Military Regional Command
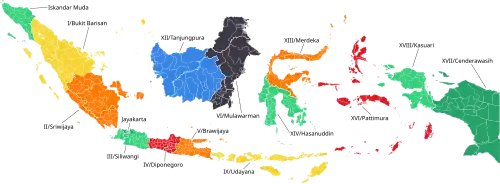

The Indonesian Military Regional Commands (Indonesian: Komando Daerah Militer; abbreviated Kodam) also known officially as Military Area Commands are military districts of the Indonesian Army that function for the territorial defense of various regions within the country. They cover one or multiple provinces.
History
The Armed Forces' military regions are known as Kodam. Their organization was established by General Sudirman, following the model of the German Wehrkreise system. The system was later codified in Strategy Order No.1 (Surat Perintah Siasat No.1), signed by General Sudirman in November 1948.[1]
The Army's structure underwent various reorganisations throughout its early years. From 1946 to 1952, the Army was organized into combined arms divisions. These were consolidated in 1951 and then dissolved in 1952. From 1952 to 1958–59, the Army was organised into seven Territorial Armies (Tentara & Teritorium) composed of regiments and independent formations at battalion level and below. In August 1958, the Indonesian Army reconsolidated its territorial organization. This created sixteen regional commands, which retained earlier divisional titles; the Siliwangi Division, for example, became Kodam VI/Siliwangi.[2] The Kodam were subdivided administratively into Areas (the former territorial regiments), Districts (the former regimental battalions), and District Sectors, and operationally composed of several specialty battalions and in some regional commands, an infantry brigade.
A reorganisation in 1985 made significant changes in the army chain of command. The four multiservice Regional Defence Commands (Kowilhan) and the National Strategic Forces Command (Kostranas) were eliminated from the defense structure, re-establishing the Military Regional Commands (Kodam) as the key organisation for strategic, tactical, and territorial operations for all services. The 16 regions were reduced to just 10.[3] The chain of command flowed directly from the ABRI commander via the Chief of Staff of the Army to the ten territorial commanders, and then to subordinate army territorial commands. In 1999, the number of regions grew to 10, and as of 2024, there are around 15 in active operation.
The territorial commands incorporate provincial and district commands each with infantry battalions, sometimes a cavalry battalion, artillery, or engineers. The number of activated infantry brigades is increasing.[4] Some have Raider battalions attached.
Six new regional commands were created on 10 August 2025, and so the number of regions grew to 21.[5][6]
Organization of Regional Commands
Each Military Regional or Area Command (Kodam) is led by a major general, assisted by a chief of staff who holds the rank of brigadier general. Kodams oversee several territorial formations under its command, which are:
- Korem or Indonesian: Komando Resor Militer also known as Military Subarea Command or Military Resort Command is a territorial army office covering a large area or multiple regencies (Kabupaten). They are further divided into two types which are type "A" and type "B". They are commanded by a brigadier general for type "A" and a colonel for type "B" respectively. It is below the Kodam and is responsible for Military Districts or Kodims.
- Kodim or Indonesian: Komando Distrik Militer also known as Military District Command is a territorial army office covering a City or Regency level. They are further divided into three types which are "independent", type "A" and type "B". They are commanded by a Colonel (for Independent and type "A"), and a Lieutenant Colonel for type "B" respectively. It is below the Korem and oversees Koramils under its supervision.
- Koramil or Indonesian: Komando Rayon Militer also known as Military Subdistrict Command is a territorial army office covering a district (kecamatan, distrik, kapanewon, and kemantren). They are further divided into two types, "A" and "B", commanded by a Major for type "A" and a Captain for type "B" respectively. It is below the Kodim. Babinsa offices and bureaux fall under its control.
- Babinsa or Indonesian: Bintara Pembina Desa, lit. 'Village Trustee' also known as Village Management Senior NCO is a senior army Non-commissioned Officer (usually holding the rank of
 Sergeant Major) or a senior Enlisted rank personnel (usually holding the rank of
Sergeant Major) or a senior Enlisted rank personnel (usually holding the rank of  Master corporal) who is in charge for carrying out territorial development and monitoring duties for a community in the village/Kelurahan level. Babinsa NCOs fall under the control of the local Koramil unit.
Master corporal) who is in charge for carrying out territorial development and monitoring duties for a community in the village/Kelurahan level. Babinsa NCOs fall under the control of the local Koramil unit.
- Babinsa or Indonesian: Bintara Pembina Desa, lit. 'Village Trustee' also known as Village Management Senior NCO is a senior army Non-commissioned Officer (usually holding the rank of
-
 The 063 "Sunan Gunung Jati" Military Area Command (Korem 063) in Cirebon, under Kodam III/Siliwangi
The 063 "Sunan Gunung Jati" Military Area Command (Korem 063) in Cirebon, under Kodam III/Siliwangi -
.jpg) The 0619 Purwakarta Military District Command (Kodim 0619), under Korem 063
The 0619 Purwakarta Military District Command (Kodim 0619), under Korem 063 -
.jpg) The 2018 Susukan Military Sector Command (Koramil 2018) in Cirebon Regency, under Kodim 0620
The 2018 Susukan Military Sector Command (Koramil 2018) in Cirebon Regency, under Kodim 0620
In addition, each of the Kodams own a Main Regiment (known as Resimen Induk Kodam or Rindam) which is responsible for the training and education of enlisted personnel and non-commissioned officers in their territory.
The office of the Regional Commander is assisted by the following territorial departments:
- Office of the Regional Inspectorate General (Itdam)
- Office of the Regional Secretariat (Setumdam)
- Regional Military Police Command (Pomdam) – responsible for military law enforcement in the territory
- Regional Public Affairs and Press Office (Pendam) – responsible for public affairs, media and civil-military relations
- Office of the Regional Adjutant General (Ajendam)
- Regional Military Physical Fitness and Sports Office (Jasdam) – responsible for physical fitness and sports affairs
- Regional Medical Department (Kesdam) – responsible for medical affairs
- Regional Veterans and National Reserves Administration (Babiminvetcadam) – responsible for military reserves formation and veterans' affairs
- Regional Topography Service (Topdam)
- Regional Chaplaincy Corps (Bintaldam) – chaplaincy service for personnel who are Muslims, Christians, Hindus, Buddhists and Confucianists
- Regional Finance Office (Kudam) – responsible for financial activities
- Regional Legal Affairs Office (Kumdam)
- Regional HQ and HQ Services Detachment (Detasemen Makodam)
- Regional C3 Unit (Puskodalops Kodam)
- Regional Information and Communications Technology Office (Infolahtadam)
- Regional Logistics and Transportation Division (Bekangdam)
- Regional Signals Division (Hubdam)
- Regional Ordnance Department (Paldam)
- Regional Engineering Division (Zidam)
- Regional Cyber Operations Service (Sandidam)
- Regional Intelligence Command (Deninteldam)
- Liaison offices of the Navy and Air Force formations in each Military Region
Operationally, each "Kodam" is organized as a territorial infantry division which oversees several Subordinate combat units:
- Infantry Brigade
- directly reporting independent Infantry battalions (including Raider Infantry)
- independent Infantry battalions which are under the Military Subarea Command or "Korem"
- Cavalry Squadron and/or Cavalry Reconnaissance Troop (Separate)
- Field Artillery Battalion/s
- Air Defense Artillery Battalions/Detachments
- Combat Engineers Battalion/s
- Construction Engineers Battalions/Detachments
Military regions
The following is a list of Military Regional Commands in Indonesia:
Former Military Regional Commands
| No | Name
|
Coat of arms
|
Headquarters
|
Formed
|
Disbanded
|
| 1. | III Military Regional Command/17 Agustus |  |
17 April 1959[10]
|
26 January 1985[11]
| |
| 2. | X Military Regional Command/Lambung Mangkurat | 17 July 1958[12]
|
1 May 1985[13]
| ||
| 3. | XI Military Regional Command/Tambun Bungai | 17 July 1958[14]
|
18 March 1974[15]
|
References
- ^ Gitiyarko, Vincentinus (1 March 2021). "Serangan Umum 1 Maret 1949". Kompas. Retrieved 29 September 2021.
- ^ Conboy, Kenneth J. (2003). Kopassus: inside Indonesia's special forces (1st ed.). Jakarta: Equinox Publishing. p. 79. ISBN 979-95898-8-6. OCLC 51242376.
- ^ Anderson, Ben (1985). "Current Data on the Indonesian Military Elite". Indonesia (40). Southeast Asia Program Publications at Cornell University: 131–64. JSTOR 3350880.
- ^ "The Military Balance". 106 (1). International Institute for Strategic Studies. 2006.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ a b c d e f g Trikarinaputri, Ervana; Panji, Novali (10 August 2025). "Daftar Enam Kodam Baru TNI AD yang Akan Diresmikan Hari Ini". Tempo.co (in Indonesian). Retrieved 10 August 2025.
- ^ a b c d e f g Marison, Walda (8 August 2025). Sitanggang, Hisar (ed.). "Panglima TNI tunjuk enam pati untuk pimpin Kodam baru". Antara News (in Indonesian). Retrieved 10 August 2025.
- ^ "Cikal Bakal Terbentuknya Kodam I/Bukit Barisan". SINDOnews Daerah (in Indonesian). Retrieved 2025-02-03.
- ^ memorandum.co.id. "Dirgahayu ke-75, Simak Sejarah HUT Kodam V/Brawijaya yang Diperingati Setiap Tanggal 17 Desember". memorandum.disway.id (in Indonesian). Retrieved 2025-02-03.
- ^ Matanasi, Petrik (2020-07-27). "Kodam Mulawarman: Perbedaan Tajam Dua Pangdam dan Penangkapan PKI". tirto.id (in Indonesian). Retrieved 2025-02-03.
- ^ Stj Soenarman (1970). Sedjarah Kodam III/17 Agustus (in Indonesian). Komando Daerah Militer III/17 Agustus. p. 470.
- ^ Petrik Matanasi, Irfan Teguh (2020-06-15). "Kodam Bukit Barisan: Dipecah Nasution untuk Mempersempit Gerak PRRI". tirto.id (in Indonesian). Retrieved 2021-04-07.
Pada masa pendudukan Jepang, di Sumatra Utara terdapat tentara sukarela yang tergabung dalam Gyugun. Setelah Proklamasi Kemerdekaan, para pemuda ini masuk ke dalam Tentara Keamanan Rakyat (TKR).
- ^ Panitia Redaksi "Kodam X/LM Membangun" (1962). Kodam X/LM Membangun (in Indonesian). Komando Daerah Militer X/Lambung Mangkurat. p. 22.
- ^ "Profil Satuan Kodim 1015/Sampit". kodim1015sampit.com. Retrieved 2021-04-08.
Pada tanggal 1 Mei 1985 Kodam X/ Lambung Mangkurat dilikuidasi menjadi Kodam VI/Tanjungpura di Balikpapan sehingga Organik Administrasi Kodim 1015/Spt yang merupakan bagian wilayah dari Korem 102/Panju Panjung di bawah Kodam VI/Tanjungpura.
- ^ Alex Prawiraatmadja (1972). Amanat-amanat pada hari ulang tahun Kodam XI/Tambun Bungai, 17 Djuli 1972, di Palangka Raja (in Indonesian). TNI Angkatan Darat. p. 16.
- ^ "SEJARAH SINGKAT KOREM 102/PANJU PANJUNG". korem102panjupanjung.com. Archived from the original on 2021-05-13. Retrieved 2021-04-08.















.png)



