1969 Malaysian general election
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 144 seats in the Dewan Rakyat 73 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Registered | 3,439,707 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 73.59% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
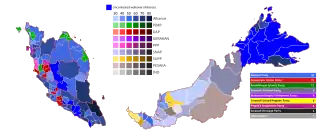
General elections were held in Malaysia on Saturday, 10 May 1969, although polling in Sabah and Sarawak was postponed until between 6 June and 4 July 1970.[1] This was the first parliamentary election in Sabah and Sarawak since the formation of Malaysia in 1963. The ruling Alliance Party, consisting of the United Malays National Organisation (UMNO), the Malayan Chinese Association (MCA) and the Malayan Indian Congress (MIC), retained power but with a reduced majority. The Parti Gerakan Rakyat Malaysia (Gerakan) and the Democratic Action Party (DAP), both of which campaigned against the Bumiputra privileges set out in Article 153 of the Constitution which they considered to be a form of institutional racism, made significant gains.[2] Voter turnout was 73.6 percent. The opposition collectively won 54 seats, causing the Alliance to lose its two-thirds parliamentary majority for the first time, a threshold required to pass most constitutional amendments.
The election also saw the Alliance lose control of the state governments in Perak, Selangor, Penang and Kelantan. The result and its aftermath triggered widespread racial violence in Kuala Lumpur on 13 May 1969, which saw hundreds of deaths, known as the 13 May incident. In response, the federal government declared a state of emergency and suspended parliament, placing the country under the administration of the National Operations Council (NOC) until 1971.[3] The incident left deep political and social scars and marked a turning point in Malaysian politics.[3]
The crisis also signalled the end of Tunku Abdul Rahman's more moderate premiership. He was succeeded several months later by Tun Abdul Razak, who pursued a more hard-line agenda and sought to further entrench Malay special rights under the Ketuanan Melayu ideology. Razak's government introduced policies to restructure society in favour of the Malays and sought to consolidate federal control. Among his initiatives was the launch of the New Economic Policy (NEP), an affirmative action program, and the creation of the Federal Territory of Kuala Lumpur, which was separated from Selangor in 1974.[4] State elections also took place in 330 state constituencies in 12 (out of 13, except Sabah) states of Malaysia on the same day.
Results
Overview
Candidates were returned uncontested in 20 constituencies, with voting in one constituency postponed.[5] West Malaysia went to the polls on 10 May, with Sabah scheduled to vote on 25 May and Sarawak on 7 June. The Alliance Party secured eight seats on nomination day, being unopposed in several constituencies, while Datu Mustapha Datu Harun's United Sabah National Organisation (USNO) won 10 of Sabah's 16 seats unopposed. At the state level, the Alliance suffered significant setbacks, continuing to lose to the Malaysian Islamic Party (PAS) in Kelantan and to the newly formed Gerakan in Penang. No party commanded an outright majority in two other states, with the Alliance holding only 14 out of 24 seats in Selangor and 19 out of 40 in Perak.[2]
The erosion of Malay support for the Alliance Party was more pronounced than that of non-Malays. In West Malaysia, Malay opposition parties saw their vote share rise sharply from around 15 percent in 1964 to 25 percent in 1969, while support for non-Malay opposition parties remained largely unchanged at about 26 percent in both elections. Despite these gains, the electoral system limited their seat increases. PAS rose from nine to 12 parliamentary seats, while the Democratic Action Party (DAP), a predominantly non-Malay party formed from the Malayan remnants of Singapore's People's Action Party (PAP) after the latter's expulsion from Malaysia, expanded from one to 13 seats. These shifts reflected the growing fragmentation of the electorate and signalled deeper political challenges for the Alliance in the years ahead.
Dewan Rakyat
| Party or alliance | Votes | % | Seats | +/– | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alliance Party | United Malays National Organisation | 1,077,499 | 44.96 | 52 | –7 | ||
| Malaysian Chinese Association | 13 | –14 | |||||
| Parti Bumiputera Sarawak | 5 | –3 | |||||
| Malaysian Indian Congress | 2 | –1 | |||||
| Sarawak Chinese Association | 2 | –2 | |||||
| Total | 74 | –22 | |||||
| Pan-Malayan Islamic Party | 501,123 | 20.91 | 12 | +3 | |||
| Democratic Action Party | 286,606 | 11.96 | 13 | +12 | |||
| Parti Gerakan Rakyat Malaysia | 178,971 | 7.47 | 8 | New | |||
| People's Progressive Party | 80,756 | 3.37 | 4 | +2 | |||
| Sarawak United Peoples' Party | 72,754 | 3.04 | 5 | +2 | |||
| Sarawak National Party | 64,593 | 2.69 | 9 | +5 | |||
| Parti Pesaka Sarawak | 30,765 | 1.28 | 2 | New | |||
| Parti Sosialis Rakyat Malaysia | 27,110 | 1.13 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Sabah Chinese Association | 18,313 | 0.76 | 3 | –1 | |||
| United Sabah National Organisation | 13,634 | 0.57 | 13 | +7 | |||
| United Malaysia Chinese Organisation | 1,808 | 0.08 | 0 | New | |||
| Independents | 42,904 | 1.79 | 1 | +1 | |||
| Total | 2,396,836 | 100.00 | 144 | –15 | |||
| Valid votes | 2,396,836 | 94.68 | |||||
| Invalid/blank votes | 134,605 | 5.32 | |||||
| Total votes | 2,531,441 | 100.00 | |||||
| Registered voters/turnout | 3,439,707 | 73.59 | |||||
| Source: CLEA[6] Tindak Malaysia Github | |||||||
Sarawak Alliance contested under Alliance Flag (though not formally under Alliance pact)
Total Electorate (1969): 3843182. Registered voters shown above refer to the contested constituencies (excluding 20 parliamentary uncontested seats
Results by state
Source:Tindak Malaysia Github[7]
Johore
| Party or alliance | Votes | % | Seats | +/– | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alliance Party | United Malays National Organisation | 82,938 | 42.21 | 11 | 0 | ||
| Malaysian Chinese Association | 49,916 | 25.40 | 5 | 0 | |||
| Total | 132,854 | 67.62 | 16 | 0 | |||
| Democratic Action Party | 42,301 | 21.53 | 0 | New | |||
| Parti Gerakan Rakyat Malaysia | 8,211 | 4.18 | 0 | New | |||
| Pan-Malayan Islamic Party | 7,933 | 4.04 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Independents | 5,183 | 2.64 | 0 | – | |||
| Total | 196,482 | 100.00 | 16 | 0 | |||
| Valid votes | 196,482 | 94.02 | |||||
| Invalid/blank votes | 12,505 | 5.98 | |||||
| Total votes | 208,987 | 100.00 | |||||
| Registered voters/turnout | 287,936 | 72.58 | |||||
Total Electorate for Johor (1969): 436 620. Above registered voter count is based on electorate of contested seats (excluding 5 uncontested seats)
Kedah
| Party or alliance | Votes | % | Seats | +/– | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alliance Party | United Malays National Organisation | 127,580 | 45.20 | 7 | –3 | ||
| Malaysian Chinese Association | 23,397 | 8.29 | 2 | 0 | |||
| Total | 150,977 | 53.49 | 9 | –3 | |||
| Pan-Malayan Islamic Party | 115,861 | 41.05 | 3 | +3 | |||
| Parti Gerakan Rakyat Malaysia | 15,402 | 5.46 | 0 | New | |||
| Total | 282,240 | 100.00 | 12 | 0 | |||
| Valid votes | 282,240 | 96.21 | |||||
| Invalid/blank votes | 11,133 | 3.79 | |||||
| Total votes | 293,373 | 100.00 | |||||
| Registered voters/turnout | 388,167 | 75.58 | |||||
Kelantan
| Party or alliance | Votes | % | Seats | +/– | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pan-Malayan Islamic Party | 126,409 | 52.40 | 6 | –2 | |||
| Alliance Party | United Malays National Organisation | 114,593 | 47.50 | 4 | +2 | ||
| Independents | 235 | 0.10 | 0 | – | |||
| Total | 241,237 | 100.00 | 10 | 0 | |||
| Valid votes | 241,237 | 96.94 | |||||
| Invalid/blank votes | 7,626 | 3.06 | |||||
| Total votes | 248,863 | 100.00 | |||||
| Registered voters/turnout | 333,754 | 74.56 | |||||
Malacca
| Party or alliance | Votes | % | Seats | +/– | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alliance Party | United Malays National Organisation | 30,458 | 28.80 | 2 | 0 | ||
| Malaysian Chinese Association | 21,136 | 19.98 | 1 | –1 | |||
| Total | 51,594 | 48.78 | 3 | –1 | |||
| Democratic Action Party | 18,562 | 17.55 | 1 | New | |||
| Pan-Malayan Islamic Party | 20,524 | 19.40 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Parti Sosialis Rakyat Malaysia | 12,436 | 11.76 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Independents | 2,655 | 2.51 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Total | 105,771 | 100.00 | 4 | 0 | |||
| Valid votes | 105,771 | 95.87 | |||||
| Invalid/blank votes | 4,561 | 4.13 | |||||
| Total votes | 110,332 | 100.00 | |||||
| Registered voters/turnout | 147,765 | 74.67 | |||||
Negri Sembilan
| Party or alliance | Votes | % | Seats | +/– | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alliance Party | United Malays National Organisation | 24,335 | 24.37 | 3 | 0 | ||
| Malaysian Chinese Association | 15,350 | 15.37 | 0 | –2 | |||
| Malaysian Indian Congress | 6,606 | 6.62 | 0 | –1 | |||
| Total | 46,291 | 46.36 | 3 | 0 | |||
| Democratic Action Party | 35,446 | 35.50 | 3 | New | |||
| Pan-Malayan Islamic Party | 16,299 | 16.32 | 0 | 0 | |||
| United Malaysia Chinese Organisation | 1,808 | 1.81 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Total | 99,844 | 100.00 | 6 | 0 | |||
| Valid votes | 99,844 | 93.43 | |||||
| Invalid/blank votes | 7,023 | 6.57 | |||||
| Total votes | 106,867 | 100.00 | |||||
| Registered voters/turnout | 142,983 | 74.74 | |||||
Total Electorate for Negri Sembilan (1969): 170 128. Above registered voter count is based on electorate of contested seats (excluding 1 uncontested seat of Rembau-Tampin)
Pahang
| Party or alliance | Votes | % | Seats | +/– | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alliance Party | United Malays National Organisation | 48,507 | 60.84 | 5 | 0 | ||
| Malaysian Chinese Association | 0 | 0.00 | 1 | 0 | |||
| Total | 48,507 | 60.84 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Pan-Malayan Islamic Party | 19,458 | 24.41 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Parti Sosialis Rakyat Malaysia | 11,764 | 14.75 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Total | 79,729 | 100.00 | 6 | 0 | |||
| Valid votes | 79,729 | 94.19 | |||||
| Invalid/blank votes | 4,916 | 5.81 | |||||
| Total votes | 84,645 | 100.00 | |||||
| Registered voters/turnout | 119,254 | 70.98 | |||||
Total Electorate for Pahang (1969): 176768. Above registered voter count is based on electorate of contested seats (excluding 2 uncontested seats which includes MCA seat)
Penang
| Party or alliance | Votes | % | Seats | +/– | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parti Gerakan Rakyat Malaysia | 83,670 | 44.55 | 5 | New | |||
| Alliance Party | United Malays National Organisation | 45,715 | 24.34 | 1 | –3 | ||
| Malaysian Chinese Association | 23,510 | 12.52 | 1 | –1 | |||
| Total | 69,225 | 36.86 | 2 | 0 | |||
| Democratic Action Party | 20,930 | 11.14 | 1 | New | |||
| Pan-Malayan Islamic Party | 13,211 | 7.03 | 0 | 0 | |||
| People's Progressive Party | 775 | 0.41 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Total | 187,811 | 100.00 | 8 | 0 | |||
| Valid votes | 187,811 | 94.06 | |||||
| Invalid/blank votes | 11,860 | 5.94 | |||||
| Total votes | 199,671 | 100.00 | |||||
| Registered voters/turnout | 257,608 | 77.51 | |||||
Total Electorate for Penang (1969): 282401. Above registered voter count is based on electorate of contested seats (excluding the uncontested seat of Bagan)
Perak
| Party or alliance | Votes | % | Seats | +/– | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alliance Party | United Malays National Organisation | 97,612 | 22.91 | 7 | –2 | ||
| Malaysian Chinese Association | 78,262 | 18.37 | 1 | –7 | |||
| Malaysian Indian Congress | 7,985 | 1.87 | 1 | 0 | |||
| Total | 183,859 | 43.16 | 9 | –9 | |||
| Democratic Action Party | 68,651 | 16.12 | 5 | New | |||
| People's Progressive Party | 79,981 | 18.78 | 4 | +2 | |||
| Pan-Malayan Islamic Party | 76,158 | 17.88 | 1 | +1 | |||
| Parti Gerakan Rakyat Malaysia | 15,641 | 3.67 | 1 | New | |||
| Independents | 1,691 | 0.40 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Total | 425,981 | 100.00 | 20 | 0 | |||
| Valid votes | 425,981 | 95.08 | |||||
| Invalid/blank votes | 22,055 | 4.92 | |||||
| Total votes | 448,036 | 100.00 | |||||
| Registered voters/turnout | 613,572 | 73.02 | |||||
Perlis
| Party or alliance | Votes | % | Seats | +/– | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alliance Party | United Malays National Organisation | 22,195 | 51.15 | 2 | 0 | ||
| Pan-Malayan Islamic Party | 18,286 | 42.14 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Parti Sosialis Rakyat Malaysia | 2,910 | 6.71 | 0 | New | |||
| Total | 43,391 | 100.00 | 2 | 0 | |||
| Valid votes | 43,391 | 96.46 | |||||
| Invalid/blank votes | 1,591 | 3.54 | |||||
| Total votes | 44,982 | 100.00 | |||||
| Registered voters/turnout | 56,060 | 80.24 | |||||
Sabah
| Party or alliance | Votes | % | Seats | +/– | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sabah Alliance | United Sabah National Organisation | 13,634 | 30.59 | 13 | 0 | ||
| Sabah Chinese Association | 18,313 | 41.09 | 3 | 0 | |||
| Total | 31,947 | 71.67 | – | 16 | |||
| Independents | 12,626 | 28.33 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Total | 44,573 | 100.00 | 16 | 0 | |||
| Valid votes | 44,573 | 96.83 | |||||
| Invalid/blank votes | 1,458 | 3.17 | |||||
| Total votes | 46,031 | 100.00 | |||||
| Registered voters/turnout | 63,522 | 72.46 | |||||
Total Electorate (1969):208861. Above registered voter count only refers to total electorate of 5 seats. Remaining 11 seats were won uncontested
Sarawak
| Party or alliance | Votes | % | Seats | +/– | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sarawak National Party | 64,593 | 26.80 | 9 | 0 | |||
| Sarawak United Peoples' Party | 72,754 | 30.19 | 5 | 0 | |||
| Sarawak Alliance | Parti Bumiputera Sarawak | 41,835 | 17.36 | 5 | – | ||
| Sarawak Chinese Association | 10,520 | 4.37 | 2 | – | |||
| Total | 52,355 | 21.73 | 7 | New | |||
| Parti Pesaka Sarawak | 30,765 | 12.77 | 2 | 0 | |||
| Independents | 20,514 | 8.51 | 1 | 0 | |||
| Total | 240,981 | 100.00 | 24 | 0 | |||
| Valid votes | 240,981 | 90.93 | |||||
| Invalid/blank votes | 24,032 | 9.07 | |||||
| Total votes | 265,013 | 100.00 | |||||
| Registered voters/turnout | 332,737 | 79.65 | |||||
Sarawak Alliance contested under Alliance Flag
Selangor
| Party or alliance | Votes | % | Seats | +/– | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alliance Party | United Malays National Organisation | 59,634 | 18.58 | 6 | 0 | ||
| Malaysian Chinese Association | 70,245 | 21.89 | 2 | –3 | |||
| Malaysian Indian Congress | 11,252 | 3.51 | 1 | 0 | |||
| Total | 141,131 | 43.97 | 9 | –3 | |||
| Democratic Action Party | 100,716 | 31.38 | 3 | New | |||
| Parti Gerakan Rakyat Malaysia | 56,047 | 17.46 | 2 | New | |||
| Pan-Malayan Islamic Party | 23,041 | 7.18 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Total | 320,935 | 100.00 | 14 | 0 | |||
| Valid votes | 320,935 | 94.39 | |||||
| Invalid/blank votes | 19,086 | 5.61 | |||||
| Total votes | 340,021 | 100.00 | |||||
| Registered voters/turnout | 516,984 | 65.77 | |||||
Trengganu
| Party or alliance | Votes | % | Seats | +/– | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alliance Party | United Malays National Organisation | 63,918 | 49.99 | 4 | –1 | ||
| Pan-Malayan Islamic Party | 63,943 | 50.01 | 2 | +1 | |||
| Total | 127,861 | 100.00 | 6 | 0 | |||
| Valid votes | 127,861 | 94.98 | |||||
| Invalid/blank votes | 6,759 | 5.02 | |||||
| Total votes | 134,620 | 100.00 | |||||
| Registered voters/turnout | 179,365 | 75.05 | |||||
State Assemblies
Aftermath
Gerakan and the Democratic Action Party (DAP) held a victory rally in Kuala Lumpur on 12 May. The gathering became increasingly disorderly when party members, who were largely Chinese, and Malay bystanders began exchanging racial epithets.[8] In response and with tensions already running high, the United Malays National Organisation (UMNO) organised its own rally on 13 May, which escalated into full-scale rioting. The violence that ensued became known as the 13 May Incident, leading to hundreds of deaths.[8]
References
- ^ Dieter Nohlen, Florian Grotz & Christof Hartmann (2001) Elections in Asia: A data handbook, Volume II, p152 ISBN 0-19-924959-8
- ^ a b Report on the parliamentary (Dewan Rakyat) and state legislative assembly general elections 1969 of the states of Malaya, Sabah, and Sarawak Archived 4 September 2012 at the Wayback Machine Election Commission of Malaysia
- ^ a b "May 13: Why Malaysiakini revisited an old, but persistent, wound". 16 May 2019.
- ^ "Kuala Lumpur History Facts and Timeline: Kuala Lumpur, Federal Territory, Malaysia".
- ^ "HISTORICAL-ELECTION-RESULTS/1969-ELECTION-RESULTS/MALAYSIA_1969_PARLIAMENT_RESULTS.csv at main · TindakMalaysia/HISTORICAL-ELECTION-RESULTS". GitHub. Retrieved 17 April 2025.
- ^ "PARLIAMENTARY RESULTS". The Straits Times. 11 May 1969. p. 4. Retrieved 5 March 2025.
- ^ "HISTORICAL-ELECTION-RESULTS/1969-ELECTION-RESULTS/MALAYSIA_1969_PARLIAMENT_RESULTS.csv at main · TindakMalaysia/HISTORICAL-ELECTION-RESULTS". GitHub. Retrieved 24 March 2025.
- ^ a b Zainon Ahmad (26 July 2007). "The tragedy of May 13, 1969 (part 2)". The Sun. Archived from the original on 13 June 2010. Retrieved 24 June 2010.
Further reading
- Drummond, Stuart; Hawkins, David (1 April 1970). "The Malaysian Elections of 1969: An Analysis of the Campaign and the Results". Asian Survey. 10 (4): 320–335. doi:10.2307/2642443. Retrieved 13 August 2025.
- Rudner, Martin (January 1970). "The Malaysian General Election of 1969: A Political Analysis". Modern Asian Studies. 4 (1): 1–21. doi:10.1017/S0026749X00010957. Retrieved 13 August 2025.
.jpg)

.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)