Olympia Regional Airport
Olympia Regional Airport Olympia Army Airfield | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Airport in August 2023 | |||||||||||||||
| Summary | |||||||||||||||
| Airport type | Public | ||||||||||||||
| Owner | Port of Olympia | ||||||||||||||
| Operator | Port of Olympia | ||||||||||||||
| Serves | Olympia, Washington | ||||||||||||||
| Location | Tumwater, Washington | ||||||||||||||
| Built | 1928 | ||||||||||||||
| Elevation AMSL | 208 ft / 63 m | ||||||||||||||
| Coordinates | 46°58′10″N 122°54′09″W / 46.96944°N 122.90250°W | ||||||||||||||
| Website | Official Website | ||||||||||||||
| Map | |||||||||||||||
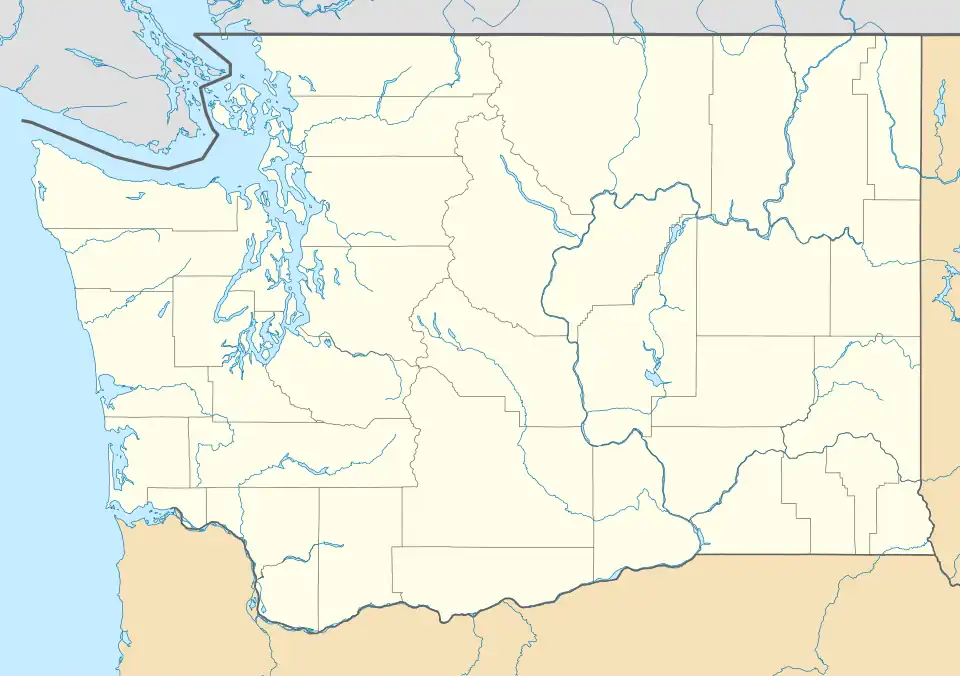 KOLM Location of Olympia Regional Airport  KOLM KOLM (the United States) | |||||||||||||||
| Runways | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
| Statistics (2019) | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
Olympia Regional Airport (IATA: OLM, ICAO: KOLM, FAA LID: OLM) is a public use airport located 4 nautical miles (7.4 km) south of Olympia, a city in Thurston County and the capital of the U.S. state of Washington.[1][2][3] It is located within the city boundaries of Tumwater, which is south of Olympia and approximately 1 mile (1.6 km) east of Interstate 5. The airport is owned and operated by the Port of Olympia.[4]
The Olympic Flight Museum is located at the Olympia Airport, and Airlift Northwest, the region's air medical transport service uses the airport as one of its medical helicopter bases; a large private-use heliport, known as Olympia Heliport (FAA LID: 0WN4) is located on airport grounds.[5] The flight museum and the airport host an annual air show in June.[6]
The airport's industrial park, 300 acres (1.2 km2) in extent, includes a U.S. Department of Commerce-designated free trade zone.
History

The airport was built in 1928 at a cost of $35,000 (equivalent to $640,921 in 2024). An aircraft hangar was built and expanded in the 1930s and the airport facilitated training and chartered flights.[7]
In 1941, after the start of World War II, the airport served as a satellite of nearby McChord Field. Between July 1942 and August 1943, it was home to the 37th Flying Training Squadron (part of the 55th Pursuit Group) and their fleet of P-43 Lancers and P-38H Lightning interceptors. The airport returned to the City of Olympia in 1947.[7]
The airport now supports large business jets, cargo aircraft, military helicopters and has a backup runway lighting system for uninterrupted operations. Olympia Airport also has an ILS (Instrument Landing System) and backup power system for operations during bad weather or low visibility. The Olympia VOR, located on the field, also provides instrument approaches into the Olympia Airport in low visibility conditions.
The FAA funded a $15 million improvement project that was completed in September 2008. The work focused on runway line-of-sight improvements and enhanced taxiway and runway signage. In the late 1990s, the airport's runway protection zone was extended with the purchase of $5.5 million worth of land on each end of the primary runway, and an above ground fuel facility was constructed.
Facilities and aircraft
Olympia Regional Airport covers an area of 845 acres (342 ha) at an elevation of 208 feet (63 m) above mean sea level. It has two asphalt paved runways: 17/35 is 5,500 by 150 feet with precision markings (1,676 x 46 m) and runway 8/26 is 4,157 by 150 feet with basic markings (1,267 x 46 m).[1] The airport has a passenger terminal, an air traffic control tower and a full-instrument landing approach system.
The field is home to fixed wing and helicopter flight instruction, major aircraft and oxygen maintenance facilities, the Washington State Patrol aviation division, and a key navigational aid (Olympia VOR) that is used by commercial flights inbound to Seattle-area airports, including Seattle-Tacoma International Airport, as well as by general aviation aircraft in the region.
Airlines
Cargo
| Airlines | Destinations |
|---|---|
| Ameriflight | Seattle |
See also
References
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from the Air Force Historical Research Agency
This article incorporates public domain material from the Air Force Historical Research Agency
- ^ a b c FAA Airport Form 5010 for OLM PDF. Federal Aviation Administration. Effective July 13, 2023.
- ^ a b "Airport list: Olympia Regional". Washington State Department of Transportation. Retrieved July 19, 2025.
- ^ a b "Olympia Regional Airport". Airport Home. Port of Olympia. Retrieved July 19, 2025.
- ^ McCarthy, Pat (April 3, 2025). "Accountability Audit Report; Port of Olympia; For the period January 1, 2023 through December 31, 2023". Office of the Washington State Auditor. p. 6. Retrieved July 19, 2025.
- ^ "0WN4 - Olympia Heliport". AirNav.com. July 10, 2025. Archived from the original on May 28, 2024. Retrieved July 19, 2025.
- ^ Gilmore, Molly (June 12, 2025). "Watch vintage planes, hang with canines or gobble up strawberries this weekend". The Olympian. Retrieved July 19, 2025.
- ^ a b O’Connell, Emmett (June 10, 2013). "Flying High: A History Of The Olympia Airport". ThurstonTalk. Retrieved July 19, 2025.
External links
- Olympia Regional Airport at Port of Olympia website
- FAA Airport Diagram (PDF), effective August 7, 2025
- FAA Terminal Procedures for OLM, effective August 7, 2025
- Resources for this airport:
- FAA airport information for OLM
- AirNav airport information for KOLM
- ASN accident history for OLM
- FlightAware airport information and live flight tracker
- NOAA/NWS weather observations: current, past three days
- SkyVector aeronautical chart, Terminal Procedures
.svg.png)