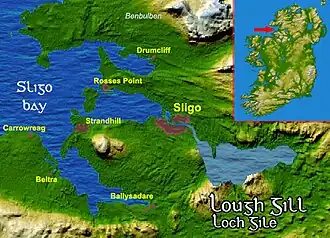
Sligo Bay
| Sligo Bay | |
|---|---|
| Cuan Shligigh | |
 Sligo Bay from Knocknarea | |
 | |
 Sligo Bay | |
| Location | County Sligo |
| Coordinates | 54°17′56″N 8°38′43″W / 54.29889°N 8.64528°W |
| Ocean/sea sources | Atlantic Ocean |
| Basin countries | Ireland |
| Islands | Coney, Oyster, Maguins |
| Settlements | Sligo, Rosses Point, Ballysadare, Drumcliff |
Sligo Bay (Irish: Cuan Shligigh)[1] is a natural ocean bay in County Sligo, Ireland.
Geography

Sligo Bay lies between Aughris Head (south side) and Roskeeragh Point (north).[2] The inner part of the bay is divided into three smaller bodies of water, at the estuaries of three rivers: the Drumcliff, Garavogue and Bonet.[3] The River Garavogue reaches the bay in its central part, Sligo Harbour, which is divided from the outer part of the bay by three small islands: Coney Island, Oyster Island, and Maguins Island. On the southern branch of Sligo Bay, the Ballisodare River has its estuary, near Ballysadare village.
Landforms and islands
The bay is characterised by the peninsulas jutting into it, which create large areas of sandy beach at low tide, along with the tidal islands which are only accessible at low tide. The notable landforms within the bay and its peninsulas are:
- Maugherow Peninsula
- Rosses Point Peninsula
- Coolera Peninsula
- Oyster Island
- Coney Island
- Maguins Island
History
Large beaches and tidal plains located around the bay are a good habitat for shellfish. This kind of food attracted settlers since the Stone Age, as demonstrated by a number of middens discovered in the area by archeologists.[4]
The bay has seen several shipwrecks over the centuries. Quite well studied is the wreck of Labia (25 September 1588), a 728-ton Venetian ship.[5] Shipwrecks became almost common during the following centuries[6] but their number decreased with the decline of the port of Sligo in the 20th century.
Transport
Sligo Airport is located on the bay's shore, near the foot of Knocknarea, a hill overlooking the peninsula between Sligo Harbour and Ballysadare Bay.
Lighthouses
There are four lighthouses in Sligo Bay.
Blackrock (Sligo) Lighthouse
The 25m high Blackrock lighthouse 54°18′28″N 8°37′4″W / 54.30778°N 8.61778°W is notable for having external steps until halfway up the tower.[7][8]
Lighthouses near Rosses Point
Sligo Bay hosts three lighthouses near Rosses Point: the Metal Man, Lower Rosses and Oyster Island lighthouses.
Touring
Sligo Bay is part of the Donegal to Mayo section of the Wild Atlantic Way.[9]
Nature

Ballysadare Bay hosts a well known seal colony.[10]
The estuaries area is protected under European legislation being listed as a NATURA 2000 site; it is also a Natural Heritage Area, defined and managed by the Irish National Parks & Wildlife Service.[11]
References
- ^ "Cuan Shligigh". Placenames Database of Ireland. Dublin City University. Retrieved 30 May 2015.
- ^ "Sea Fishing around Sligo". www.fishinginireland.info. Retrieved 29 May 2015.
- ^ "Sligo Bay". www.britannica.com. Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 29 May 2015.
- ^ "Sligo Bay - Cuan Sligeach". www.infomar.ie. Geological Survey of Ireland. Retrieved 30 May 2015.
- ^ Carlo Beltrame; Sauro Gelichi; Igor Miholjek (2014). Sveti Pavao Shipwreck: A 16th century Venetian merchantman from Mljet, Croatia. Oxbow Books. ISBN 9781782977063. Retrieved 30 May 2015.
- ^ "SLIGO". www.irishwrecksonline.net. Geological Survey of Ireland. Retrieved 30 May 2015.
- ^ "Blackrock Lighthouse co. Sligo". 4 May 2009. Retrieved 29 March 2017.
- ^ "Black Rock (Sligo)". Commissioners of Irish Lights. Retrieved 29 March 2017.
- ^ "Donegal to Mayo section". www.discoverireland.ie. Fáilte Ireland. Retrieved 29 May 2015.
- ^ "Ballisodare Bay & the Seal Colony". sligokayaktours.com. Retrieved 29 May 2015.
- ^ "Estuary Conservation". sligokayaktours.com. Retrieved 29 May 2015.