Soriana
 | |
| Company type | Sociedad Anónima Bursátil de Capital Variable |
|---|---|
| BMV: SORIANA B | |
| Industry | Retail |
| Founded | 1968 |
| Headquarters | , Mexico |
Key people | Francisco Javier Martín, (Chairman) Ricardo Martin Bringas, (CEO) |
| Products | Consumer goods |
| Revenue | |
Number of employees | 93,700 |
| Website | www |
Organización Soriana is a Mexican public company and one of the largest retailers in Mexico, operating more than 824 stores.[2] It is a grocery and department store chain headquartered in Monterrey, Nuevo Leon. The company is fully capitalized in Mexico and has been publicly traded on the Mexican Stock Exchange (Bolsa Mexicana de Valores) since 1987 under the ticker symbol Soriana.
Overview
Soriana was founded in 1968 by Mexican entrepreneurs and brothers, Francisco and Armando Martín Borque in Torreón, Coahuila. As of 2013, the company operated under the brands Soriana, Clubes City Club, Hipermart, Mercado Soriana, and Super City. Super City serves as the company's convenience store division. Soriana manages supermarkets and department stores catering to both consumer and wholesale markets.

Soriana's main competitors include H-E-B, La Comer, Chedraui, S-Mart, and Walmex. The company highlights its Mexican ownership and operations in its branding. A common retail practice in its stores involves displaying competitors' advertising circulars, such as those from Wal-Mart, Bodega Aurrerá, Superama, Chedraui, Alsuper, or H-E-B, with specific items marked to show lower prices at Soriana.
On December 6, 2007, Organización Soriana acquired Supermercados Gigante for US$1.35 billion. In 2008, Soriana replaced the Gigante brand in most of its stores, including seven locations in the United States, which were subsequently sold to Chedraui in May of that year. Many of the former Gigante stores in Mexico retained existing infrastructure, such as point-of-sale systems and food equipment.
By 2012, the company operated more than 606 stores in 208 cities across Mexico under five store formats: 249 Soriana Híper, 105 Soriana Súper, 147 Mercado Soriana, 72 Soriana Express, and 33 City Club. Soriana also maintained 14 distribution centers. In 2006, for reporting and administrative purposes, the company relocated its headquarters from Torreón to Monterrey.
History
The Beginnings of La Soriana

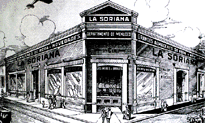
Soriana traces its origins to 1905, when Pascual Borque, a native of Soria, Spain, established a fabric and perfumery business in Torreón, Coahuila, under the name La Soriana. In 1920, the company incorporated wholesale merchandise into its operations, becoming a prominent reference point for trade and consumption in Torreón.[3][4][5]
In 1930, brothers Armando and Francisco Martín Borque assumed management of the business and expanded operations into municipalities across Coahuila, Durango, Chihuahua, and Sonora. In subsequent years, La Soriana shifted its focus from wholesale to retail.
Beginnings as a supermarket

In 1968, La Soriana discontinued its textiles and perfumery operations and transitioned to the supermarket model. That year, the company opened its first hypermarket, then described as a commercial center, in downtown Torreón, Coahuila. This marked the formal beginning of Organización Soriana and the start of its territorial expansion.

Soriana began its geographic expansion in 1974 with the opening of its first hypermarket in Monterrey, Nuevo León, known as Soriana Vallarta. This was the company's first store in both the city and the state. In the same year, Soriana opened additional branches in Durango and Chihuahua, consolidating its presence in northern Mexico and establishing itself as a regional supermarket chain. On October 30, 1975, Soriana opened its first shopping center in downtown Gómez Palacio, Durango, becoming the first national supermarket chain to operate in that city.[6][7]
The 1980s


During the 1980s, Soriana continued its expansion in northern Mexico. In 1984, it opened its first store in the border city of Ciudad Juárez, Chihuahua, and another branch in Torreón, Coahuila, known as Soriana Constitución.[8] Two years later, in 1986, the company opened a store in Reynosa, Tamaulipas (Soriana Hidalgo). On September 30, 1987, Soriana began trading on the Mexican Stock Exchange under the ticker symbol SORIANA.
Toward the end of the decade, differences arose between the Martín Borque brothers, leading to a business split. Francisco Martín Borque continued operating Soriana under the name Tiendas de Descuento del Nazas (Sorimex), while Armando Martín Borque established a new venture in Monterrey, Nuevo León. There, he created the Hipermart chain, formally named Sultana Discount Stores (Organización Soriana). In 1989, the first Hipermart stores opened in Monterrey (Cumbres and San Pedro), Ciudad Juárez (San Lorenzo), and Torreón (Independencia).
As part of Sorimex, Soriana also expanded into western Mexico. In 1988, it opened its first store in Aguascalientes, known as Soriana Aguascalientes Universidad. The following year, the company inaugurated its first store in Zacatecas (Soriana Zacatecas).
The 1990s

In 1990, Soriana opened its first store on the Mexican Pacific coast in Baja California, with the Soriana Tijuana Plaza Carrousel branch. However, following an agreement with Casa Ley, the store was closed four years later and subsequently replaced by a Comercial Mexicana location. Soriana later reacquired this property in 2015 and reopened it under its original name in 2017 after the conversion of Comercial Mexicana stores into Soriana Híper.

In 1994, the Martín Borque brothers reunited and merged their commercial chains (Soriana and Hipermart), forming Centros Comerciales Soriana, which later became Tiendas Soriana. That same year, Soriana expanded into the state of Jalisco with two stores in the Guadalajara metropolitan area: Soriana Bugambilias in Zapopan (originally operating under the pseudonym Hiperama until its rebranding as Soriana Híper in 2016) and Soriana Río Nilo in Guadalajara. The company also entered Guanajuato with stores in León (Soriana Malecón) and Irapuato (Soriana Jacarandas).
In 1995, Soriana continued its expansion with the opening of its first store in Tampico, Tamaulipas (Soriana Ejército). In 1997, it entered Querétaro with the Soriana Quintana branch, marking the company's presence in central Mexico. From 1998 onward, Soriana expanded further with stores in San Luis Potosí (Soriana El Paseo), Veracruz (Soriana Coatzacoalcos El Palmar), and Tlaxcala (Soriana Tlaxcala). On May 1, 1998, Soriana inaugurated its first store in Ciudad Mante, Tamaulipas, with an investment of 350 million pesos.[9] In December 1998, Francisco Martín Borque, founder and key promoter of the company, passed away.
In 1999, Soriana expanded into additional regions, opening stores in Michoacán (Soriana Uruapan), Colima (Soriana Plaza Colima), Hidalgo (Soriana Plaza del Valle Pachuca), Puebla (Soriana Torrecillas), Tabasco (Soriana Villahermosa Guayabal—the company's first store in southeastern Mexico), and Sinaloa (Soriana Culiacán Zapata), marking its return to the Pacific market following the dissolution of its non-compete agreement with Casa Ley.
2000–2007
Opening of store no. 100 and expansion into new states
In December 2000, Soriana entered the state of Nayarit for the first time with the opening of its 100th branch in the city of Tepic (Soriana Cigarrera). With this, it became the fourth self-service retail chain in Mexico to operate 100 stores under the same commercial name, following Cifra-Walmart, Tiendas Gigante, and Comercial Mexicana.[10]
Between 2001 and 2003, Soriana expanded into the southeast of Mexico, opening its first stores in Oaxaca (2001), Yucatán and Chiapas (2002), and Campeche and Quintana Roo (2003). In 2002, the company also entered La Paz, Baja California Sur. In 2004, Fundación Soriana, A.C. was established to strengthen and formalize corporate social responsibility programs.
Creation of new store formats: City Club, Mercado Soriana, and Súper City

On 17 July 2002, Soriana launched the price-club format City Club, in Torreón, Coahuila. This model targeted both families with high consumption and businesses by offering wholesale and semi-wholesale merchandise.[11][12] That same year, Soriana introduced its loyalty card, La Tarjeta del Aprecio (renamed Tarjeta Recompensas in 2015 and Tarjeta Recompensas Payback in 2018), which allowed customers to accumulate points to redeem for discounts, free products, or exclusive items.
In July 2003, Soriana created the Mercado Soriana format, opening its first branch in Salamanca, Guanajuato. This model consisted of medium-sized supermarkets with sales areas of 3,500 to 5,000 m², offering around 25,000 products at competitive prices. It was designed for towns of 50,000 to 150,000 inhabitants and popular urban areas where a Soriana Híper could not be established. During 2003, additional Mercado Soriana stores were opened in Navojoa and Guaymas (Sonora) and Puebla (Soriana Mercado Puebla Bosques).[13] From then on, Soriana included smaller cities and popular neighborhoods of large metropolitan areas in its expansion strategy through the Mercado Soriana format, while continuing to grow with its hypermarkets and City Club stores.
In 2005, Soriana entered the convenience store sector with the creation of the Súper City format. Designed to compete with Oxxo and 7-Eleven, these stores operated under a franchise system.[14] That same year, Carrefour withdrew from Mexico. While most of its stores in central, western, southern, and southeastern Mexico were acquired by Chedraui and one Monterrey branch by Walmart, Soriana purchased three Carrefour stores: in Saltillo, Coahuila (Echeverría), Chihuahua (Saucito and Ciudad Juárez Alameda Iglesias), and Hermosillo, Sonora (Bachoco). This marked Soriana's second acquisition of supermarket branches.[15][16]
Expansion in central Mexico; return to Baja California Norte
In 2005, Soriana opened its first store in the metropolitan area of the Valley of Mexico: Mercado Soriana Ciudad Azteca in Ecatepec, Estado de México. This marked a significant step in the company's expansion into central Mexico.[17][18]

On 13 May 2006, Soriana opened two new stores in Gómez Palacio, Durango, one under the Soriana brand and another as City Club, both located in the Plaza Centenario shopping complex. In April of that year, Soriana also inaugurated its 200th store in Ciudad Frontera, Coahuila.[19]
In 2006, the company tested a new supermarket format with the opening of Soriana Súper Playa de Oro in Puerto Vallarta, Jalisco (closed in May 2020). The format was designed to provide a quicker shopping experience focused on daily-consumption products. That year, Soriana also returned to Baja California Norte after a 12-year absence, opening branches in Mexicali (Calafia) and Tijuana (Otay). It additionally opened its first hypermarkets in the Estado de México, including Ixtapaluca, Cofradías (in the Mexico City metropolitan area), and Plaza Sendero Toluca (in the Toluca metropolitan area).[20]
In 2007, Soriana expanded further, opening its first store in Mexico City (Mercado Soriana Ermita) and its first store in the state of Guerrero (Mercado Soriana Iguala), marking its entry into the Guerrero market.[21]
2007–2008
Third supermarket acquisition: Supermercados Gigante; creation of the Soriana Súper format; expansion into new cities and transition to a national supermarket chain
On December 6, 2007, Soriana acquired 199 Supermercados Gigante stores from Grupo Gigante for US$1.35 billion. The transaction included stores operating under the formats Gigante, Bodega Gigante, Súper Gigante, Súper G, and Súper Maz in Mexico, as well as seven Gigante USA branches in the United States (later sold to Chedraui and converted into its El Súper format). This acquisition strengthened Soriana's national presence and allowed the company to formally expand into the Mexico City market.
As part of the transition, from December 7, 2007, until April 17, 2008, Gigante operated as a subsidiary of Soriana. At the beginning of 2008, Soriana introduced the Soriana Súper format, aimed at providing a quicker shopping experience. This format was used to convert former Súper G and Súper Maz locations, as well as certain Gigante and Bodega Gigante branches with sales areas smaller than 3,500 square meters.
On April 18, 2008, the Gigante formats were officially discontinued, and all stores were rebranded under Soriana’s formats, including the newly established Soriana Súper. Through this process, Soriana entered the State of Morelos by converting a former Bodega Gigante branch in Cuernavaca. With this acquisition, Soriana expanded its presence to all 32 states of the Mexican Republic, establishing itself as a national supermarket chain.
The conversion also allowed Soriana to enter cities where it previously had no presence but Gigante did, such as Ensenada and Tecate (Baja California Norte), Campeche (Campeche), Mexico City, Silao and San Miguel de Allende (Guanajuato), Acapulco (Guerrero), Cuernavaca (Morelos), Cozumel (Quintana Roo), Apizaco (Tlaxcala), and Valladolid (Yucatán). Additionally, it increased the number of branches in cities where Soriana already operated.[22]
2008–2014
Following the acquisition of 199 Gigante stores and their conversion into different company formats, Soriana became a national chain as of April 18, 2008. With its hypermarket, supermarket, warehouse, and price club formats, the company began to compete directly with other national chains, its main competitor being Walmart, which held a strong presence in central Mexico.[23]
In February 2010, as part of its multi-format strategy and ongoing geographic expansion, Soriana introduced the Soriana Express format in the municipality of Centla, Tabasco. This format consisted of supermarkets with a sales floor of 800 to 1,500 square meters, aimed at small cities and localities with populations between 10,000 and 50,000 inhabitants, as well as densely populated areas in larger cities.[24][25][26] The first Soriana Express stores opened in late May 2010 in Ixtlán del Río, Nayarit, and El Rosario, Sinaloa.[27]
In 2011, Soriana expanded the Soriana Express format nationwide. On February 9, 2011, it opened its first store of this type in Zacatecas, located in the municipality of Jerez de García Salinas with a 1,294 m² sales floor and an investment of 29 million pesos.[28] On March 10, 2011, the first Soriana Express stores in Jalisco opened in the municipalities of Tala and Zapotiltic.[29] Additional stores followed in Tlajomulco de Zúñiga (April 27, 2011),[30] Sayula (May 4, 2011),[31] and Ameca (August 25, 2011). On the same day, Soriana also opened its first Soriana Express store in Morelos, in the municipality of Yautepec de Zaragoza.[32]
As part of its multi-format strategy, Soriana restructured its organizational model in September 2011, segmenting its self-service formats according to market niches.[33] That year, the company also introduced Soriana Súper VIP, a premium supermarket concept, beginning with the remodeled Soriana Súper Marne branch in San Pedro Garza García, Nuevo León. The store featured a 2,230 m² sales floor with gourmet products, imported wines, liquors, delicatessen items, and prepared foods.[34][35] On October 7, 2011, Soriana opened additional Soriana Express stores in Culiacán, Sinaloa (El Dorado), and in Nacozari de García, Sonora.[36] On December 9, 2011, the company inaugurated its first hypermarkets in the capitals of Guerrero and Quintana Roo, located in Chilpancingo and Chetumal, respectively.[37]
Following the deaths of Soriana's founding brothers, leadership passed to Ricardo Martín Bringas, the youngest son of Francisco Martín Borque. By 2020, Martín Bringas had an estimated net worth of US$2.1 billion. Under his direction, Grupo Soriana expanded to more than 600 stores across 200 cities and towns, supported by 14 distribution centers nationwide. In 2006, the company relocated its headquarters from Torreón to Monterrey. Outside of Soriana, Martín Bringas and his wife founded Innovasport in 1999, specializing in athletic apparel, footwear, and sporting goods, along with a sneaker-focused spinoff chain, Innvictus, which together grew to more than 100 stores across Mexico. In 2010, he was named one of Expansión magazine's "100 Most Important Entrepreneurs in Mexico."[38]
In 2013, Soriana built its first wind power plant in Reynosa, Tamaulipas, as part of its long-term sustainability strategy. On April 24, 2014, the company inaugurated its first hypermarket in the state of Morelos, located in Plaza Cedros, Jiutepec, with a 5,843 m² sales floor and an investment of more than 101 million pesos.[39][40][41] At the end of 2014, Soriana introduced a new corporate image for both the company and its store formats. The first location to adopt this updated image was the Soriana Súper San Agustín store in Tlajomulco de Zúñiga, Jalisco.
2015–2018: Acquisition of Comercial Mexicana Stores
On January 28, 2015, Soriana acquired a significant portion of Controladora Comercial Mexicana's 160 stores for a total of MXN 39,194,000. The acquisition included stores under the Comercial Mexicana, MEGA, Bodega Comercial Mexicana, and Alprecio formats, which became part of Soriana as of January 4, 2016.
In addition to the stores, Soriana obtained strategically important assets, including real estate for 118 stores, lease agreements for 42 stores, operating equipment, inventory, and the Julio Regalado promotional program, which had been established by Comercial Mexicana in 1980 and became part of Soriana in 2016.[42][43] Due to conditions imposed by the Mexican Federal Economic Competition Commission (COFECE), only 143 branches were purchased, as the acquisition of the full 160 stores would have affected 27 markets, potentially reducing competition and increasing consumer prices. Consequently, 27 stores were not acquired and were later sold to third parties.[44][45]
As a result, Comercial Mexicana retained 14 conditioned stores, while Soriana kept 13 for future sale. On January 4, 2016, the smaller formats Fresko, Sumesa, and City Market became part of Grupo LaComer, while the larger formats — Comercial Mexicana, MEGA, Bodega, and Alprecio — joined Soriana. Soriana obtained a license to use the Comercial Mexicana brand for more than two years before renaming the stores to Soriana formats.[46][47]
During the transition, Soriana relaunched the Julio Regalado promotion on June 3, 2016, across the recently acquired Comercial Mexicana formats MEGA, Bodega, and Alprecio.[48] On June 10, 2016, Soriana introduced the Soriana Híper Plus format, a premium hypermarket concept targeting middle- and high-income consumers, offering gourmet products and specialized departments such as cheese, wine, European breads, pastries, and exotic meats. The first store opened in the Miyana shopping center in Polanco, Mexico City, with a 7,245 m² sales floor.[49] In December 2016, Soriana reopened the Soriana Híper San Pedro store in Monterrey, Nuevo León, with a new premium concept and a sales floor of 8,637 m², making it the second Soriana Híper Plus location in Mexico.[50]
Some stores were closed as part of the integration process. On February 16, 2017, Soriana Súper Plaza Fiesta in Matamoros, Tamaulipas was permanently closed due to the proximity of another Soriana branch. On March 7, 2017, Soriana Híper Tepeyac in Zapopan, Jalisco, closed permanently due to low sales, as another Soriana Híper store was located nearby.[51][52]
Starting in March 2017, Soriana began converting Comercial Mexicana stores to its own formats, beginning in Baja California with 14 branches converted to Soriana Híper. MEGA Comercial Mexicana branches in Baja California Sur, Sonora, and Sinaloa were also converted. In Mexico City, the Soriana Híper División del Norte branch (formerly Gigante) was converted into MEGA Soriana, alongside the opening of new MEGA Soriana stores in Patio Tollocan, Toluca, State of Mexico, and Plaza Citadina, Villa Corregidora, Querétaro. Additional Comercial Mexicana stores were similarly converted, including a branch in Zamora, Michoacán, which became Soriana Híper Zamora Madero in November 2017.
By March 1, 2018, Soriana completed the conversion of the remaining Comercial Mexicana stores into the following formats:
- MEGA Soriana: Most Comercial Mexicana, all MEGA Comercial Mexicana, and some Bodega Comercial Mexicana stores were converted to this format.
- Soriana Híper: Selected Comercial Mexicana and MEGA stores in León, Celaya, Puerto Vallarta, Veracruz, Coatzacoalcos, and Mérida were converted to the main Soriana Híper format.
- Soriana Súper: Stores with sales floors under 3,500 m², such as Comercial Mexicana Acapulco Costa Azul and Cancún Tulúm, were converted to this format.
- Soriana Mercado: Certain Bodega Comercial Mexicana stores in Aguascalientes and Veracruz, as well as Comercial Mexicana Texcoco Aeropuerto, were converted to Soriana Mercado. Other Bodega Comercial Mexicana stores were temporarily operated as Bodega Soriana until December 31, 2018, before permanently becoming Soriana Mercado on January 1, 2019.[53]
- Soriana Express: Three Alprecio branches (Ojo de Agua, Lerma, and Yautepec) were initially converted to Bodega Soriana in 2018, and then to Soriana Express on January 1, 2019.
- City Club: Between 2022 and 2023, MEGA Comercial Mexicana branches in Ciudad Victoria, Tamaulipas, and Ciudad del Carmen, Campeche, were converted to City Club.
- Sodimac Homecenter: MEGA Comercial Mexicana stores in Cuernavaca, Morelos, and Boca del Río, Veracruz, were converted to this format.

On May 31, 2018, Controladora Comercial Mexicana officially ceased operations. The Bodega Soriana format was discontinued on December 31, 2018, with most stores converted to Soriana Mercado; four became MEGA Soriana, and three became Soriana Express due to their small sales floor areas and previous Alprecio designation.[54][55]
2018–Present: Store openings, closures, and Sodimac Homecenter expansion
In mid-April 2016, Soriana entered into a strategic alliance with the Chilean company Falabella, investing USD 600 million for expansion. The agreement included the opening of home improvement stores under the Sodimac Homecenter brand, as well as financial services with the CMR credit card.[56] The first Sodimac Homecenter store opened in August 2018 in Cuautitlán Izcalli, State of Mexico, with a sales floor of 10,700 m².[57] Subsequent openings included stores in Arboledas, Naucalpan; Cuernavaca, Morelos (replacing a MEGA Comercial Mexicana store);[58][59] Boca del Río, Veracruz;[60] Plaza San Mateo, Naucalpan;[61] and San Luis Potosí (El Paseo shopping center).[62]
On May 20, 2021, Sodimac opened its seventh store in León, Guanajuato, replacing a City Club that closed on February 29, 2020, due to low sales.[63][64] At the end of August 2021, Sodimac entered the Monterrey metropolitan area with a store in Sendero Monterrey, followed by a second store in Santa Catarina, Nuevo León, on December 3, 2021.[65][66]
On June 16, 2022, Sodimac opened its tenth store in Mexico City at the Plaza Central shopping center, a smaller-format store with over 4,000 m² of sales space.[67][68] Additional openings at the end of 2022 included Saltillo, Coahuila (Soriana Echeverría shopping plaza) [69] and Mexico City (Gran Sur Shopping Center).[70] On July 27, 2023, the Interlomas branch in Huixquilucan, State of Mexico, opened with 5,081 m² of sales area and 30,000 products.[71]
Following the full integration of Comercial Mexicana stores, Soriana made operational adjustments to its more than 800 branches due to cannibalization, inventory shortages, and competitive pressures in central Mexico.[72]
During 2019–2020, Soriana closed several branches to comply with COFECE conditions, address low sales, or renovate stores. Notable closures included Soriana Híper Iglesias in Ciudad Juárez, Chihuahua, temporarily closed on February 2, 2020, and reopened on May 17, 2023, as Soriana Súper Alameda Iglesias;[73][74] the City Club in León, Guanajuato, closed on February 29, 2020;[75] and several stores during the COVID-19 pandemic, including:
- Soriana Mercado Plaza Inn, Tlaxcala, Tlaxcala (March 15, 2020)[76]
- MEGA Soriana Acapulco Las Hamacas, Acapulco, Guerrero (April 30, 2020)[77]
- Soriana Súper Playa de Oro, Puerto Vallarta, Jalisco (May 1, 2020; later acquired by Chedraui)[78]
- Soriana Híper Campestre, Celaya, Guanajuato (May 31, 2020; later replaced by Chedraui)[79]
- Soriana Híper Plaza Las Ánimas, Puebla, Puebla (June 30, 2020)[80]
- Soriana Híper Misión, Ensenada, Baja California, and Soriana Híper León Campestre, León, Guanajuato (July 31, 2020)[81]
- Soriana Híper Glorieta, San Luis Potosí, San Luis Potosí, and Soriana Híper Plaza Morelia, Morelia, Michoacán (August 2020)[82][83]
- Soriana Súper Gavilanes, Zacatecas, Zacatecas (temporarily closed September 24, 2020; reopened September 23, 2021, as Soriana Súper and City Club).[84][85]
From 2021, Soriana resumed expansion and format renovations, including the reopening of Soriana Súper Gavilanes and City Club Zacatecas on September 23, 2021.[86] On October 28, 2021, Soriana Súper Sendera Colima opened in Villa de Álvarez, Colima, with a 2,897 m² gourmet concept.[87]
In 2022, Soriana opened additional stores, including Soriana Híper and City Club in Tapachula, Chiapas (June 8, 2022), City Club Ciudad Victoria, Tamaulipas (November 10, 2022), and Soriana Mercado Prado Norte, Cancún, Quintana Roo (December 2022).[88][89] Soriana Mercado Pino Suárez, San Juan del Río, Querétaro, closed permanently on December 16, 2022, after 37 years of operation[90]
In 2023, Soriana opened 10 new stores and remodeled 47 existing units, including:
- Soriana Híper Viñedos, Torreón, Coahuila (February 1, 2023)[91]
- Soriana Mercado Comitán, Comitán de Domínguez, Chiapas[92]
- City Club Ciudad del Carmen, Campeche[93]
- Soriana Súper Alameda Iglesias and Soriana Súper Talamás, Ciudad Juárez, Chihuahua[94][95]
- Soriana Súper López de Lara, Nuevo Laredo, Tamaulipas
- Soriana Híper Abasolo and Soriana Súper Campestre Saltillo, Saltillo, Coahuila
- Soriana Express Hernán Cortés, Veracruz, Veracruz (reopened November 23, 2023)[96]
- City Club Cordilleras, Zapopan, Jalisco (November 15, 2023)[97][98]
Closures in 2023 included Soriana Mercado El Sauz, Guadalajara; Soriana Súper Maldonado, Nuevo Laredo; Soriana Híper Abasolo, Saltillo; Soriana Híper Santa Cecilia, Monterrey; Soriana Mercado Hernán Cortés, Veracruz; and Soriana Súper Agua Caliente, Tijuana.[99][100][101][102] On October 4, 2024, City Club Cordilleras in Guadalajara closed after a fire.[103]
As of 2024, Soriana operates 804 stores nationwide, including 368 Soriana Híper, 162 Soriana Mercado, 129 Soriana Súper, 106 Soriana Express, 39 City Club, and 13 Sodimac Homecenter locations.
Store formats
Soriana Híper


Soriana Híper is the flagship store format of Organización Soriana, created in 1968. The format consists of hypermarkets primarily located in cities with more than 150,000 inhabitants. Stores typically have a sales floor ranging from 4,000 to 11,000 m². They operate under a retail model with a wide assortment of merchandise, carrying approximately 50,000 stock-keeping units (SKUs) across divisions such as clothing, general merchandise, groceries, and perishable foods. Most stores are part of shopping centers that include 40 to 50 smaller retail outlets rented to third parties.
Soriana Híper competes with:
- Walmart Supercenter (Walmart), its main nationwide competitor
- Chedraui (Grupo Comercial Chedraui)
- Casa Ley (hypermarket format)
- H-E-B (in certain markets)
- La Comer (in certain markets)
- Until January 3, 2016, it also competed with Comercial Mexicana (Controladora Comercial Mexicana).
In 2008, most former Gigante stores were converted into Soriana Híper, along with some Bodega Gigante units, three Súper Gigante stores in Baja California, and one Súper Maz location in Mérida.
In 2017, 14 former Comercial Mexicana stores in Baja California were converted to Soriana Híper. In 2018, part of the 47 Comercial Mexicana units acquired in 2016 were also converted, mainly in northern cities such as Mazatlán, Culiacán, Hermosillo, La Paz, Veracruz, Mérida, Zamora, and Celaya.
Soriana Híper Plus
Soriana Híper Plus is a subformat of Soriana Híper, aimed at mature markets with high-income consumers. In addition to the products offered in Soriana Híper, it includes premium selections such as wines and gourmet foods. These stores typically carry up to 60,000 SKUs and feature redesigned interiors.
Competitors include:
- H-E-B (primarily)
- La Comer (Grupo La Comer, primarily)
- Walmart Supercenter (partially)
- Selecto Chedraui (main nationwide competitor)
- Until January 3, 2016, it also competed with Mega Comercial Mexicana.
Examples of Soriana Híper Plus stores include:
- Gran Terraza Coapa (Mexico City)
- Plaza Miyana Polanco (Mexico City)
- Pilares (Mexico City)
- COAPA (Mexico City)
- Viñedos (Torreón)
- Hipermart Independencia (Torreón)
- San Pedro (Monterrey)
- San Nicolás (Monterrey)
- Galerías Valle Oriente (Monterrey)
- San Jerónimo (Monterrey)
- Cumbres (Monterrey)
- Aviación (Guadalajara)
- Bugambilias (Guadalajara)
- Cordilleras (Guadalajara)
- Acapulco Diamante (Acapulco)
- Zihuatanejo (Zihuatanejo)
- Bahía de Banderas (Bahía de Banderas)
- Tezal (Los Cabos)
MEGA Soriana

MEGA Soriana is another subformat of Soriana Híper, created in 2017 following the acquisition of Comercial Mexicana. Soriana adopted the Mega name after obtaining 70 properties associated with the former Mega Comercial Mexicana format. This was the only brand from the acquisition that Soriana retained.
Mega Soriana stores are generally located in cities with more than 150,000 inhabitants and carry around 60,000 SKUs. In addition to standard Soriana Híper products, they offer gourmet foods, wines, and services previously associated with Mega Comercial Mexicana, such as Grand Café, Bocatto, and Fábrica de Quesos. Store interiors retain design elements from Comercial Mexicana, including coffee shops and bakeries. Their sales floor areas range from 4,500 to 14,000 m².
The first conversion occurred in March 2017, when Soriana Híper División del Norte (Mexico City) became Mega Soriana. In 2018, most former Comercial Mexicana and Mega Comercial Mexicana stores in central, southern, and southeastern Mexico were also converted, as well as some Bodega Comercial Mexicana units in the states of Mexico, Guerrero, Hidalgo, San Luis Potosí, and Morelos.
Main competitors include:
- H-E-B
- La Comer
- Walmart Supercenter
- Chedraui and Selecto Chedraui
Soriana Súper
Soriana Súper is a supermarket format created in 2008, derived from the acquisition of Tiendas Gigante. It was based on the original Super G stores. These stores focus on daily consumer products such as groceries, perishables, and prepared foods, designed to provide customers with agile and quick purchases. The sales floor area ranges from 500 to 4,000 m². Stores are typically located in three types of areas:
- Residential subdivisions with middle- and high-income populations.
- Locations where the space or size does not allow for a Soriana Híper.
- Cities with a significant number of former Gigante stores, which were converted into Soriana Súper.
As a general supermarket format, Soriana Súper competes with:
- Calimax
- Sumesa (La Comer Group)
- Walmart Express
- Super Ley and Super Ley Express
- Super Chedraui
- Superbodega (Grupo Arteli)
In 2008, all Super G stores were converted into Soriana Súper (except one branch in Tijuana and two in Ensenada, which became Soriana Híper), as well as most Super MAZ stores and several Gigante and Bodega Gigante stores with sales areas under 4,000 m².
In 2015, Soriana acquired and converted four Super Frutería del Sol stores in San Luis Río Colorado, Sonora, into Soriana Súper.
In 2018, two Comercial Mexicana stores in Acapulco and Cancún were converted into Soriana Súper, as both had areas of less than 3,000 m².
Sub-formats
Soriana Súper operates two sub-formats: Soriana Súper Plus and Soriana Supermarket, both of which follow a "fresh market" concept.
Soriana Súper Plus
Introduced in 2011, Soriana Súper Plus is the premium sub-format of Soriana Súper. In addition to the standard product offering, these stores feature imported and specialty items such as exotic meats. The first Soriana Súper Plus was established on the site of Soriana Super Marne, a former Gigante store.
As a premium supermarket, its main competitors include:
- Aladdin's
- Selecto Chedraui
- City Market (Grupo La Comer)
Soriana Supermarket
Launched in 2020, Soriana Supermarket is another fresh market sub-format. It offers groceries, perishable goods, prepared foods, wines, and gourmet products.
Its competitors include:
- Super Ley Express Fresh (Casa Ley)
- Super Chedraui
- Fresko (Grupo La Comer)
- Walmart Express (since November 2020, following the rebranding of Superama)
Notable Soriana Súper Plus and Soriana Supermarket locations
- Marne (San Pedro Garza García, Nuevo León)
- Pueblo Serena (Monterrey, Nuevo León)
- Valle (San Pedro Garza García, Nuevo León)
- Plaza Nativa (San Pedro Garza García, Nuevo León)
- Valle Poniente (San Pedro Garza García, Nuevo León)
- Plaza Universidad (Zapopan, Jalisco)
- Plaza Terranova (Guadalajara, Jalisco)
- Pablo Neruda (Guadalajara, Jalisco)
- Cititower (Guadalajara, Jalisco)
- Urbania (Zapopan, Jalisco)
- Eugenia (Mexico City)
- Santa Fe Paradox (Mexico City)
- Toriello (Mexico City)
- Town Square Metepec (Toluca)
- Kukulkan Plaza (Cancún)
- Misión San José (San José del Cabo, BCS)
- Gavilanes (Zacatecas)
- Sendera Colima (Villa de Álvarez, Colima)
- Costa Azul (Acapulco)
- Alameda Iglesias (Ciudad Juárez, Chihuahua)
- Campestre (Saltillo, Coahuila)
Soriana Mercado


Soriana Mercado was created in 2003 as a self-service warehouse format with an average sales floor area of 4,000 to 5,000 m². It is primarily aimed at cities with populations between 50,000 and 150,000 inhabitants, as well as popular areas in large and medium-sized cities where it is not feasible to establish a Soriana Híper store. The format focuses on fast-moving products in the grocery, perishables, and prepared food divisions, along with a limited selection of clothing and general merchandise. Stores generally feature modest decoration with a basic level of comfort.
In some cities, Soriana Mercado locations are later converted into Soriana Híper if demand increases, while in other cases they are converted into Soriana Express if demand is lower than expected.
As a self-service warehouse format, Soriana Mercado competes mainly with:
- Bodega Aurrerá
- Chedraui and Super Che
- Casa Ley
- Until January 3, 2016, it also competed with Comercial Mexicana in its Bodega Comercial Mexicana format.
In 2008, Soriana converted most Bodega Gigante stores and some Gigante locations into Soriana Mercado. In 2018, Soriana transformed many of the 32 Bodega Comercial Mexicana stores into Soriana Mercado. In central Mexico, the Bodega Comercial Mexicana name was temporarily retained before being changed permanently to Soriana Mercado in 2019. That same year, the Comercial Mexicana Texcoco Aeropuerto store was converted into Soriana Mercado, due to its floor area of less than 4,900 m², which made conversion into a MEGA Soriana unfeasible.
Soriana Express
Soriana Express is a sub-format of Soriana Mercado created in 2010. It is designed for areas, cities, or towns where neither Soriana Híper nor Soriana Mercado can be established, typically in municipalities with populations of 10,000 to 90,000. Stores have an average sales floor area of about 1,500 m² and are located mainly in lower- and middle-income areas. They offer a range of groceries, clothing, prepared foods, perishables, and general merchandise in a compact but comprehensive format.
As a rural supermarket, Soriana Express competes primarily with:
- Mi Bodega Aurrerá
- Ley Express and Súper Ley Express
- Súper Kompras Micro
- Súper Che
- Independent local stores in each town where Soriana operates
- Until January 3, 2016, it also competed with Alprecio, operated by Comercial Mexicana.
During the 2010s, Soriana converted some Gigante, Bodega Gigante, and Super MAZ stores into Soriana Express where conditions were suitable. In 2019, after temporarily using the Bodega Soriana name, Soriana rebranded three Alprecio stores as Soriana Express.
City Club is a warehouse club format created in 2002. Stores range in size from 7,000 to 11,000 m² of sales floor area and require a paid membership for entry. The format targets high-volume household consumers as well as institutional clients such as hospitals, hotels, restaurants, and small businesses.
City Club operates under wholesale and semi-wholesale models, offering products in bulk containers and multipacks. The stores emphasize large purchase volumes and low margins, carrying approximately 5,000 SKUs across grocery, perishables, clothing, and general merchandise categories.
Its main competitors are:
- Sam's Club (nationwide)
- Costco Wholesale (nationwide)
- Ley Mayoreo and Súper Mayoreo Ley (regional competitor, through its wholesale sales model)
- Central or municipal supply markets in the cities where City Club is present
In 2008, Soriana converted several former Gigante locations into City Club stores. These included two stores in Mexico City, two in Monterrey, one in Querétaro, and one Bodega Gigante in Puebla. The conversions took place mainly in areas where Soriana already operated nearby stores or in locations where Gigante had multiple branches, allowing one of the buildings to be adapted into the City Club format.

Super City is a convenience store format created in 2005. Stores have a sales area of between 70 and 80 m² and no longer operate under a franchise system. They primarily offer last-minute shopping products such as coffee, snacks, sweets, bakery items, groceries, and beverages.
Its main competitors are:
- Oxxo (FEMSA)
- 7-Eleven (Casa Chapa)
- Extra (Grupo Modelo)
- Circle K
- Super Kiosko (limited to Sinaloa, Nayarit, Jalisco, Colima, and Michoacán)
- Bodega Aurrerá Express (to some extent, as an express supermarket)
- Chedraui Supercito (to some extent, as an express supermarket)
- Farmacias Guadalajara (to some extent, as a super-pharmacy competitor)
Sodimac Homecenter
In 2016, Soriana entered into a collaboration agreement with the Chilean retail company Falabella to open Sodimac stores in Mexico. The partnership established a joint venture with equal 50–50 ownership of Sodimac's Mexican subsidiary. The first store opened on August 3, 2018, in Cuautitlán Izcalli, State of Mexico, within the metropolitan area of the Valley of Mexico, adjacent to a Mega Soriana supermarket. Subsequent locations were opened in Tlalnepantla and Naucalpan (State of Mexico), Cuernavaca (Morelos), and in the states of Veracruz and San Luis Potosí.
Sodimac stores in Mexico operate under two formats: Sodimac Homecenter, focused on hardware, home improvement, and DIY, and Sodimac Constructor, oriented toward construction materials. Many of these outlets were established on properties where Soriana already operated other formats, particularly Mega Soriana and Soriana Híper stores.
Its main national competitor is The Home Depot, along with local hardware chains such as Ferreterías Fix and Comex. Due to its product range, Sodimac also competes indirectly with The Home Store (Grupo Gigante), Zara Home (Grupo Inditex), and Bed Bath & Beyond. Until its exit from the Mexican market, Lowe's was also a competitor.
Promotions
Soriana promotes the Tarjeta del Aprecio (Appreciation Card), a loyalty program through which customers earn points on purchases. Accumulated points can be redeemed for merchandise or store credits, including discounts of up to 20% on general merchandise.
Sponsor
Soriana is the official shirt sponsor of Santos Laguna, a football club in Mexico's top professional league, the Liga MX.
Slogans and trade names
Over the years, Soriana has used several slogans in its advertising campaigns, including:
- Donde todos los días son buenos días ("Where All Days Are Good Days") – late 1970s
- Responde cuando usted lo necesita ("Responds When You Need It") – 1988
- Todos los caminos conducen a Soriana ("All Ways Lead to Soriana") – 1990
- Lo mejor al mejor precio ("The Best at the Best Prices") – 1993
- En suma pagas menos (pun meaning both "Pay Less for the Total" and "In Short, Pay Less") – mid-1990s
- Nuestros precios hablan ("Our Prices Speak") – 1999, 2011
- Apre¢io por ti / A pre¢io por ti (pun meaning both "At the Right Pri¢e for You" and "E$teem for You") – 2000
- Mejores ofertas a precios más bajos ("Better Offers at Lower Prices") – 2001
- El precio más bajo garantizado ("The Lowest Price Guaranteed") – 2002
- El mayor ahorro ("The Greatest Savings") – 2007
- Porque nos importas tú ("Because We Care for You") – 2008
- ¡Hazlo híper, y ahorra! ("Do Hyper, and Save!") – 2013
-
 2000 slogan.
2000 slogan. -
 2018 slogan – shared with Comercial Mexicana during the transition of stores
2018 slogan – shared with Comercial Mexicana during the transition of stores -
 General slogan.
General slogan. -
 Corporate slogan.
Corporate slogan.
Evolution
Soriana expanded gradually across Mexico, opening stores in different states as follows:
- 1968 – Coahuila
- 1971 – Durango
- 1972 – Chihuahua
- 1974 – Nuevo León
- 1984 – Tamaulipas
- 1989 – Zacatecas
- 1990 – Aguascalientes
- 1994 – Jalisco, Guanajuato
- 1997 – Querétaro
- 1998 – San Luis Potosí, Veracruz, Tlaxcala
- 1999 – Michoacán, Colima, Sinaloa, Sonora, Tabasco, Hidalgo, Puebla
- 2000 – Nayarit
- 2001 – Oaxaca
- 2002 – Yucatán, Chiapas, Baja California Sur
- 2003 – Campeche, Quintana Roo
- 2005 – State of México
- 2006 – Baja California
- 2007 – Distrito Federal (today Mexico City), Guerrero
- 2008 – Morelos
Criticisms and controversies
2012 presidential election gift card scandal
During the 2012 Mexican presidential election, candidate Andrés Manuel López Obrador alleged that the Institutional Revolutionary Party (PRI) engaged in electoral fraud by distributing Soriana pre-paid gift cards in exchange for votes in favor of its candidate, Enrique Peña Nieto.[104] López Obrador also claimed that other gifts were provided to attract voters.[105]
Both the PRI and Soriana denied the accusations,[106] with the PRI threatening legal action against López Obrador.[105] Peña Nieto stated that anyone, including members of his own party, would face imprisonment if found guilty of electoral fraud.[107] Nevertheless, videos and testimonies from citizens regarding the alleged distribution of Soriana cards were circulated on YouTube and other media platforms.[108][109]
See also
- List of companies traded on the Bolsa Mexicana de Valores
- List of Mexican companies
- Economy of Mexico
- Comercial Mexicana
- Chedraui
References
- ^ a b "SORIANAB: Organizacion Soriana SAB de CV Stock Price Quote - BMV Mexico - Bloomberg". Archived from the original on 2012-10-12.
- ^ Farfan, Barbara. "The Largest Mexican Retailers Gain on Global Competitors Like Walmart". The Balance Small Business.
- ^ "La Soriana y su evolución". retailers.mx. Retrieved 2019-01-11.
- ^ "Primer "Soriana" fue una tienda de telas: ¿Cuál es la historia y quién es el dueño del supermercado?". www.radioformula.com.mx. Retrieved 2019-01-11.
- ^ "¿Qué significa la palabra Soriana y cuál es el origen de este supermercado?". www.radioformula.com.mx. Retrieved 2019-01-11.
- ^ "Historia de Soriana, el supermercado mexicano que nació en Coahuila". www.telediario.mx. Retrieved 2023-06-13.
- ^ "Soriana nació como una tienda de telas en una pequeña esquina de Torreón". www.elsoldelalaguna.com.mx. Retrieved 2022-11-11.
- ^ "Telas Soriana, el origen de la famosa tienda comercial". www.america-retail.com. Retrieved 2022-06-17.
- ^ "A 25 años de la inauguración de la tienda Soriana, El 1 de mayo de 1998, desfile, inicio de la feria y la apertura de un centro comercial que costó 350 millones de pesos, símbolo del progreso de esta región cañera". www.elecodelmante.com/. Retrieved 2023-05-11.
- ^ "Nuestra Historia / Corporativo Soriana". www.organizacionsoriana.com. Retrieved 2023-07-03.
- ^ "City Club cumple 20 años al servicio de sus 1.4 millones de socios". Revista Contacto. Retrieved 2022-07-25.
- ^ "City Club de Soriana cumple 20 años". Retailers. Retrieved 2022-07-25.
- ^ "Llega Mercado Soriana". Retailers. Retrieved 2011-09-20.
- ^ "Super City busca competir con Oxxo". Expansión. Retrieved 2008-01-25.
- ^ "Vende Carrefour sus activos a la cadena Chedraui". Jornada. Retrieved 2005-03-11.
- ^ "La compra de Carrefour". Expansión. Retrieved 2011-09-14.
- ^ "La Mega Soriana, un Gigante de la Laguna". El Sol de México. Retrieved 2008-01-25.
- ^ "Soriana incursiona en el DF". El Siglo de Torreón. Retrieved 2008-01-25.
- ^ "Estrenará Soriana la Plaza Centenario". El Siglo de Torreón. Retrieved 2007-03-13.
- ^ "Abre sus puertas Plaza Sendero Toluca". Vlex. Retrieved 2006-10-03.
- ^ "Historia de Soriana". Historia de Grandes Exitos. Retrieved 2012-03-21.
- ^ "Soriana compra las tiendas de Gigante". Expansión. Retrieved 2007-12-06.
- ^ "Soriana da la batalla a Walmart". Expansión. Retrieved 2008-06-17.
- ^ "Soriana registró ganancias de 261%". El Economista. Retrieved 2010-02-23.
- ^ "Soriana, 10 años de su formato Express". El Economista. Retrieved 2020-02-07.
- ^ "Soriana crea táctica para captar clientes". El Universal. Retrieved 2010-06-07.
- ^ "SORIANA ANUNCIA LA APERTURA DE SUS NUEVAS TIENDAS "IXTLAN DEL RIO Y EL ROSARIO"" (PDF). Soriana. Retrieved 2010-05-27.
- ^ "SORIANA ANUNCIA LA APERTURA DE SU NUEVA TIENDA "JEREZ"" (PDF). Soriana. Retrieved 2011-02-10.
- ^ "SORIANA CELEBRA LA APERTURA DE SUS DOS NUEVAS TIENDAS "TALA Y ZAPOTILTIC"" (PDF). Soriana. Retrieved 2011-03-10.
- ^ "SORIANA CELEBRA LA APERTURA DE SUS TRES NUEVAS TIENDAS SORIANA EXPRESS" (PDF). Soriana. Retrieved 2011-05-05.
- ^ "Soriana Celebra la Apertura de Nueva Tienda "Sayula"" (PDF). Soriana. Retrieved 2011-05-05.
- ^ "SORIANA ANUNCIA LA APERTURA DE DOS NUEVAS TIENDAS EXPRESS EN JALISCO Y MORELOS" (PDF). Soriana. Retrieved 2011-08-26.
- ^ "Soriana se reorganiza para vender más". Expansión. Retrieved 2011-09-19.
- ^ "Soriana va por consumidores pudientes". Expansión. Retrieved 2011-09-09.
- ^ "Soriana anuncia la reapertura de su tienda Soriana Súper Marne". retailers.mx. Retrieved 2011-09-14.
- ^ "SORIANA EXPRESS LLEGA A SONORA Y SINALOA" (PDF). Soriana. Retrieved 2011-10-07.
- ^ "Soriana Anuncia el Cierre de su Plan Expansión 2011" (PDF). Soriana. Retrieved 2011-12-09.
- ^ "Borque Family". Tharawat. 15 October 2020. Retrieved 7 December 2023.
- ^ "Soriana Celebra la Apertura de su Primer Hipermercado en el Estado de Morelos" (PDF). Soriana. Retrieved 2014-04-24.
- ^ "SORIANA ABRE SU PRIMER HIPERMERCADO EN MORELOS". Retailers.mx. Retrieved 2014-04-29.
- ^ "Soriana da 'banderazo' de aperturas de tiendas. Inaugura una sucursal en el estado de Morelos; así inicia su plan de nuevos establecimientos". Milenio Digital. Retrieved 2014-04-24.
- ^ "Soriana compra a la Comercial Mexicana por más de 39 mil millones de pesos". Aristegui Noticias. Retrieved 2015-01-29.
- ^ "Soriana compra 160 tiendas de La Comer por 39,194 mdp". El Financiero. Retrieved 2015-01-29.
- ^ "Cofece frena a Soriana para venta de tiendas de Comercial Mexicana". El Universal. Retrieved 2018-10-10.
- ^ "SORIANA ya tiene a 'JulioRegalado'". Conexión 360. Retrieved 2016-06-09.
- ^ "Aprueban a La Comer inicio de Escisión". Entre Veredas. Retrieved 2015-07-03.
- ^ "Al pelícano de La Cómer le quedan dos años de vida con Soriana". Forbes. Retrieved 2015-11-05.
- ^ "Julio Regalado arranca por primera vez de la mano de Soriana". Expansión. Retrieved 2016-06-08.
- ^ "Soriana buscará conquistar al sector 'premium' de México". Expansión. Retrieved 2016-06-23.
- ^ "Soriana abre tienda premium con inversión de 154 mdp". Milenio. Retrieved 2016-12-14.
- ^ "Cierran una de las tiendas Soriana, los trabajadores serán instalados en otras sucursales". En Línea Directa. Retrieved 2017-02-16.
- ^ "Cierra Soriana Tepeyac". El Norte. Retrieved 2017-03-07.
- ^ "Tendrá Soriana formato Bodega sólo meses". Mural. Retrieved 2018-08-28.
- ^ "Adiós a la Comercial Mexicana, desaparecerá en mayo". Criterio Hidalgo. Retrieved 2018-05-22.
- ^ "¡Adiós para siempre a Comercial Mexicana!". Forbes. Retrieved 2018-05-22.
- ^ "Soriana confirma un acuerdo con chilena Falabella para abrir tiendas en México". Expansión. Retrieved 2016-07-28.
- ^ "Sodimac abre primera tienda en México". El Economista. Retrieved 2018-08-02.
- ^ "Sodimac consolida operaciones en México con apertura de 3 tiendas en 2018 y hasta 6 en 2019". La Tercera. Retrieved 2018-11-22.
- ^ "Gran inauguración de Sodimac Cuernavaca". Diario de Morelos. Retrieved 2018-12-23.
- ^ "Sodimac inaugura cuarta tienda". Milenio. Retrieved 2019-11-29.
- ^ "México: Sodimac sigue creciendo y abre su quinta tienda". perú Retail. Retrieved 2019-12-20.
- ^ "México: Sodimac abre su sexta tienda en México en San Luis Potosí". perú Retail. Retrieved 2020-02-25.
- ^ "México: Sodimac crece en el país y abre su séptima tienda en la zona Lomas del Campestre o Cerro Gordo en León". perú Retail. Retrieved 2021-05-20.
- ^ "Adiós a la tienda City Club de León". perú Retail. Retrieved 2020-02-23.
- ^ "Sodimac abre su primera tienda en Monterrey". Inmobiliare. Retrieved 2021-08-31.
- ^ "Sodimac abre su segunda tienda en Nuevo León". Milenio. Retrieved 2021-12-03.
- ^ "Sodimac abre su decima tienda en México". Notifix. Retrieved 2022-06-22.
- ^ "Sodimac inaugura su primera tienda de colonia en Ciudad de México". Inmobiliare. Retrieved 2022-06-16.
- ^ "Inauguran sucursal de Sodimac en Saltillo". El Heraldo de Saltillo. Retrieved 2022-12-08.
- ^ "Sodimac México abrirá una nueva sucursal al sur de la CDMX". Inmobiliare. Retrieved 2022-12-14.
- ^ "Sodimac inaugura una nueva sucursal en Interlomas, la número 13 a nivel nacional". Inmobiliare. Retrieved 2023-07-28.
- ^ "A cinco años de su compra, Soriana sufre con la integración de Comercial Mexicana". El Ceo. Retrieved 2020-02-04.
- ^ "Se va Soriana Iglesias. Llega megacomplejo Alameda Iglesias". Al Diario. Retrieved 2020-02-06.
- ^ "Abre Soriana en 'town center' En junio será inaugurada toda la plaza comercial". El Diario. Mx. Retrieved 2023-05-17.
- ^ "Adiós a la tienda City Club de León". Cuéntame León. Retrieved 2020-02-23.
- ^ "¡Justo en la nostalgia! Cierra sus puertas Soriana Mercado de la capital". El Sol de Tlaxcala. Retrieved 2020-03-18.
- ^ "Cierra sucursal Soriana de playa Las Hamacas". El Sol de Acapulco. Retrieved 2020-04-11.
- ^ "Cierra sus puertas Soriana Playa de Oro". El Vallartense Noticias. Retrieved 2020-05-07.
- ^ "Cierra Soriana Campestre; llega Chedraui". El Sol del Bajío. Retrieved 2020-05-23.
- ^ "Cierran Soriana "Las Ánimas"". Curul Puebla. Retrieved 2020-07-01.
- ^ "Supermercado de León afectado por covid: anuncia cierre definitivo". La Silla Rota Guanajuato. Retrieved 2020-07-30.
- ^ "Cierra Soriana de la glorieta Juárez". Pulso, Diario de San Luis Potosí. Retrieved 2020-08-21.
- ^ "OFICIAL: SORIANA PLAZA MORELIA CERRARÁ SUS PUERTAS ESTE 31 DE AGOSTO". Revolución.News. Retrieved 2020-08-31.
- ^ "Cerrará tienda Soriana Súper de la colonia Gavilanes". Pórtico. Retrieved 2020-09-23.
- ^ "Inauguran Soriana Súper Gavilanes y City Club en Zacatecas". Retailers. Retrieved 2020-09-23.
- ^ "Organización Soriana inaugura Soriana Súper Gavilanes y City Club en Zacatecas". ZHN. Retrieved 2021-09-23.
- ^ "El día de hoy Organización Soriana inaugura su séptima tienda en Colima bajo el formato de Soriana Súper". Colima al día. Retrieved 2021-10-28.
- ^ "Organización Soriana suma 800 tiendas a nivel nacional con la inauguración de Soriana Híper y City Club en Tapachula". Noticias de Chiapas. Retrieved 2022-06-08.
- ^ "Inaugura Soriana su tienda 16 en Cancún. Organización Soriana abrió las puertas de su nueva tienda Soriana Mercado Prado Norte en el municipio de Benito Juárez". Ruptura 360. Retrieved 2022-12-07.
- ^ "Dejará de operar Soriana Mercado en San Juan del Río". El Sol de San Juan del Río. Retrieved 2022-12-15.
- ^ "Inauguran tienda Soriana en sector Viñedos de Torreón". El Siglo de Torreón. February 2023. Retrieved 2023-02-01.
- ^ "Organización Soriana llega por primera vez a Comitán, Chiapas". Mural Chiapas. 30 March 2023. Retrieved 2023-03-30.
- ^ "Soriana inaugurará sucursal City Club en Ciudad del Carmen". La Jornada Campeche. Retrieved 2023-04-27.
- ^ "Soriana Súper Iglesias abre sus puertas en Ciudad Juárez". A Diario Network. 18 May 2023. Retrieved 2023-05-18.
- ^ "Soriana de locura en apertura de tienda. Cientos de juarenses abarrotaron el estacionamiento del supermercado para ingresar a comprar". El Diario de Juárez. Retrieved 2023-12-21.
- ^ "Reinauguran Soriana Expres en Centro de Veracruz". Plumas Libres. 24 November 2023. Retrieved 2023-11-24.
- ^ "Traerá Soriana su club de precios a Zapopan". Mural. Retrieved 2023-07-12.
- ^ "Abren nuevas tiendas en la ZMG City Club en Jalisco abre sus puertas este miércoles 15 de noviembre". Mural. Retrieved 2023-11-14.
- ^ "Cierran Soriana Maldonado en Nuevo Laredo; contará con nueva ubicación y formato". El Mañana. 2 March 2023. Retrieved 2023-03-02.
- ^ "Cierra Soriana Abasolo, se prepara para ser demolida; construirán plaza comercial". Zócalo. Retrieved 2023-03-31.
- ^ "Soriana del Blvd Agua Caliente será sustituido por el Hotel Westin". KSDY 50 San Diego-Baja California. 25 January 2024. Retrieved 2024-01-25.
- ^ "Waldos y Soriana Súper cierran definitivamente estas sucursales en Tijuana". Yahoo News. 8 January 2024. Retrieved 2024-01-08.
- ^ "Se registra fuerte incendio en City Club de Zapopan". Primera Linea (in Spanish). Retrieved 2024-10-05.
- ^ "Pena Nieto set to become Mexico's president". Al Jazeera. 3 July 2012. Retrieved 18 July 2012.
- ^ a b Diaz, Lizbeth (9 July 2012). "Mexican leftist refuses to accept election result". Reuters. Retrieved 18 July 2012.
- ^ "Mexican retailer lashes out at losing presidential candidate". 2 August 2012.
- ^ Oppenheimer, Andres (15 July 2012). "Mexico's president-elect vows to imprison vote buyers". Miami Herald. Retrieved 19 July 2012.
- ^ Tuckman, Jo (4 July 2012). "Mexico elections: claims of dirty tricks cast shadow over Peña Nieto's victory". The Guardian – via www.theguardian.com.
- ^ "Throngs in Mexico hit stores with gift cards they say came from election-winning PRI". nydailynews.com. Associated Press. 3 July 2012.