Portal:Astronomy
Introduction

Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxies, meteoroids, asteroids, and comets. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions, gamma ray bursts, quasars, blazars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation. More generally, astronomy studies everything that originates beyond Earth's atmosphere. Cosmology is the branch of astronomy that studies the universe as a whole.
Astronomy is one of the oldest natural sciences. The early civilizations in recorded history made methodical observations of the night sky. These include the Egyptians, Babylonians, Greeks, Indians, Chinese, Maya, and many ancient indigenous peoples of the Americas. In the past, astronomy included disciplines as diverse as astrometry, celestial navigation, observational astronomy, and the making of calendars.
Professional astronomy is split into observational and theoretical branches. Observational astronomy is focused on acquiring data from observations of astronomical objects. This data is then analyzed using basic principles of physics. Theoretical astronomy is oriented toward the development of computer or analytical models to describe astronomical objects and phenomena. These two fields complement each other. Theoretical astronomy seeks to explain observational results and observations are used to confirm theoretical results.
Astronomy is one of the few sciences in which amateurs play an active role. This is especially true for the discovery and observation of transient events. Amateur astronomers have helped with many important discoveries, such as finding new comets. (Full article...)
General images -
 Featured article -
Featured article -
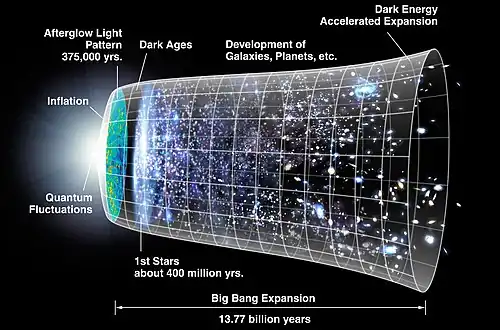
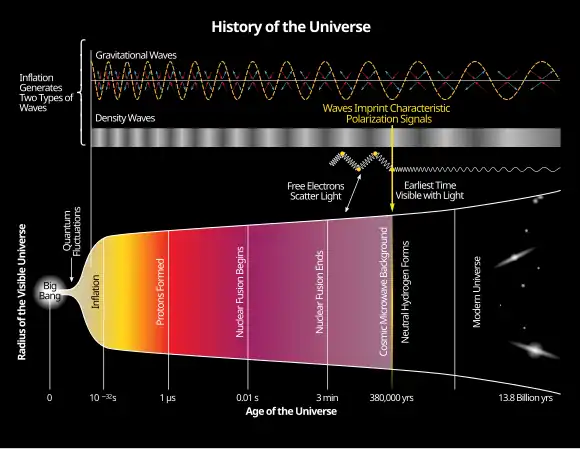
Extrapolating this cosmic expansion backward in time using the known laws of physics, the models describe an extraordinarily hot and dense primordial universe. Physics lacks a widely accepted theory that can model the earliest conditions of the Big Bang. As the universe expanded, it cooled sufficiently to allow the formation of subatomic particles, and later atoms. These primordial elements—mostly hydrogen, with some helium and lithium—then coalesced under the force of gravity aided by dark matter, forming early stars and galaxies. Measurements of the redshifts of supernovae indicate that the expansion of the universe is accelerating, an observation attributed to a concept called dark energy. (Full article...)
Did you know -
- ... that lenticular galaxy NGC 1553 is located at the center of the Dorado Group, and has a spiral feature that is only visible in X-rays?
- ... that giant diffuse galaxies, located in the centre of galaxy clusters, often possess a halo of devoured star matter extending as far out as 3 million light years?
- ... that the giant pulses of PSR B1937+21, the first discovered millisecond pulsar, are the brightest radio emission ever observed?
- ... that the star BX Circini is thought to have formed from the merger of two white dwarfs?
- ... that when astronomer Lacaille originally charted the constellation Caelum, it was recognized as an "engraver's chisel"?
- ... that the gamma-ray burst GRB 080319B was visible to the naked eye even though it was 7.5 billion light year away (z=0.937)?
More Did you know (auto generated)

- ... that 1ES 1927+654, a galaxy in Draco, exhibited such extreme nuclear activity that it challenged conventional models of black-hole environments?
- ... that Na drugą planetę, published in 1895 as one of the earliest Polish science-fiction novels, was later criticized by communist-era censors for its perceived "adoration for America"?
- ... that Kim Ye-ji's performance in the 10 meter air pistol at the 2024 Summer Olympics led her to be dubbed the "coolest person on the planet"?
- ... that some exoplanets are evaporating catastrophically?
- ... that the active galaxy 3C 120 was given the variable-star designation BW Tauri because of its variability in the visible spectrum?
- ... that the star TRAPPIST-1 has seven planets, several of which may have temperatures that would allow the existence of liquid water (artist's impression depicted)?
WikiProjects

|
|
| WikiProject Astronomy | WikiProject Solar System |
|---|---|
| WikiProject Cosmology | WikiProject Spaceflight |
Selected image -

The Musket Ball Cluster (DLSCL J0916.2+2951) is a galaxy cluster that exhibits separation between its baryonic matter and dark matter components. The cluster is a recent merger of two galaxy clusters in Cancer constellation. This composite image shows the Chandra (red) and Hubble (yellow and white) observation data.
Astronomy News
- 23 June 2025 –
- The Vera C. Rubin Observatory in Chile releases the first light images from its new 8.4-meter (28 ft) telescope. (Scientific American)
August anniversaries
- 4 August 2007 – The Phoenix Mars Lander is launched from Cape Canaveral, carrying science instruments to analyze soil samples of the Martian northern polar region
- 6 August 2012 – The Mars rover Curiosity lands on the Red Planet as part of NASA's Mars Science Laboratory mission
- 7 August 1996 – Announcement of possible microfossils found in ALH84001 Martian Meteorite
- 20 August 1977 – Voyager 2 space probe is launched by NASA to study the outer planets and interstellar space beyond the Sun's heliosphere
- 21 August 2017 – NASA.gov conducts a broadcast of the total solar eclipse with more than 50 million views of the live broadcast, and almost 31 million unique views on Facebook before and after the eclipse
- 24 August 2006 – The International Astronomical Union votes to approve a new definition of "planet" that excludes Pluto
- 25 August 2003 – The Spitzer Space Telescope (SIRTF) is launched, dedicated to infrared astronomy
- 27 August 1962 – Mariner 2 launches on a journey to Venus, and is the first robotic space probe to conduct a successful planetary encounter
- 31 August 1913 – Bernard Lovell, a British physicist and radio astronomer is born
Space-related Portals
Astronomical events
All times UT unless otherwise specified.
| 1 August, 20:37 | Moon at apogee |
| 9 August, 07:55 | Full moon |
| 12 August, 19:47 | Perseids peak |
| 14 August, 18:01 | Moon at perigee |
| 19 August, 09:59 | Mercury at greatest western elongation |
| 23 August, 06:06 | New moon |
| 29 August, 15:34 | Moon at apogee |
Topics
Subcategories
Things you can do
|
Here are some Open Tasks :
Astronomy featured article candidates:
Astronomy articles for which peer review has been requested:
|
Wikibooks

These books may be in various stages of development. See also the related Science and Mathematics bookshelves.
- Astronomy
- GAT: A Glossary of Astronomical Terms
- Introduction to Astrophysics
- General relativity
- Observing the Sky from 30°S
- Observing the Sky from 40°N
Wikijunior
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
-
 List of all portals
List of all portals -

-

-

-

-

-
-

-

-

-
 Random portal
Random portal -
 WikiProject Portals
WikiProject Portals
Shortcuts to this page: Astronomy portal • P:ASTRO
.jpg)










_(cropped).jpg)






_(cropped).jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)