Portal:Economics
Portal maintenance status: (December 2018)
|
Introduction
Economics (/ˌɛkəˈnɒmɪks, ˌiːkə-/) is a behavioral science that studies the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services.
Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of economic agents and how economies work. Microeconomics analyses what is viewed as basic elements within economies, including individual agents and markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers. Macroeconomics analyses economies as systems where production, distribution, consumption, savings, and investment expenditure interact; and the factors of production affecting them, such as: labour, capital, land, and enterprise, inflation, economic growth, and public policies that impact these elements. It also seeks to analyse and describe the global economy. (Full article...)
Selected general articles
-
 Image 1
Image 1 Pierre Samuel du Pont de Nemours, a prominent physiocrat. In his book La Physiocratie, du Pont advocated low tariffs and free trade.
Pierre Samuel du Pont de Nemours, a prominent physiocrat. In his book La Physiocratie, du Pont advocated low tariffs and free trade.
Physiocracy (French: physiocratie; from the Greek for "government of nature") is an economic theory developed by a group of 18th-century Age of Enlightenment French economists. They believed that the wealth of nations derived solely from the value of "land agriculture" or "land development" and that agricultural products should be highly priced. Their theories originated in France and were most popular during the second half of the 18th century. Physiocracy became one of the first well-developed theories of economics.
François Quesnay (1694–1774), the Marquis de Mirabeau (1715–1789) and Anne-Robert-Jacques Turgot (1727–1781) dominated the movement, which immediately preceded the first modern school, classical economics, which began with the publication of Adam Smith's The Wealth of Nations in 1776. (Full article...) -
 Image 2
Image 2 Ostrom in 2009
Ostrom in 2009
Elinor Claire "Lin" Ostrom (née Awan; August 7, 1933 – June 12, 2012) was an American political scientist and political economist whose work was associated with New Institutional Economics and the resurgence of political economy. In 2009, she was awarded the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for her "analysis of economic governance, especially the commons", which she shared with Oliver E. Williamson; she was the first woman to win the prize.
Trained in political science at UCLA, Ostrom was a faculty member at Indiana University Bloomington for 47 years. Beginning in the 1960s, Ostrom was involved in resource management policy and created a research center, the Workshop in Political Theory and Policy Analysis, which attracted scientists from different disciplines from around the world. Working and teaching at her center was created on the principle of a workshop, rather than a university with lectures and a strict hierarchy. Late in her career, she held an affiliation with Arizona State University. (Full article...) -
![Image 3 Ludwig Heinrich Edler von Mises (/vɒn ˈmiːzɪz/; German: [ˈluːtvɪç fɔn ˈmiːzəs]; September 29, 1881 – October 10, 1973) was an Austrian and American political economist and philosopher of the Austrian school. Mises wrote and lectured extensively on the social contributions of classical liberalism and the central role of consumers in a market economy. He is best known for his work in praxeology, particularly for studies comparing communism and capitalism, as well as for being a defender of classical liberalism in the face of rising illiberalism and authoritarianism throughout much of Europe during the 20th century. In 1934, Mises fled from Austria to Switzerland to escape the Nazis and he emigrated from there to the United States in 1940. On the day German forces entered Vienna, they raided his apartment, confiscating his papers and library, which were believed lost or destroyed until rediscovered decades later in Soviet archives. At the time, Mises was living in Geneva, Switzerland. However, with the imminent Nazi occupation of France threatening to isolate Switzerland within Axis-controlled territory, he and his wife fled through France—avoiding German patrols—and reached the United States via Spain and Portugal. (Full article...)](./_assets_/Blank.png) Image 3
Image 3
Ludwig Heinrich Edler von Mises (/vɒn ˈmiːzɪz/; German: [ˈluːtvɪç fɔn ˈmiːzəs]; September 29, 1881 – October 10, 1973) was an Austrian and American political economist and philosopher of the Austrian school. Mises wrote and lectured extensively on the social contributions of classical liberalism and the central role of consumers in a market economy. He is best known for his work in praxeology, particularly for studies comparing communism and capitalism, as well as for being a defender of classical liberalism in the face of rising illiberalism and authoritarianism throughout much of Europe during the 20th century.
In 1934, Mises fled from Austria to Switzerland to escape the Nazis and he emigrated from there to the United States in 1940. On the day German forces entered Vienna, they raided his apartment, confiscating his papers and library, which were believed lost or destroyed until rediscovered decades later in Soviet archives. At the time, Mises was living in Geneva, Switzerland. However, with the imminent Nazi occupation of France threatening to isolate Switzerland within Axis-controlled territory, he and his wife fled through France—avoiding German patrols—and reached the United States via Spain and Portugal. (Full article...) -
 Image 4
Image 4 Marshall circa the release of Principles (1890)
Marshall circa the release of Principles (1890)
Alfred Marshall FBA (26 July 1842 – 13 July 1924) was an English economist and one of the most influential economists of his time. His book Principles of Economics (1890) was the dominant economic textbook in England for many years, and brought the ideas of supply and demand, marginal utility, and costs of production into a coherent whole, popularizing the modern neoclassical approach which dominates microeconomics to this day. As a result, he is known as the father of scientific economics. (Full article...) -
 Image 5Behavioral economics is the study of the psychological (e.g. cognitive, behavioral, affective, social) factors involved in the decisions of individuals or institutions, and how these decisions deviate from those implied by traditional economic theory.
Image 5Behavioral economics is the study of the psychological (e.g. cognitive, behavioral, affective, social) factors involved in the decisions of individuals or institutions, and how these decisions deviate from those implied by traditional economic theory.
Behavioral economics is primarily concerned with the bounds of rationality of economic agents. Behavioral models typically integrate insights from psychology, neuroscience and microeconomic theory. (Full article...) -
 Image 6New Institutional Economics (NIE) is an economic perspective that attempts to extend economics by focusing on the institutions (that is to say the social and legal norms and rules) that underlie economic activity and with analysis beyond earlier institutional economics and neoclassical economics.
Image 6New Institutional Economics (NIE) is an economic perspective that attempts to extend economics by focusing on the institutions (that is to say the social and legal norms and rules) that underlie economic activity and with analysis beyond earlier institutional economics and neoclassical economics.
The NIE assume that individuals are rational and that they seek to maximize their preferences, but that they also have cognitive limitations, lack complete information and have difficulties monitoring and enforcing agreements. As a result, institutions form in large part as an effective way to deal with transaction costs. (Full article...) -
![Image 7 Friedrich von Wieser (German: [fɔn ˈviːzɐ]; 10 July 1851 – 22 July 1926) was an early (so-called "first generation") economist of the Austrian School of economics. Born in Vienna, the son of Privy Councillor Leopold von Wieser, a high official in the war ministry, he first trained in sociology and law. In 1872, the year he took his degree, he encountered Austrian-school founder Carl Menger's Grundsätze and switched his interest to economic theory. Wieser held posts at the universities of Vienna and Prague until succeeding Menger in Vienna in 1903, where along with his brother-in-law Eugen von Böhm-Bawerk he shaped the next generation of Austrian economists including Ludwig von Mises, Friedrich Hayek and Joseph Schumpeter in the late 1890s and early 20th century. He was the Austrian Minister of Commerce from August 30, 1917, to November 11, 1918. Wieser is renowned for two main works, Natural Value, which carefully details the alternative-cost doctrine and the theory of imputation; and his Social Economics (1914), an ambitious attempt to apply it to the real world. His explanation of marginal utility theory was decisive, at least terminologically. It was his term Grenznutzen (building on von Thünen's Grenzkosten) that developed into the standard term "marginal utility", not William Stanley Jevons's "final degree of utility" or Menger's "value". His use of the modifier "natural" indicates that he regarded value as a "natural category" that would pertain to any society, no matter what institutions of property had been established. (Full article...)](./_assets_/Blank.png) Image 7
Image 7
Friedrich von Wieser (German: [fɔn ˈviːzɐ]; 10 July 1851 – 22 July 1926) was an early (so-called "first generation") economist of the Austrian School of economics. Born in Vienna, the son of Privy Councillor Leopold von Wieser, a high official in the war ministry, he first trained in sociology and law. In 1872, the year he took his degree, he encountered Austrian-school founder Carl Menger's Grundsätze and switched his interest to economic theory. Wieser held posts at the universities of Vienna and Prague until succeeding Menger in Vienna in 1903, where along with his brother-in-law Eugen von Böhm-Bawerk he shaped the next generation of Austrian economists including Ludwig von Mises, Friedrich Hayek and Joseph Schumpeter in the late 1890s and early 20th century. He was the Austrian Minister of Commerce from August 30, 1917, to November 11, 1918.
Wieser is renowned for two main works, Natural Value, which carefully details the alternative-cost doctrine and the theory of imputation; and his Social Economics (1914), an ambitious attempt to apply it to the real world. His explanation of marginal utility theory was decisive, at least terminologically. It was his term Grenznutzen (building on von Thünen's Grenzkosten) that developed into the standard term "marginal utility", not William Stanley Jevons's "final degree of utility" or Menger's "value". His use of the modifier "natural" indicates that he regarded value as a "natural category" that would pertain to any society, no matter what institutions of property had been established. (Full article...) -
 Image 8
Image 8
John Bates Clark (January 26, 1847 – March 21, 1938) was an American neoclassical economist. He was one of the pioneers of the marginalist revolution and opponent to the Institutionalist school of economics, and spent most of his career as a professor at Columbia University. He was one of the most prominent American economists of his time. (Full article...) -
 Image 9The neoclassical synthesis (NCS), or neoclassical–Keynesian synthesis is an academic movement and paradigm in economics that worked towards reconciling the macroeconomic thought of John Maynard Keynes in his book The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money (1936) with neoclassical economics.
Image 9The neoclassical synthesis (NCS), or neoclassical–Keynesian synthesis is an academic movement and paradigm in economics that worked towards reconciling the macroeconomic thought of John Maynard Keynes in his book The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money (1936) with neoclassical economics.
The neoclassical synthesis is a macroeconomic theory that emerged in the mid-20th century, combining the ideas of neoclassical economics with Keynesian economics. The synthesis was an attempt to reconcile the apparent differences between the two schools of thought and create a more comprehensive theory of macroeconomics. (Full article...) -
 Image 10
Image 10 Portrait by Thomas Phillips, c. 1821
Portrait by Thomas Phillips, c. 1821
David Ricardo (18 April 1772 – 11 September 1823) was a British economist and politician. He is recognized as one of the most influential classical economists, alongside figures such as Thomas Malthus, Adam Smith and James Mill.
Ricardo was born in London as the third surviving child of a successful stockbroker and his wife. He came from a Sephardic Jewish family of Portuguese origin. At 21, he eloped with a Quaker and converted to Unitarianism, causing estrangement from his family. He made his fortune financing government borrowing and later retired to an estate in Gloucestershire. Ricardo served as High Sheriff of Gloucestershire and bought a seat in Parliament as an earnest reformer. He was friends with prominent figures like James Mill, Jeremy Bentham, and Thomas Malthus, engaging in debates over various topics. Ricardo was also a member of The Geological Society, and his youngest sister was an author. (Full article...) -
 Image 11This is a list of important publications in economics, organized by field.
Image 11This is a list of important publications in economics, organized by field.
Some basic reasons why a particular publication might be regarded as important:- Topic creator – A publication that created a new topic
- Breakthrough – A publication that changed scientific knowledge significantly
- Influence – A publication which has significantly influenced the world or has had a massive impact on the teaching of economics.
-
 Image 12Marginalism is a theory of economics that attempts to explain the discrepancy in the value of goods and services by reference to their secondary, or marginal, utility. It states that the reason why the price of diamonds is higher than that of water, for example, owes to the greater additional satisfaction of the diamonds over the water. Thus, while the water has greater total utility, the diamond has greater marginal utility.
Image 12Marginalism is a theory of economics that attempts to explain the discrepancy in the value of goods and services by reference to their secondary, or marginal, utility. It states that the reason why the price of diamonds is higher than that of water, for example, owes to the greater additional satisfaction of the diamonds over the water. Thus, while the water has greater total utility, the diamond has greater marginal utility.
Although the central concept of marginalism is that of marginal utility, marginalists, following the lead of Alfred Marshall, drew upon the idea of marginal physical productivity in explanation of cost. The neoclassical tradition that emerged from British marginalism abandoned the concept of utility and gave marginal rates of substitution a more fundamental role in analysis. Marginalism is an integral part of mainstream economic theory. (Full article...) -
 Image 13Frank Hyneman Knight (November 7, 1885 – April 15, 1972) was an American economist who spent most of his career at the University of Chicago, where he became one of the founders of the Chicago School.
Image 13Frank Hyneman Knight (November 7, 1885 – April 15, 1972) was an American economist who spent most of his career at the University of Chicago, where he became one of the founders of the Chicago School.
Nobel laureates Milton Friedman, George Stigler and James M. Buchanan were all students of Knight at Chicago. Ronald Coase said that Knight, without teaching him, was a major influence on his thinking. F.A. Hayek considered Knight to be one of the major figures in preserving and promoting classical liberal thought in the twentieth century. (Full article...) -
 Image 14
Image 14
World GDP per capita, 1400–2003
Economic history is the study of history using methodological tools from economics or with a special attention to economic phenomena. Research is conducted using a combination of historical methods, statistical methods and the application of economic theory to historical situations and institutions. The field can encompass a wide variety of topics, including equality, finance, technology, labour, and business. It emphasizes historicizing the economy itself, analyzing it as a dynamic entity and attempting to provide insights into the way it is structured and conceived.
Using both quantitative data and qualitative sources, economic historians emphasize understanding the historical context in which major economic events take place. They often focus on the institutional dynamics of systems of production, labor, and capital, as well as the economy's impact on society, culture, and language. Scholars of the discipline may approach their analysis from the perspective of different schools of economic thought, such as mainstream economics, Austrian economics, Marxian economics, the Chicago school of economics, and Keynesian economics. (Full article...) -
 Image 15
Image 15 Rothbard in the 1970s
Rothbard in the 1970s
Murray Newton Rothbard (/ˈrɒθbɑːrd/; March 2, 1926 – January 7, 1995) was an American economist of the Austrian School, economic historian, political theorist, and activist. Rothbard was a central figure in the 20th-century American libertarian movement, particularly its right-wing strands, and was a founder and leading theoretician of anarcho-capitalism. He wrote over twenty books on political theory, history, economics, and other subjects.
Rothbard argued that all services provided by the "monopoly system of the corporate state" could be provided more efficiently by the private sector and wrote that the state is "the organization of robbery systematized and writ large". He called fractional-reserve banking a form of fraud and opposed central banking. He categorically opposed all military, political, and economic interventionism in the affairs of other nations. (Full article...) -
 Image 16
Image 16 Koopmans in 1967
Koopmans in 1967
Tjalling Charles Koopmans (August 28, 1910 – February 26, 1985) was a Dutch-American mathematician and economist. He was the joint winner with Leonid Kantorovich of the 1975 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for his work on the theory of the optimum allocation of resources. Koopmans showed that on the basis of certain efficiency criteria, it is possible to make important deductions concerning optimum price systems. (Full article...) -
![Image 17 Hoppe in 2024 Hans-Hermann Hoppe (/ˈhɒpə/; German: [ˈhɔpə]; born 2 September 1949) is a German-American academic associated with Austrian School economics, anarcho-capitalism, right-wing libertarianism, and opposition to democracy. He is professor emeritus of economics at the University of Nevada, Las Vegas (UNLV), senior fellow of the Mises Institute think tank, and the founder and president of the Property and Freedom Society. Hoppe has written extensively in opposition to democracy, notably in his 2001 book Democracy: The God That Failed. The book favors exclusionary "covenant communities" that are "founded for the purpose of protecting family and kin". A section of the book favoring exclusion of democrats and homosexuals from society helped popularize Hoppe on the far-right. (Full article...)](./_assets_/Blank.png) Image 17
Image 17.jpg) Hoppe in 2024
Hoppe in 2024
Hans-Hermann Hoppe (/ˈhɒpə/; German: [ˈhɔpə]; born 2 September 1949) is a German-American academic associated with Austrian School economics, anarcho-capitalism, right-wing libertarianism, and opposition to democracy. He is professor emeritus of economics at the University of Nevada, Las Vegas (UNLV), senior fellow of the Mises Institute think tank, and the founder and president of the Property and Freedom Society.
Hoppe has written extensively in opposition to democracy, notably in his 2001 book Democracy: The God That Failed. The book favors exclusionary "covenant communities" that are "founded for the purpose of protecting family and kin". A section of the book favoring exclusion of democrats and homosexuals from society helped popularize Hoppe on the far-right. (Full article...) -
 Image 18
Image 18
Piero Sraffa FBA (5 August 1898 – 3 September 1983) was an influential Italian political economist who served as lecturer of economics at the University of Cambridge. His book Production of Commodities by Means of Commodities is taken as founding the neo-Ricardian school of economics. (Full article...) -
 Image 19Behavioral economics is the study of the psychological (e.g. cognitive, behavioral, affective, social) factors involved in the decisions of individuals or institutions, and how these decisions deviate from those implied by traditional economic theory.
Image 19Behavioral economics is the study of the psychological (e.g. cognitive, behavioral, affective, social) factors involved in the decisions of individuals or institutions, and how these decisions deviate from those implied by traditional economic theory.
Behavioral economics is primarily concerned with the bounds of rationality of economic agents. Behavioral models typically integrate insights from psychology, neuroscience and microeconomic theory. (Full article...) -
 Image 20
Image 20.jpg)
Silvio Gesell (1862–1930), the founder of Freiwirtschaft and Freigeld
Freiwirtschaft (German for "free economy") is an economic theory and proposal founded by the German-Argentine economist Silvio Gesell in his 1916 book, The Natural Economic Order (German: Die natürliche Wirtschaftsordnung durch Freiland und Freigeld). Some of the basic economic ideas of Freiwirtschaft were also independently published in 1890 by the Hungarian-Austrian economist Theodor Hertzka in his novel Freiland - ein soziales Zukunftsbild (Freeland - A Social Anticipation). (Full article...) -
 Image 21
Image 21
William Stanley Jevons FRS (/ˈdʒɛvənz/; 1 September 1835 – 13 August 1882) was an English economist and logician.
Irving Fisher described Jevons's book A General Mathematical Theory of Political Economy (1862) as the start of the mathematical method in economics. It made the case that economics, as a science concerned with quantities, is necessarily mathematical. In so doing, it expounded upon the "final" (marginal) utility theory of value. Jevons' work, along with similar discoveries made by Carl Menger in Vienna (1871) and by Léon Walras in Switzerland (1874), marked the opening of a new period in the history of economic thought. Jevons's contribution to the marginal revolution in economics in the late 19th century established his reputation as a leading political economist and logician of the time. (Full article...) -
 Image 22Supply-side economics is a macroeconomic theory postulating that economic growth can be most effectively fostered by lowering taxes, decreasing regulation, and allowing free trade. According to supply-side economics theory, consumers will benefit from greater supply of goods and services at lower prices, and employment will increase. Supply-side fiscal policies are designed to increase aggregate supply, as opposed to aggregate demand, thereby expanding output and employment while lowering prices. Such policies are of several general varieties:
Image 22Supply-side economics is a macroeconomic theory postulating that economic growth can be most effectively fostered by lowering taxes, decreasing regulation, and allowing free trade. According to supply-side economics theory, consumers will benefit from greater supply of goods and services at lower prices, and employment will increase. Supply-side fiscal policies are designed to increase aggregate supply, as opposed to aggregate demand, thereby expanding output and employment while lowering prices. Such policies are of several general varieties:- Investments in human capital, such as education, healthcare, and encouraging the transfer of technologies and business processes, to improve productivity (output per worker). Encouraging globalized free trade via containerization is a major recent example.
- Tax reduction, to provide incentives to work, invest and take risks. Lowering income tax rates and eliminating or lowering tariffs are examples of such policies.
- Investments in new capital equipment and research and development (R&D), to further improve productivity. Allowing businesses to depreciate capital equipment more rapidly (e.g., over one year as opposed to 10) gives them an immediate financial incentive to invest in such equipment.
- Reduction in government regulations, to encourage business formation and expansion.
A basis of supply-side economics is the Laffer curve, a theoretical relationship between rates of taxation and government revenue. The Laffer curve suggests that when the tax level is too high, lowering tax rates will boost government revenue through higher economic growth, though the level at which rates are deemed "too high" is disputed. Critics also argue that several large tax cuts in the United States over the last 40 years have not increased revenue. (Full article...) -
![Image 23 Sen in 2012 Amartya Kumar Sen (Bengali: [ˈɔmortːo ˈʃen]; born 3 November 1933) is an Indian economist and philosopher. Sen has taught and worked in England and the United States since 1972. In 1998, Sen received the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for his contributions to welfare economics. He has also made major scholarly contributions to social choice theory, economic and social justice, economic theories of famines, decision theory, development economics, public health, and the measures of well-being of countries. Sen is currently the Thomas W. Lamont University Professor, and Professor of Economics and Philosophy, at Harvard University. He previously served as Master of Trinity College at the University of Cambridge. In 1999, he received India's highest civilian honour, Bharat Ratna, for his contribution to welfare economics. The German Publishers and Booksellers Association awarded him the 2020 Peace Prize of the German Book Trade for his pioneering scholarship addressing issues of global justice and combating social inequality in education and healthcare. (Full article...)](./_assets_/Blank.png) Image 23
Image 23 Sen in 2012
Sen in 2012
Amartya Kumar Sen (Bengali: [ˈɔmortːo ˈʃen]; born 3 November 1933) is an Indian economist and philosopher. Sen has taught and worked in England and the United States since 1972. In 1998, Sen received the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for his contributions to welfare economics. He has also made major scholarly contributions to social choice theory, economic and social justice, economic theories of famines, decision theory, development economics, public health, and the measures of well-being of countries.
Sen is currently the Thomas W. Lamont University Professor, and Professor of Economics and Philosophy, at Harvard University. He previously served as Master of Trinity College at the University of Cambridge. In 1999, he received India's highest civilian honour, Bharat Ratna, for his contribution to welfare economics. The German Publishers and Booksellers Association awarded him the 2020 Peace Prize of the German Book Trade for his pioneering scholarship addressing issues of global justice and combating social inequality in education and healthcare. (Full article...) -
 Image 24Socialist economics comprises the economic theories, practices and norms of hypothetical and existing socialist economic systems. A socialist economic system is characterized by social ownership and operation of the means of production that may take the form of autonomous cooperatives or direct public ownership wherein production is carried out directly for use rather than for profit. Socialist systems that utilize markets for allocating capital goods and factors of production among economic units are designated market socialism. When planning is utilized, the economic system is designated as a socialist planned economy. Non-market forms of socialism usually include a system of accounting based on calculation-in-kind to value resources and goods.
Image 24Socialist economics comprises the economic theories, practices and norms of hypothetical and existing socialist economic systems. A socialist economic system is characterized by social ownership and operation of the means of production that may take the form of autonomous cooperatives or direct public ownership wherein production is carried out directly for use rather than for profit. Socialist systems that utilize markets for allocating capital goods and factors of production among economic units are designated market socialism. When planning is utilized, the economic system is designated as a socialist planned economy. Non-market forms of socialism usually include a system of accounting based on calculation-in-kind to value resources and goods.
Socialist economics has been associated with different schools of economic thought. Marxian economics provided a foundation for socialism based on analysis of capitalism while neoclassical economics and evolutionary economics provided comprehensive models of socialism. During the 20th century, proposals and models for both socialist planned and market economies were based heavily on neoclassical economics or a synthesis of neoclassical economics with Marxian or institutional economics. (Full article...) -
![Image 25 Kuznets in 1971 Simon Smith Kuznets (/ˈkʌznɛts/ KUZ-nets; Russian: Семён Абра́мович Кузне́ц, IPA: [sʲɪˈmʲɵn ɐˈbraməvʲɪtɕ kʊzʲˈnʲets]; April 30, 1901 – July 8, 1985) was a Russian-born American economist and statistician who received the 1971 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences "for his empirically founded interpretation of economic growth which has led to new and deepened insight into the economic and social structure and process of development." Kuznets made a decisive contribution to the transformation of economics into an empirical science and to the formation of quantitative economic history. Kuznets pioneered the concept of gross domestic product, which seeks to capture all economic production in a state by a single measure. (Full article...)](./_assets_/Blank.png) Image 25
Image 25 Kuznets in 1971
Kuznets in 1971
Simon Smith Kuznets (/ˈkʌznɛts/ KUZ-nets; Russian: Семён Абра́мович Кузне́ц, IPA: [sʲɪˈmʲɵn ɐˈbraməvʲɪtɕ kʊzʲˈnʲets]; April 30, 1901 – July 8, 1985) was a Russian-born American economist and statistician who received the 1971 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences "for his empirically founded interpretation of economic growth which has led to new and deepened insight into the economic and social structure and process of development."
Kuznets made a decisive contribution to the transformation of economics into an empirical science and to the formation of quantitative economic history. Kuznets pioneered the concept of gross domestic product, which seeks to capture all economic production in a state by a single measure. (Full article...)
Did you know...
- ... that in the essay "Toward European Unity" George Orwell presumed that one of the greatest obstacles to a federal Europe would be economic pressure by the United States?
- ... that Michael Kremer's O-ring theory of economic development was inspired by his forgetting to purchase toilet paper for a training session?
- ... that Francois Massaquoi, who studied economics at New York University, later led the Lofa Defense Force during the First Liberian Civil War?
- ... that developmental economist Michael Lipton showed that poor farmers were more resource efficient than rich farmers?
- ... that a banker was named the prime minister of Equatorial Guinea after his predecessor resigned during an economic crisis?
- ... that scientists from the Institutum Divi Thomae raised silkworms at Saint Gregory Seminary during World War II as a form of economic warfare against Japan?
Need help?
Do you have a question about Economics that you can't find the answer to?
Consider asking it at the Wikipedia reference desk.
Get involved
For editor resources and to collaborate with other editors on improving Wikipedia's Economics-related articles, see WikiProject Economics.
Selected images
-
-
-

-

-
-
 Image 6An environmental scientist sampling water
Image 6An environmental scientist sampling water -
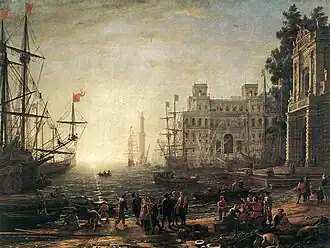 Image 7A 1638 painting of a French seaport during the heyday of mercantilism
Image 7A 1638 painting of a French seaport during the heyday of mercantilism -
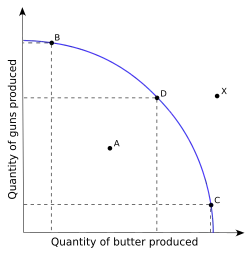
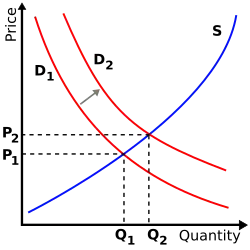 Image 8The supply and demand model describes how prices vary as a result of a balance between product availability and demand. The graph depicts an increase in demand from D1 to D2 and the resulting increase in price and quantity required to reach a new equilibrium point on the supply curve (S).
Image 8The supply and demand model describes how prices vary as a result of a balance between product availability and demand. The graph depicts an increase in demand from D1 to D2 and the resulting increase in price and quantity required to reach a new equilibrium point on the supply curve (S). -
_per_capita_in_2022_by_IMF.png)
-
 Image 10The Marxist critique of political economy comes from the work of German philosopher Karl Marx.
Image 10The Marxist critique of political economy comes from the work of German philosopher Karl Marx. -
 Image 11Economists study trade, production, and consumption decisions, including those that occur in a traditional marketplace
Image 11Economists study trade, production, and consumption decisions, including those that occur in a traditional marketplace -
 Image 12The publication of Adam Smith's The Wealth of Nations in 1776 is considered to be the first formalisation of economic thought.
Image 12The publication of Adam Smith's The Wealth of Nations in 1776 is considered to be the first formalisation of economic thought. -
 Image 13Pollution can be a simple example of market failure; if costs of production are not borne by producers but are by the environment, accident victims or others, then prices are distorted.
Image 13Pollution can be a simple example of market failure; if costs of production are not borne by producers but are by the environment, accident victims or others, then prices are distorted. -
 Image 14São Paulo Stock Exchange in Brazil, an electronic trading network that brings together buyers and sellers through an electronic trading platform
Image 14São Paulo Stock Exchange in Brazil, an electronic trading network that brings together buyers and sellers through an electronic trading platform
In the news
- 13 August 2025 – Australia–Vanuatu relations
- Australia and Vanuatu agree to implement a A$500 million (US$327 million) deal over the next decade to provide funding for economic development, security cooperation, labour mobility, and climate resilience. (Reuters)
- 4 August 2025 – India–Philippines relations, Territorial disputes in the South China Sea
- The Indian and Philippine navies conduct their first joint exercise in the Philippine-designated exclusive economic zone in the South China Sea. The Indian Navy deployed guided missile destroyers, tankers, and corvettes, while the Philippines sent two frigates. (AP) (Reuters)
- 8 July 2025 – German economic crisis
- German vehicle manufacturer Daimler Truck announces it will cut around 5,000 jobs in the country by 2030 in an effort to save €1 billion following a drop in sales. (DW)
Subcategories

- Select [►] to view subcategories
Subtopics
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus