Quercy Phosphorites Formation
| Quercy Phosphorites Formation | |
|---|---|
| Stratigraphic range: latest Bartonian-Late Oligocene ~ | |
| Type | Formation |
| Overlies | Fissure fillings in karstified Jurassic and Triassic rocks |
| Lithology | |
| Primary | Phosphorite |
| Location | |
| Coordinates | 44°18′N 1°36′E / 44.3°N 1.6°E |
| Approximate paleocoordinates | 42°48′N 2°00′W / 42.8°N 2.0°W |
| Region | Occitanie |
| Country | France |
| Type section | |
| Named for | Quercy |
| Named by | Thévenin |
| Year defined | 1903 |
 Quercy Phosphorites Formation (France) | |
The Quercy Phosphorites Formation (French: Phosphorites du Quercy; Occitan: Fosforits de Quercy) is a geologic formation and lagerstätte in Occitanie, southern France. It preserves fossils dated to the Paleogene period (latest Bartonian to Late Oligocene),[1][2] or MP16 to MP28 zones of the European land mammal age classification, ranging from approximately 38 to 25 Ma.
It qualifies as a Lagerstätte because beside a large variety of mammals, birds, turtles, crocodiles, flora and insects, it also preserves the soft tissues of amphibians and squamates, in addition to their articulated skeleton in what has been called natural mummies.[3]
The genera Quercylurus, Quercymegapodius, Quercypsitta, Quercypodargus, Quercycerta and Quercygama, and species Mosaicomeryx quercyi, Robiacina quercyi, Palaeophyllophora quercyi, Archaeomys quercyi, Eomys quercyi, Eucricetodon quercyi and Tarnomys quercynus, as well as the lizards Paraplacosauriops quercyi and Pseudolacerta quercyini and the insect Palaeortona quercyensis were named after the formation.
Description
The first phosphate deposits in Quercy were discovered in 1869 and published by Daubré and Trutat independently in 1871.[4] The first fossils from the formation were described by Delfortie (1872) and Gervais in the same year and extensively studied by Filhol from 1877 onwards. The first geologic investigation of the formation was performed by Thévenin in 1903, and apart from a description by Gèze in 1938, the paleontological richness was not studied until a team of researchers of the Universities of Montpellier and Paris visited the site in 1965.[5]
The karstified phosphate deposits are found from the Lot and Célé river valleys in the north to the left bank of the Aveyron in the south and from the Villefranche Fault in the east to the lacustrine deposits of the Aquitaine Basin in the west. The formation is found in fissures (karst) incising Jurassic and Triassic rocks east of Cahors.[6] The age of the fossiliferous unit, in which almost 12,000 specimens were found ranges from the MP16 to MP28 zones of the European land mammal age classification.[5] These ages correspond to the latest Bartonian to Chattian, from about 38 to 25 Ma.[7]
Paleontological significance
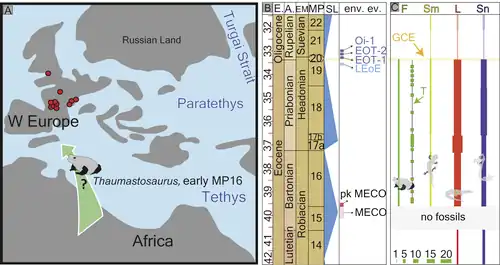
The Quercy Phosphorites Formation is a highly fossiliferous unit designated as a Lagerstätte due to the excellent preservation of fossils. The phosphorite conserves up to the nerves, digestive tract and stomach content,[8] insect larvae and other elements of the paleobiology in the formation. Nearly all Quercy fly pupae were preserved as isolated endocasts, of which many were still covered by the puparium, the hardened skin of the last larval instar.[9] The formation also straddles the Grande Coupure and shows diversity changes (number of species) of frog, salamander, lizard and snake fossil records across the formation.[10] It is assumed that the Quercy arthropods fossilized by a rapid fixation by phosphate-rich water followed by encrustation and mineralization.[11]
Fossil content
The following fossils have been reported from the formation:[1][2][12][13]
Mammals
Apatemyidae
| Genus | Species | Location | Time | Material | Note | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chardinyus | C. sp.[12] | An apatotheria. | ||||
| Heterohyus | H. (Chardinyus) nanus[12] | An apatemyid. | ||||
| H. (Gervaisyus) pygmaeus[12] | ||||||
| Gervaisyus | G. sp.[12] |
| Genus | Species | Location | Time | Material | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bachitherium | B. guirounetensis[13] | |||||
| B. lavocati[13] | ||||||
| Cryptomeryx | C. gaudryi[14] | |||||
| Dichobune | D. sigei[13] | |||||
| Dichodon | D. vidalenci[13] | |||||
| Iberomeryx | I. matsoui[13] | |||||
| Mosaicomeryx | M. quercyi[15] | |||||
| Paroxacron | P. bergeri[16] | |||||
| Plesiomeryx | P. cadurcensis[16] | |||||
| Prodremotherium | P. elongatum[15] | |||||
| Pseudamphimeryx | P. salesmei[13] | |||||
| Robiacina | R. lavergnensis[13] | |||||
| R. quercyi[13] | ||||||
| Tapirulus | T. perrierensis[13] |
Carnivora
| Genus | Species | Location | Time | Material | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amphicynodon | A. typicus[17] | Pech Crabet locality | Oligocene | Two hemi-mandibles | An early amphicynodontidae caniform | |
| Cephalogale | C. sp.[18] | A piece of hemi-mandible | ||||
| Cynodyctis | C. lacustris neboulensis[13] | Sainte Néboule | A mandible | An amphicynodontidae caniform. | ||
| Dinailurictis | D. bonali[19][20] | La Tuque | Oligocene. | Several holotype consists of a fragment of the left upper canine, lower canine, distal right humerus, distal left ulna, and a proximal piece of right femur. | A nimravid felidae | |
| Eofelis | E. edwardsii[21][22] | A nimravid | ||||
| E. giganteus[23] | Phosphorites du Quercy | A mandible | ||||
| cf. E. sp.[24] | ||||||
| Eusmilus | E. bidentatus[21][22] | Eocene/Oligocene | A edentulous hemi-mandible and a fragment of upper canine | A nimravid | ||
| Huntictis | H. minima | Gardiol 3 locality | Early Oligocene | A holotype consists of a dentition. | A small musteloid | |
| Mustelictis | M. cf. major[25] | A part of right hemi-mandible with alveolus of p1, p2, fragments of p3 roots, and p4-m1. | ||||
| M. aff. olivieri[25] | A holotype specimen consists of a skull and a hemi-mandible. | |||||
| Nimravus | N. intermedius[19][20] | MP 22 localities, La Plante2, Mas de Got and Valbro localities | Oligocene | A left hemi-mandible with m1 | A nimravid felidae. | |
| Pachycynodon | P. amphictina[26] | Oligocene | Multiple specimens consist of hemi-mandible and dentitions. | |||
| P. crassirostris[27] | ||||||
| P. cf. dubius[26] | ||||||
| P. cf. filholi[28] | ||||||
| Palaeogale | P. sectoria[22] | Valbro locality | Oligocene | A specimen consists of p4 dentition. | An early feliformia | |
| Peignictis | P. pseudamphictis[29] | Valbro locality | Early Oligocene | A posterior part of hemi-mandible | A carnivoran with uncertain affinities | |
| Quercylurus | Q. major[19] | Phosphorites du Quercy | Oligocene | A maxilla | A nimravid | |
| Storchictis | S. miacinus | Phosphorites du Quercy | Late Eocene | A mandible | An Amphicyonidae | |
| Wangictis | W. tedfordi[30] | Phosphorites du Quercy | Early Oligocene | A left hemi-mandible with c-m2 | An Amphicynodontidae |
Chiroptera
| Genus | Species | Location | Time | Material | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hipposideros | H. pseudorhinolophus sehlosseri[12] | An early roundleaf bat. | ||||
| H. pseudorhinolophus trassounius[12] | ||||||
| H. pseudorhinolophus zbrjdi[12] | ||||||
| Leuconoe | L. lavocati[12] | An early vespertilionid bat. | ||||
| Palaeophyllophora | P. oltina[12] | An early hipposiderid bat. | ||||
| P. quercyi[12] | ||||||
| Stehlinia | S. bonisi[12] | An early natalidae bat | ||||
| S. minor[12] | ||||||
| Vaylatsia | V. garouillasensis[12] | |||||
| Vespertiliavus | V. gerscheli[12] | An early Emballonurid bat | ||||
| V. gracilis[12] | ||||||
| V. lapradensis[12] |
Creodonta
| Genus | Species | Location | Time | Material | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paracynohyaenodon | P. magnus[12] | ||||
| Parapterodon | P. lostangensis[12] |
Euarchonta
| Genus | Species | Location | Time | Material | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Darbonetus | D. aubrelongensis[31] |
Hyaenodonta
| Genus | Species | Location | Time | Material | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paroxyaena | P. pavlovi[32] | Phosphorites du Quercy | Late Eocene | A partial skull | A hyaenodont |
Lipotyphla
| Genus | Species | Location | Time | Material | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amphidozotherium | A. cayluxi[12] | |||||
| Darbonetus | D. aubrelongensis[12] | |||||
| D. tuberi[12] | ||||||
| Myxomygale | M. antiqua[33] | |||||
| Saturninia | S. beata[12] | |||||
| S. pelissiei[12] |
Marsupials
| Genus | Species | Location | Time | Material | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amphiperatherium | A. bourdellense[12] | Le Bretou Locality | Oligocene | |||
| A. lamandini[12] | ||||||
| A. minutum | ||||||
| Peratherium | P. bretouense[12] | |||||
| P. cayluxi[12] | ||||||
| P. lavergnense[12] | ||||||
| P. perrierense[12] |
Perissodactyls
| Genus | Species | Location | Time | Material | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pachynolophus | P. bretovense[13] |
Primates
| Genus | Species | Location | Time | Material | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cryptadapis | C. tertius[12] | An adapiform primate. |
Proeutheria
| Genus | Species | Location | Time | Material | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudorhyncocyon | P. cayluxi[12] |
Rodents
| Genus | Species | Location | Time | Material | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Archaeomys | A. intermedius[13] | Pech du Fraysse | Oligocene | A theridomyidae rodent | ||
| A. quercyi[13] | Oligocene | |||||
| Bernardia | B. marandati[13] | |||||
| Blainvillimys | B. gemellus[13] | |||||
| B. gousnatensis[13] | ||||||
| B. langei[13][34] | ||||||
| B. rotundidens[35] | ||||||
| Elfomys | E. medius[13] | |||||
| Eomys | E. gigas[13] | Pech du Fraysse Locality | Late Oligocene | A specimen | An eomyidae rodent | |
| E. minus[13] | Pech du Fraysse Locality | A specimen | ||||
| E. quercyi[13] | Pech du Fraysse Locality | A specimen |
 | |||
| Eucricetodon | E. atavus[34] | |||||
| E. quercyi[13] | ||||||
| Gliravus | G. garouillensis[13] | |||||
| G. itardiensis[13] | ||||||
| Issiodoromys | I. limognensis[13] | |||||
| I. pauffiensis[13][34] | ||||||
| Palaeosciurus | P. goti[13][34] | |||||
| Paradelomys | Paradelomys spelaeus[13] | |||||
| Patriotheridcmys | P. altus[13] | |||||
| P. altus neboulensis[13] | ||||||
| P. sudrei[13] | ||||||
| Pseudoltinomys | P. gaillardi[34] | |||||
| P. major[13] | ||||||
| P. phosphoricus[13] | ||||||
| Sciuromys | S. cayluxi[36] | |||||
| S. rigali[13] | ||||||
| Tarnomys | T. quercynus[13] | |||||
| Theridomys | T. ludensis[13] |
Birds
| Genus | Species | Location | Time | Material | Note | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ameghinornis | A. sp.[12] | |||||
| Euronyctibius | E. kurochkini[37] | Phosphorites du Quercy | Eocene | A right humerus | An early nightjar | |
| Horusornis | H. vianeyliaudae[12] | La Bouffie Locality | Eocene | A specimen | An early accipitriformes | |
| Dynamopterus | D. velox[12] | Near Caylus | Oligocene | Almost complete right humerus | An extinct cuckoo bird, synonymous with Dynamopterus velox | |
| Itardiornis | I. hessae[12] | |||||
| Leptoganga | L. sp.[12] | |||||
| Necrobyas | N. minimus[12] | |||||
| Nocturnavis | N. sp.[12] | |||||
| Palaeoglaux | P. perrierensis[12] | An early owl | ||||
| Palaeotodus | P. escampsiensis[12] | |||||
| P. itardiensis[12] | ||||||
| Paleseyvus | P. escampensis[12] | |||||
| Primocolius | P. sigei[12] | |||||
| P. minor[12] | ||||||
| Quercymegapodius | Q. brodkorbi[12] | |||||
| Quercypodargus | Q. olsoni[37] | |||||
| Quercypsitta | Q. ivani[12] | |||||
| Q. sudrei[12] | ||||||
| Recurvirostra | R. sanctaeneboulae[12] | |||||
| Sylphornis | S. bretouensis[12] | |||||
| Ventivorus | V. ragei[12] | Le Bertou Locality | An early nightjar |
Reptiles
Crocodiles
| Genus | Species | Location | Time | Material | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alligator | A. gaudryi[38] |
Lizards
| Genus | Species | Location | Time | Material | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ayalasaurus | A. tenuis[39] | |||||
| Bauersaurus | B. cosensis[40] | Cos Locality | Uppermost Early Eocene | The upper maxilla) and lower jaw fragments. | A pan-gekkotan lizard. | 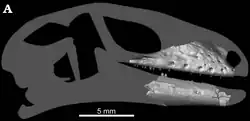 |
| Brevisaurus | B. smithi[39] | |||||
| Cadurciguana | C. hoffstetteri[12] | |||||
| Cadurcogekko | C. piveteaui[39] | |||||
| Cadurcopanoplos | C. vaylatsensis[41] | La Bouffie locality | Late Eocene | Two holotypes consist of a single incomplete frontal bone and a partial right mandible. | A Glyptosaurinae anguid. | |
| Dracaenosaurus | D. croizeti[39] | |||||
| Eurheloderma | E. gallicum[39] | |||||
| Geiseltaliellus | G. lamandini[39] | |||||
| Mediolacerta | M. roceki[39] | |||||
| Necrosaurus | N. cayluxi[39] | |||||
| N. eucarinatus[39] | ||||||
| Omoiotyphlops | O. priscus[39] | |||||
| Paraplacosauriops | P. quercyi[39] | |||||
| Phosphoriguana | P. peritechne[41] | La Bouffie Locality | Late Eocene | A single partial lower jaw | A probable member of pleurodonta | |
| Placosaurus | P. rugosus[39] | |||||
| P. sp.[39] | ||||||
| Plesiolacerta | P. lydekkeri[39] | |||||
| Pseudeumeces | P. cadurcensis[39] | |||||
| Pseudolacerta | P. mucronata[39] | |||||
| P. quercyini[39] | ||||||
| Quercycerta | Q. maxima[39] | |||||
| Quercygama | Q. galliae[39] | |||||
| Uromastyx | U. europaeus[39] |
Snakes
| Genus | Species | Location | Time | Material | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cadurcoboa | C. insolita[12] | |||||
| Coluber | C. cadurci[12] | |||||
| Dunnophis | D. cadurcensis[12] | |||||
| Eoanilius | E. europae[12] | |||||
| Natrix | N. mlynarskii[12][42] | |||||
| Palaeopython | P. cadurcensis[38] | |||||
| P. filholi[38] | ||||||
| P. neglectus[38] | ||||||
| Paleryx | P. cayluxi[38] | |||||
| Platyspondylia | P. lepta[12] | |||||
| Plesiotortrix | P. edwardsi[38] |
Turtles
| Genus | Species | Location | Time | Material | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ptychogaster | P. cayluxensis[43] | |||||
| Testudinidae | indeterminate [43] | |||||
| Testudo | T. phosphoritarum[38] |
Amphibians
- Frogs
| Genus | Species | Location | Time | Material | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bufo | B. serratus[38] | Phosphorites du Quercy | Eocene | A specimen | An early true toad. | |
| Thaumastosaurus | T. bottii[38] | Phosphorites du Quercy | Eocene | A specimen | An early Pyxicephalinae frog | |
| T. gezei[3] | Phosphorites du Quercy | Eocene | A mummified preserved skeleton |
- Salamanders
| Genus | Species | Location | Time | Material | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heteroclitotriton | H. zitteli[38] | Phosphorites du Quercy locality | Late Eocene | A specimen | An early salamander | |
| Megalotriton | M. filholi[38] | Phosphorites du Quercy locality | Late Eocene | A specimen | An extinct salamander | |
| M. portisi[38] | A specimen | |||||
| Phosphotriton | P. sigei[44] | Phosphorites du Quercy locality | Late Eocene | A mummified skeleton. | A frog-eating salamander. |
 |
Insects
Blattodea
| Family | Genus | Species | Location | Age | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Various cockroaches[45] |
Diptera
| Family | Genus | Species | Location | Age | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Various flies[45] |
Coleoptera
| Family | Genus | Species | Location | Age | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
†O. intermedius[45] |
||||||
|
Various beetles[45] |
Hymenoptera
| Family | Genus | Species | Location | Age | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diapriidae |
†C. anka[46] |
Near Bach |
Paleogene |
An early Diapriinae wasp |
||
|
†Palaeortona |
†P. quercyensis[46] |
Near Bach |
Paleogene |
An early Diapriinae wasp |
||
| †Xenomorphia |
†X. handschini[46] |
Near Bach |
Paleogene |
An early Diapriinae wasp |
||
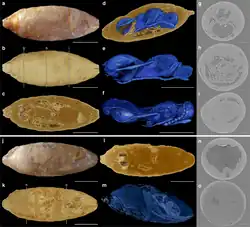
|
†X. resurrecta[9] |
Near Bach |
Paleogene |
An early Diapriinae wasp |
 | ||
|
Various wasps/ants/bees[45] |
Lepidoptera
| Family | Genus | Species | Location | Age | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Various butterflies/moths[45] |
Orthoptera
| Family | Genus | Species | Location | Age | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Myriapoda
| Family | Genus | Species | Location | Age | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Various centipedes and millipedes[45] |
Flora
| Family | Genus | Species | Location | Age | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Indeterminate[47] |
Indeterminate[47] |
Indeterinate anacardiaceous fossils |
||||
|
Palmocaulon[48] |
Palmocaulon sp.[48] |
A palm tree relative |
||||
|
Indeterminate[49] |
Indeterminate[49] |
indeterminate malvaceous fossils |
||||
|
Indeterminate[49] |
Indeterminate[49] |
Indeterminate menispermaceous fossils |
||||
|
Indeterminate[49] |
Indeterminate[49] |
Indeterminate sapotaceous fossils |
||||
|
Indeterminate[49] |
Indeterminate[49] |
Indeterminate ulmaceous fossils |
||||
|
Indeterminate[47] |
Indeterminate[47] |
Indeterminate vitaceous fossils |
||||
|
Indeterminate |
Indeterminate[49] |
Indeterminate[49] |
Indeterminate caryophyllalean fossils |
References
- ^ a b Quercy Phosphorites Formation at Fossilworks.org
- ^ a b Phosphorites du Quercy Formation at Fossilworks.org
- ^ a b Laloy et al., 2013
- ^ Legendre et al., 1997, p.331
- ^ a b Legendre et al., 1997, p.332
- ^ Astruc & Pellissié, 1988, p.8
- ^ Legendre et al., 1997, p.333
- ^ Tissier et al., 2017, p.6
- ^ a b Van de Kamp et al., 2018, p.2
- ^ Vasilyan, 2018, p.19
- ^ Van de Kamp et al., 2018, p.12
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at au av aw ax ay az ba bb bc bd be bf Legendre et al., 1997, p.334
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak Legendre et al., 1997, p.335
- ^ Sudre, 1984
- ^ a b Mennecart & Métais, 2015
- ^ a b Blondel, 2005
- ^ Bonis et al., 2019, p.603
- ^ Bonis et al., 2019, p.612
- ^ a b c Peigné, 2003
- ^ a b Bonis et al., 2019, p.616
- ^ a b Peigné & Brunet, 2001
- ^ a b c Bonis et al., 2019, p.618
- ^ Peigné, 2000
- ^ Peigné, 2001
- ^ a b Bonis et al., 2019, p.614
- ^ a b Bonis et al., 2019, p.610
- ^ Bonis et al., 2019, p.604
- ^ Bonis et al., 2019, p.608
- ^ Bonis et al., 2019, p.615
- ^ Bonis et al., 2019, p.611
- ^ Hooker, 2018, p.236
- ^ Lavrov, 2007
- ^ Hugueney & Maridet, 2017
- ^ a b c d e Ginot et al., 2016, p.7
- ^ Hartenberger & Vianey-Liaud, 1978
- ^ Vianey-Liaud & Schmid, 2009
- ^ a b Mourer-Chauviré, 1989
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Rage, 2006
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t Augé, 2005
- ^ Čerňanský, A.; Daza, J. D.; Tabuce, R.; Saxton, E.; Vidalenc, D. (2023). "An early Eocene pan-gekkotan from France could represent an extra squamate group that survived the K/Pg extinction". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 68 (4): 695–708. doi:10.4202/app.01083.2023.
- ^ a b Lemierre, Alfred; Georgalis, Georgios L. (2025). "Diversity in a greenhouse world: Herpetofauna from the late Eocene (MP 17A) of la Bouffie, Quercy Phosphorites (Lot, SW France)". Swiss Journal of Palaeontology. 144 40. doi:10.1186/s13358-025-00370-9.
- ^ Rage, 1988
- ^ a b Broin, 1977
- ^ Tissier et al., 2016
- ^ a b c d e f g h Schmied et al., 2013, p.145
- ^ a b c Van de Kamp et al., 2018, p.4
- ^ a b c d De Franceschi et al., 2006, p.100
- ^ a b De Franceschi et al., 2006, p.99
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j De Franceschi et al., 2006, p.101
Bibliography
- Map reports
- Astruc, J.G.; Pellissié, T. (1988), Notice explicative de la feuille Cahors 1:50,000 (PDF), BRGM, pp. 1–39, retrieved 2020-09-13
- Paleontology
- De Bonis, Louis; Gardin, Axelle; Blondel, Cécile (2019), "Carnivora from the early Oligocene of the 'Phosphorites du Quercy' in southwestern France", Geodiversitas, 41 (15): 601–621, doi:10.5252/geodiversitas2019v41a15, retrieved 2020-09-13
- Hooker, Jerry J (2018), "Eocene antiquity of the European nyctitheriid euarchontan mammal Darbonetus", Acta Palaeontologica Polonica, 63: 235–239, doi:10.4202/app.00457.2018, retrieved 2020-09-13
- Van de Kamp, Thomas; Schwermann, Achim H.; dos Santos Rolo, Tomy; Lösel, Philipp D.; Engler, Thomas; Etter, Walter; Faragó, Tomáš; Göttlicher, Jörg; Heuveline, Andreas Kopmann, Bastian Mähler, Thomas Mörs, Janes Odar, Jes Rust, Nicholas Tan Jerome, Matthias Vogelgesang, Tilo Baumbach and Lars Krogmann, Vincent (2018), "Parasitoid biology preserved in mineralized fossils", Nature Communications, 9 (1): 1–14, Bibcode:2018NatCo...9.3325V, doi:10.1038/s41467-018-05654-y, PMC 6113268, PMID 30154438
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Vasilyan, Davit (2018), "Eocene Western European endemic genus Thaumastosaurus: new insights into the question "Are the Ranidae known prior to the Oligocene?"", PeerJ, 6: 1–24, doi:10.7717/peerj.5511, PMC 6118198, PMID 30186689, retrieved 2020-09-13
- Hugueney, M.; Maridet, O. (2017), "Evolution of Oligo-Miocene talpids (Mammalia, Talpidae) in Europe: focus on the genera Myxomygale and Percymygale n. gen", Historical Biology
- Tissier, Jérémy; Rage, Jean-Claude; Laurin, Michel (2017), "Exceptional soft tissues preservation in a mummified frog-eating Eocene salamander", PeerJ, 5: 1–14, doi:10.7717/peerj.3861, PMC 5629955, PMID 29018606
- Ginot, Samuel; Hautier, Lionel; Marivaux, Laurent; Vianey-Liaud, Monique (2016), "Ecomorphological analysis of the astragalo-calcaneal complex in rodents and inferences of locomotor behaviours in extinct rodent species", PeerJ, 4: 1–49, doi:10.7717/peerj.2393, PMC 5068370, PMID 27761303
- Tissier, J.; Rage, J.-C.; Boistel, R.; Fernández, V.; Pollet, N.; García, G.; Laurin, M. (2016), "Synchrotron analysis of a 'mummified' salamander (Vertebrata: Caudata) from the Eocene of Quercy, France", Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society, 177: 147–164, doi:10.1111/zoj.12341
- Mennecart, B.; Métais, G. (2015), "Mosaicomeryx gen. nov., a ruminant mammal from the Oligocene of Europe and the significance of 'gelocids'", Journal of Systematic Palaeontology, 13 (7): 581–600, Bibcode:2015JSPal..13..581M, doi:10.1080/14772019.2014.948505
- Laloy, F.; Rage, J.-C.; Evans, S. E.; Boistel, R.; Lenoir, N.; Laurin, M. (2013), "A Re-Interpretation of the Eocene Anuran Thaumastosaurus Based on MicroCT Examination of a 'Mummified' Specimen", PLoS ONE, 8 (9): e74874:1, Bibcode:2013PLoSO...874874L, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0074874, PMC 3783478, PMID 24086389
- Schmied, Heiko; Schwermann, Achim H.; van de Kamp, Thomas; dos Santos Rolo, Tomy; Baumbach, Tilo (2013), Inside the Clown. Synchrotron X-ray microtomography reveals extraordinary details of internal and genital structures of 30 million old beetles, Joachim Reitner, Yang Qun, Wang Yongdong and Mike Reich (eds.) Palaeobiology and Geobiology of Fossil Lagerstätten through Earth History, pp. 1–218, ISBN 978-3-86395-135-1
- Vianey-Liaud, M.; Schmid, B. (2009), "Diversité, datation et paléoenvironnement de la faune de mammifères oligocène de Cavalé (Quercy, SO France) : contribution de l'analyse morphométrique des Theridomyinae (Mammalia, Rodentia)", Geodiversitas, 31 (4): 909–941, doi:10.5252/g2009n4a909
- Lavrov, A. V (2007), "New Species of Paroxyaena (Hyaenodontidae, Creodonta) from Phosphorites of Quercy, Late Eocene, France", Paleontological Journal, 41 (3): 298–311, Bibcode:2007PalJ...41..298L, doi:10.1134/S0031030107030094
- De Franceschi, D.; Le Gall, C.; Escarguel, G.; Hugueney, M.; Legendre, S.; Simon-Coinçon, R.; Pélissié, T.; Sigé, B. (2006), "Une paléoflore des phosphatières karstiques du Quercy (Sud-Ouest France) : première découverte, résultats et perspectives - A paleoflora from the Quercy phosphorites Paleokarsts (Southwestern France): first discovery, results and perspectives", Strata, 13: 97–101, retrieved 2020-09-13
- Rage, J.-C (2006), "The lower vertebrates from the Eocene and Oligocene of the Phosphorites du Quercy (France): an overview", Strata, 1: 161–173
- Augé, M. L (2005), "Evolution des lézards du Paléogène en Europe", Mémoires du Muséum National d'Histoire Naturelle, 192: 1–369
- Blondel, C (2005), "New data on the Cainotheriidae (Mammalia, Artiodactyla) from the early Oligocene of south-western France", Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society, 144 (2): 125–166, doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.2005.00166.x
- Wesley-Hunt, Gina D.; Werdelin, Lars (2005), "Basicranial morphology and phylogenetic position of the upper Eocene carnivoramorphan Quercygale", Acta Palaeontologica Polonica, 50: 837–846, retrieved 2020-09-13
- Peigné, S (2003), "Systematic review of European Nimravinae (Mammalia, Carnivora, Nimravidae) and the phylogenetic relationships of Palaeogene Nimravidae", Zoologica Scripta, 32 (3): 199–229, doi:10.1046/j.1463-6409.2003.00116.x
- Peigné, S (2001), "A primitive nimravine skull from the Quercy fissures, France: implications for the origin and evolution of Nimravidae (Carnivora)", Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society, 132 (4): 401–410, doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.2001.tb02467.x
- Peigné, S.; Brunet, M. (2001), "Une nouvelle espèce du genre Eusmilus (Carnivora: Nimravidae) de l'Oligocène (MP 22) d'Europe", Geobios, 34 (6): 657–672, Bibcode:2001Geobi..34..657P, doi:10.1016/S0016-6995(01)80027-9
- Peigné, S (2000), "A new species of Eofelis (Carnivora: Nimravidae) from the Phosphorites of Quercy, France", Comptes Rendus de l'Académie des Sciences, Série IIA, 330 (9): 653–658, Bibcode:2000CRASE.330..653P, doi:10.1016/S1251-8050(00)00199-3
- Legendre, Serge; Sigé, Bernard; Astruc, Jean Guy; de Bonis, Louis; Crochet, Jean-Yves; Denys, Christiane; Godinot, Marc; Hartenberger, Jean-Louis; Lévêque, Bernard Marandat, Cécile Mourer-Chauviré, Jean-Claude Rage, Jean Albert Remy, Jean Sudre and Monique Vianey-Liaud, François (1997), "Les phosphorites du Quercy: 30 ans de recherche. Bilan et perspectives - The phosphorites of Quercy: 30 years of investigations. Results and prospects", Geobios, 20: 331–345, doi:10.1016/S0016-6995(97)80038-1, retrieved 2020-09-13
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Wolsan, Mieczysław; Lange-Badré, Brigitte (1996), "An arctomorph carnivoran skull from the Phosphorites du Quercy and the origin of procyonids", Acta Palaeontologica Polonica, 41: 277–298, retrieved 2020-09-13
- Mourer-Chauviré, C (1989), Les Caprimulgiformes et les Coraciiformes de l'Éocène et de l'Oligocène des phosphorites du Quercy et description de deux genres nouveaux de Podargidae et Nyctibiidae, Acta XIX congressus internationalis ornithologici, pp. 2047–2055
- Rage, J.-C (1988), "The oldest known colubrid snakes. The state of the art", Acta Zoologica Cracoviensia, 31: 457–474
- Sudre, J (1984), "Cryptomerix Schlosser, 1886, Tragulidé de l'oligocène d'Europe; relations du genre et considérations sur l'origine des ruminants", Palaeovertebrata, 14: 1–31
- Hartenberger, J.-L.; Vianey-Liaud, M. (1978), "La poche a phosphate de Ste-Néboule (Lot) et sa faune de vertebres du Ludien Superieur. 13. - Rongeurs", Palaeovertebrata, 8: 313–318
- Broin, F (1977), "Contribution a l'etude des Cheloniens. Cheloniens continentaux due Cretace et du Tertiare de France", Mémoires du Muséum National d'Histoire Naturelle, Série C, Sciences de la terre, Nouvelle série, 38: 1–366
Further reading
- Reitner, Joachim; Qun, Yang; Yongdong, Wang; Reich, Mike (2013), Palaeobiology and Geobiology of Fossil Lagerstätten through Earth History (PDF), Universitätsverlag Göttingen, pp. 1–218, ISBN 978-3-86395-135-1, retrieved 2020-09-15
External links
![]() Media related to Quercy Phosphorites Formation at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Quercy Phosphorites Formation at Wikimedia Commons