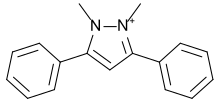
Difenzoquat
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1,2-dimethyl-3,5-diphenylpyrazolium
| |
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,2-dimethyl-3,5-diphenylpyrazol-1-ium | |
| Other names
1,2-dimethyl-3,5-diphenyl-1H-pyrazolium
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.051.352 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C17H17N2 | |
| Molar mass | 249.337 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colourless, odourless crystals[1] |
| Melting point | 155 °C (311 °F; 428 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | Decomposes before boiling[1] |
| Hazards | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
470mg/kg (oral, rat)[1] |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
Difenzoquat metilsulfate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
Difenzoquat is a selective, postemergent herbicide used to control wild oats in barley and wheat, and first registered in the US in 1975.[2]
Difenzoquat is a phenylpyrazole and pyrazole herbicide, and a quarternary ammonium compound. It is absorbed via the foliage and acts by rapidly destroying cell membranes.[1]
Usage
In the US, difenzoquat is applied once per season as a ground or aerial broadcast treatment; it is sold as a soluble concentrate (96%) or liquid (e.g. "Avenge", a 31.2% formulation), and 64 to 77% of difenzoquat sold is applied to wheat, as of 1994.[2]
It has also been marketed as "Finaven", "Yeh-Yan-Ku"[1] and "Mataven".[3]
Safety
Difenzoquat is a severe eye irritant, and has moderate acute toxicity on skin contact or via ingestion. Subchronic oral trials showed no effects on dogs, but rabbits in a dermal study developed skin reactions. In chronic trials, rats lost weight without other effect; dogs lost weight, suffered high mortality, developing tremors, lethargy and irregular gait.[2]
Difenzoquat appears to be non-carcinogenic. It is not mutagenic. The EPA estimates that humans are exposed to extremely low-level residues which pose no known risks.[2] Its NOEL is 25 mg/kg/day.[4]
Environmental behaviour
Difenzoquat is persistent and relatively immobile in soil, with little risk of groundwater contamination. Difenzoquat's persistence is slighty uncertain though, field trials indicate it dissipates much quicklier than believed.[2]
Difenzoquat is practically non-toxic to birds (LD50 of 10338 mg/kg) and freshwater fish, (LC50 of 76 mg/L) but moderately toxic to freshwater invertebrates. (LC50 of 2.6mg/L) It is non-toxic to honey bees. Chronic ecological toxicity is thought to be unlikely.[2][1]
Chemical properties
Aqueous solutions of difenzoquat can be effectively filtered with activated charcoal adsorption. One test removed 99.9% of difenzoquat this way, and 47% of paraquat and 46% of diquat, although with electrosorption those could be filtered to over 98%.[5]
References
- ^ a b c d e f g Hertfordshire, University of. "Difenzoquat (Ref: BAS 450H)". sitem.herts.ac.uk. Retrieved 19 July 2025.
- ^ a b c d e f "RED Facts Difenzoquat" (PDF). US EPA, Office of Prevention, Pesticides and Toxic Substances. Retrieved 19 July 2025.
- ^ "Integrated Risk Information System (IRIS) Chemical Assessment Summary" (PDF). US EPA. July 2016.
- ^ Assessment, US EPA National Center for Environmental. "Difenzoquat". US EPA.
- ^ Tongur, Timur; Ayranci, Erol (1 August 2021). "Adsorption and electrosorption of paraquat, diquat and difenzoquat from aqueous solutions onto activated carbon cloth as monitored by in-situ uv–visible spectroscopy". Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering. 9 (4): 105566. doi:10.1016/j.jece.2021.105566.
External links
- Difenzoquat in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB)