of American botanists in the 1890s. Evolutionary concepts relating to adaptation and natural selection are cornerstones of modern ecological theory. Ecosystems are dynamically interacting systems of organisms, the communities they make up, and the non-living (abiotic) components of their environment. Ecosystem processes, such as primary production, nutrient cycling, and niche construction, regulate the flux of energy and matter through an environment. Ecosystems have biophysical feedback mechanisms that moderate processes acting on living (biotic) and abiotic components of the planet. Ecosystems sustain life-supporting functions and provide ecosystem services like biomass production (food, fuel, fiber, and medicine), the regulation of climate, global biogeochemical cycles, water filtration, soil formation, erosion control, flood protection, and many other natural features of scientific, historical, economic, or intrinsic value. (Full article...) Selected article - Hydrology (from Ancient Greek ὕδωρ (húdōr) 'water' and -λογία (-logía) 'study of') is the scientific study of the movement, distribution, and management of water on Earth and other planets, including the water cycle, water resources, and drainage basin sustainability. A practitioner of hydrology is called a hydrologist. Hydrologists are scientists studying earth or environmental science, civil or environmental engineering, and physical geography. Using various analytical methods and scientific techniques, they collect and analyze data to help solve water related problems such as environmental preservation, natural disasters, and water management. Hydrology subdivides into surface water hydrology, groundwater hydrology (hydrogeology), and marine hydrology. Domains of hydrology include hydrometeorology, surface hydrology, hydrogeology, drainage-basin management, and water quality. (Full article...) Selected image - Credit: Martin St-Amant The Iguazu Falls, on the border of Brazil and Argentina are waterfalls of the Iguazu River located on the border of the Brazilian State of Paraná and the Argentine Province of Misiones.
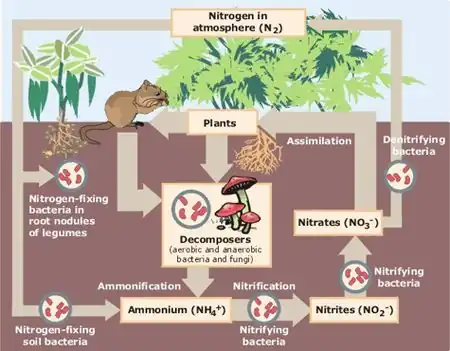
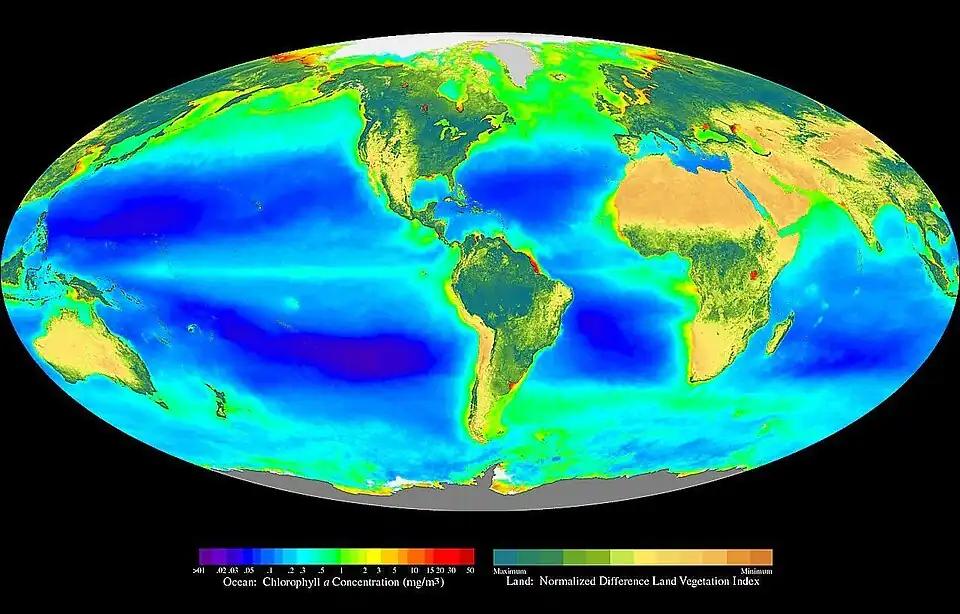
General imagesThe following are images from various ecology-related articles on Wikipedia.
Related WikiProjectsWikiProject Ecology
Things you can do
|
| “ | To halt the decline of an ecosystem, it is necessary to think like an ecosystem. | ” |
—Douglas P. Wheeler, EPA Journal, September-October 1990 |
Ecology news
- April 23: European Union to reduce carbon emissions by 55% of 1990 levels by 2030
- November 27: Wikinews interviews Craig Farquharson, Liberal Democrat candidate for 2020 Groom by-election
- November 27: Wikinews interviews Sandra Jephcott, Sustainable Australia candidate for 2020 Groom by-election
- December 14: Greta Thunberg named 2019 Time Person of the Year
- November 23: Researchers break down deaths due to power plant pollution in the United States
- November 21: Slippery business: Materials scientists invent new coating for self-cleaning, water-efficient toilets
- October 19: Northern Arapaho Tribe welcomes buffalo herd in Wyoming, United States
- October 12: Scientists describe how 'upside-down rivers' of warm water break Antarctica's ice shelf
- October 5: Voracious fish defend coral reefs against warming, say scientists
- September 8: Scientists report skyrocketing phytoplankton population in aftermath of Kīlauea eruption
- November 5, 2009: "New ocean forming in African desert."
Selected publication -
Plant Ecology is a scientific journal on plant ecology, formerly known as Vegetatio. The journal publishes original scientific papers on the ecology of vascular plants and terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems. The editor in chief is Neal J. Enright (Murdoch University). (Full article...)
Related portals
More did you know -
Related articles
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
Web resources
-
 List of all portals
List of all portals -

-

-

-

-

-
-

-

-

-
 Random portal
Random portal -
 WikiProject Portals
WikiProject Portals



_18.jpg)




_peeking_from_a_leaf_hole_of_an_Alnus_nepalensis_tree_(cropped).jpg)

.jpg)