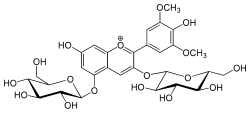
Malvin
Names
IUPAC name
3,5-Bis(β-D -glucopyranosyloxy)-4′ ,7-dihydroxy-3′ ,5′ -dimethoxyflavylium
Systematic IUPAC name
7-Hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-3,5-bis{[(2S ,3R ,4S ,5S ,6R )-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy}-1λ4 -benzopyran-1-ylium
Other names
Malvidin 3,5-diglucoside
Identifiers
ChEBI
ChemSpider
ECHA InfoCard 100.037.063
KEGG
UNII
(cation): InChI=1S/C29H34O17/c1-40-15-3-10(4-16(41-2)20(15)33)27-17(44-29-26(39)24(37)22(35)19(9-31)46-29)7-12-13(42-27)5-11(32)6-14(12)43-28-25(38)23(36)21(34)18(8-30)45-28/h3-7,18-19,21-26,28-31,34-39H,8-9H2,1-2H3,(H-,32,33)/p+1/t18-,19-,21-,22-,23+,24+,25-,26-,28-,29-/m1/s1
Key: CILLXFBAACIQNS-BTXJZROQSA-O
(chloride): InChI=1S/C29H34O17.ClH/c1-40-15-3-10(4-16(41-2)20(15)33)27-17(44-29-26(39)24(37)22(35)19(9-31)46-29)7-12-13(42-27)5-11(32)6-14(12)43-28-25(38)23(36)21(34)18(8-30)45-28;/h3-7,18-19,21-26,28-31,34-39H,8-9H2,1-2H3,(H-,32,33);1H/t18-,19-,21-,22-,23+,24+,25-,26-,28-,29-;/m1./s1
Key: RHKJIVJBQJXLBY-FTIBDFQESA-N
(cation): COC1=CC(=CC(=C1O)OC)C2=C(C=C3C(=CC(=CC3=[O+]2)O)O[C@H]4[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O4)CO)O)O)O)O[C@H]5[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O5)CO)O)O)O
(chloride): [Cl-].O[C@@H]5[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H]5Oc2cc(O)cc3[o+]c(c(O[C@@H]1O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O)cc23)c4cc(OC)c(O)c(OC)c4
Properties
C29 H35 O17 + (cation) C29 H35 O17 Cl (chloride)
Molar mass
655.578 mg/L (cation) 691.031 mg/L (chloride)
Appearance
Reddish blue, odorless powder[ 1]
Nearly insoluble[ 1]
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their
standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
Malvin is a naturally occurring chemical of the anthocyanin family.
Malvin reacts in the presence of H2 O2 to form malvone.[ 2] [ 3]
Natural occurrences
It is a diglucoside of malvidin mainly found as a pigment in herbs like Malva (Malva sylvestris Primula Rhododendron [ 4] M. sylvestris also contains malonylmalvin (malvidin 3-(6″-malonylglucoside)-5-glucoside).[ 5]
The characteristic floral jade coloration of Strongylodon macrobotrys copigmentation , a result of the presence of malvin and saponarin (a flavone glucoside ) in the ratio 1:9.
Presence in food
Malvin can be found in a variety of common foods, including peaches (Clingstone variety[ 6]
References
^ a b MSDS from CarlRoth (German)^ Oxidation of the anthocyanidin-3,5-diglucosides with H2O2: The structure of malvone. G. Hrazdina, Phytochemistry, July 1970, Volume 9, Issue 7, Pages 1647–1652, doi :10.1016/S0031-9422(00)85290-5
^ Oxidation products of acylated anthocyanins under acidic and neutral conditions. Géza Hrazdina and Angeline J. Franzese, Phytochemistry, January 1974, Volume 13, Issue 1, Pages 231–234, doi :10.1016/S0031-9422(00)91300-1
^ J. A. Joule, K. Mills: Heterocyclic Chemistry. , S. 173, Blackwell Publishing, 2000, ISBN 978-0-632-05453-4
^ Malonated anthocyanins in malvaceae: Malonylmalvin from Malva sylvestris. Kosaku Takeda, Shigeki Enoki, Jeffrey B. Harborne and John Eagles, Phytochemistry, 1989, Volume 28, Issue 2, Pages 499–500, doi :10.1016/0031-9422(89)80040-8
^ Chang, S; Tan, C; Frankel, EN; Barrett, DM (2000). "Low-density lipoprotein antioxidant activity of phenolic compounds and polyphenol oxidase activity in selected clingstone peach cultivars". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry . 48 (2): 147– 51. doi :10.1021/jf9904564 . PMID 10691607 .
3-Hydroxyanthocyanidins 3-Deoxyanthocyanidins O -Methylated anthocyanidinsAnthocyanins Glucosides:
Diglucosides:
Cyanin (Cyanidin 3,5-O -diglucoside )
Delphin (Delphinidin 3,5-O -diglucoside)
(Malvidin 3,5-diglucoside)
Pelargonin (Pelargonidin 3,5-O -diglucoside)Peonin (Peonidin 3,5-O -diglucoside)
Petunin (Petunidin 3,5-O -diglucoside) Others glycosides:
Antirrhinin (Cyanidin 3-O -rutinoside)Idaein (Cyanidin 3-O -galactoside)Delphinidin 3-O -rhamnoside
Petunidin 3-O -arabinoside
Petunidin 3-O -galactoside
Petunidin 3-O -rhamnoside
Petunidin 3-O -rutinoside
Primulin (Malvidin 3-O -galactoside)Pulchellidin 3-rhamnoside
Tulipanin (Delphinidin 3-O -rutinoside)Acylated anthocyanins
Acetylated anthocyanins
Cyanidin 3-O -(6-acetyl)glucoside
Delphinidin 3-O -(6-acetyl)glucoside
Malvidin 3-O -(6-acetyl)glucoside
Petunidin 3-O -(6-acetyl)galactoside
Petunidin 3-O -(6-acetyl)glucoside
Peonidin 3-O -(6-acetyl)glucoside
Coumaroylated anthocyaninscis - and trans -) Caffeoylated anthocyanins
Malvidin 3-O -(6-p -caffeoyl)glucoside
Peonidin 3-O -(6-p -caffeoyl)glucoside Malonylated anthocyanins
Malonylmalvin (malvidin 3-(6″-malonylglucoside)-5-glucoside) Acylated anthocyanin diglycosides
Cyanidin 3-O -(di-p -coumarylglucoside)-5-glucoside
Gentiodelphin (delphinidin 3-''O''-glucosyl-5-''O''-(6-''O''-caffeoyl-glucosyl)-3′-''O''-(6-''O''-caffeoyl-glucoside))
Nasunin (Delphinidin 3-(p -coumaroylrutinoside)-5-glucoside)Petanin (petunidin 3-[6-O -(4-O -(E )-p -coumaroyl-O -α-l-rhamnopyranosyl)-β-D -glucopyranoside]-5-O -β-D -glucopyranoside)
Violdelphin (Delphinidin 3-rutinoside-7-O -(6-O -(4-(6-O -(4-hydroxybenzoyl)-β-D -glucosyl)oxybenzoyl)-β-D -glucoside)
Flavanol-anthocyanin adducts
Malvidin glucoside-ethyl-catechin Catechin(4α→8)pelargonidin 3-O -β-glucopyranoside
Epicatechin(4α→8)pelargonidin 3-O -β-glucopyranoside
Afzelechin(4α→8)pelargonidin 3-O -β-glucopyranoside
Epiafzelechin(4α→8)pelargonidin 3-O -β-glucopyranoside Miscellaneous