Oryzalin
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.038.873 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
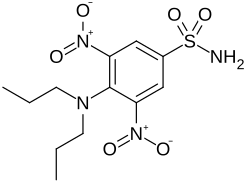
| Formula | C12H18N4O6S |
| Molar mass | 346.36 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 137 to 139 °C (279 to 282 °F) |
| |
| |
| | |
Oryzalin is a herbicide of the dinitroaniline class. It acts through the disruption (depolymerization) of microtubules, thus blocking anisotropic growth of plant cells.[1] It can also be used to induce polyploidy in plants as an alternative to colchicine.[2]
Oryzalin's mode of action is inhibition of microtubule assembly, so its HRAC classification is Group D (Australia), Group K1 (global) or Group 3 (numeric).[3]
Roughly 250,000 pounds (110 t) was used in the US in 2019, down from about 750,000 pounds (340 t) in 2010, and 1,000,000 pounds (450 t) in 1995 (by USGS estimates).[4]
References
- ^ Taiz L, Zeiger E (2010). Plant Physiology (5th ed.). Sinauer Associates. pp. 433–434. ISBN 978-0-87893-866-7.
- ^ Klíma M, Vyvadilová M, Kucera V (January 2008). "Chromosome doubling effects of selected antimitotic agents in Brassica napus microspore culture" (PDF). Czech Journal of Genetics and Plant Breeding. 44 (1): 30–36. doi:10.17221/1328-CJGPB.
- ^ "Classification of Herbicides According to Site of Action". www.weedscience.org. WSSA. Retrieved 3 July 2025.
- ^ "Pesticide Use Maps - Oryzalin". water.usgs.gov. USGS. Retrieved 15 August 2025.
External links
- Oryzalin in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB)