Lambda Scorpii
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Scorpius |
| Pronunciation | /ˈʃɔːlə/[1][2] |
| Right ascension | 17h 33m 36.520s[3] |
| Declination | −37° 06′ 13.76″[3] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 1.63[4] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | B1.5IV + B2IV[5][6] |
| U−B color index | −0.880[7] |
| B−V color index | −0.240[7] |
| Variable type | Beta Cephei (Aa1)[8] + Algol (Aa1/2) [9] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −3.00[10] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −8.90[3] mas/yr[3] Dec.: −29.95 mas/yr[3] |
| Parallax (π) | 5.71±0.90 mas[3] |
| Distance | approx. 570 ly (approx. 180 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −3.70[11] |
| Orbit[12] | |
| Primary | Aa |
| Companion | Ab |
| Period (P) | 2.8825 yr |
| Semi-major axis (a) | 49.3 mas |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0.121 |
| Inclination (i) | 77.2° |
| Orbit[12] | |
| Primary | Aa1 |
| Companion | Aa2 |
| Period (P) | 5.9520 d |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0.26 |
| Semi-amplitude (K1) (primary) | 39.3 km/s |
| Details | |
| λ Sco Aa1 (A) | |
| Mass | 10.4[5] M☉ |
| Radius | 8.8±1.2[8] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 36,300[8] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 3.8[6] cgs |
| Temperature | 25,000±1,000[8] K |
| Rotation | 3.4±0.5[8] days |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 150[8] km/s |
| λ Sco Aa2 (a) | |
| Mass | 2.0±0.2[8] M☉ |
| Radius | 1.5±0.2[8] R☉ |
| λ Sco Ab (B) | |
| Mass | 8.1[5] M☉ |
| Radius | 4.7±1.0[8] R☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 4.0[6] cgs |
| Temperature | 25,000±1,000[8] K |
| Other designations | |
| Shaula, 35 Scorpii, 35 Sco, CD−37 11673, FK5 652, HD 158926, HIP 85927, HR 6527, SAO 208954, CCDM J17336-3706A | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
Lambda Scorpii is a triple star system and the second-brightest object in the constellation of Scorpius. It is formally named Shaula; Lambda Scorpii is its Bayer designation, which is Latinised from λ Scorpii and abbreviated Lambda Sco or λ Sco. With an apparent visual magnitude of 1.63, it is one of the brightest stars in the night sky.
Nomenclature
λ Scorpii (Latinised to Lambda Scorpii) is the star system's Bayer designation.
It bore the traditional name Shaula, which comes from the Arabic الشولاء al-šawlā´ meaning 'the raised [tail]', as it is found in the tail of Scorpius, the scorpion. In 2016, the International Astronomical Union organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN)[13] to catalog and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN's first bulletin of July 2016[14] included a table of the first two batches of names approved by the WGSN, which included Shaula for the star λ Scorpii Aa1.
In Chinese, 尾宿 (Wěi Xiù), meaning Tail, refers to an asterism consisting of λ Scorpii, ε Scorpii, ζ1 Scorpii, ζ2 Scorpii, η Scorpii, θ Scorpii, ι1 Scorpii, ι2 Scorpii, κ Scorpii, μ1 Scorpii, and υ Scorpii.[15] Consequently, the Chinese name for λ Scorpii itself is 尾宿八 (Wěi Xiù bā), "the Eighth Star of Tail".[16]
Together with υ Scorpii (Lesath), Shaula is listed in the Babylonian compendium MUL.APIN as dSharur4 u dShargaz, meaning "Sharur and Shargaz".[17]
In Coptic, it was called Minamref.[18]
The indigenous Boorong people of northwestern Victoria (Australia) named it (together with Upsilon Scorpii) Karik Karik,[19] "the Falcons".[20]
Properties
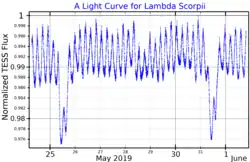
Lambda Scorpii is located approximately 570 light-years away from the Sun.
Spectroscopic and interferometric observations have shown that it is actually a triple star system consisting of two B-type stars and a pre-main-sequence star.[8] The primary star is a Beta Cephei variable star with rapid brightness changes of about a hundredth of a magnitude.[6][5] The pre-main-sequence star has an orbital period of 6 days and the B-type companion has a period of 1,053 days. The three stars lie in the same orbital plane, strongly suggesting that they were formed at the same time. The masses of the primary, pre-main-sequence star and the B-type companion are 14.5, 2.0 and 10.6 solar masses, respectively. The age of the system is estimated to be in the range 10–13 million years.
A 15th-magnitude star has a separation of 42 arcseconds, whereas a 12th-magnitude star is 95 arcseconds away. It is not known whether or not these components are physically associated with Lambda Scorpii. If they both were, the first would have a projected linear separation of approximately 7,500 astronomical units (AU) and the second approximately 17,000 AU (0.27 light-years) away. Gaia Data Release 3 reports that the fainter of these two stars is a little larger and brighter than the sun and about 420 light years away,[22] while the brighter star is a background object.[23]
In culture
Shaula appears on the flag of Brazil, symbolizing the state of Rio Grande do Norte.
USS Shaula (AK-118) was a U.S. Navy Crater-class cargo ship named after the star.
References
- ^ Kunitzsch, Paul; Smart, Tim (2006). A Dictionary of Modern star Names: A Short Guide to 254 Star Names and Their Derivations (2nd rev. ed.). Cambridge, Massachusetts: Sky Pub. ISBN 978-1-931559-44-7.
- ^ "IAU Catalog of Star Names". Retrieved 28 July 2016.
- ^ a b c d e Van Leeuwen, F. (2007). "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 474 (2): 653–664. arXiv:0708.1752. Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357. S2CID 18759600.
- ^ Høg, E.; Fabricius, C.; Makarov, V. V.; Urban, S.; Corbin, T.; Wycoff, G.; Bastian, U.; Schwekendiek, P.; Wicenec, A. (2000). "The Tycho-2 catalogue of the 2.5 million brightest stars". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 355. Bibcode:2000A&A...355L..27H.
- ^ a b c d Tango, W. J.; Davis, J.; Ireland, M. J.; Aerts, C.; Uytterhoeven, K.; Jacob, A. P.; Mendez, A.; North, J. R.; Seneta, E. B.; Tuthill, P. G. (2006). "Orbital elements, masses and distance of λ Scorpii a and B determined with the Sydney University Stellar Interferometer and high-resolution spectroscopy". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 370 (2): 884–890. arXiv:astro-ph/0605311. Bibcode:2006MNRAS.370..884T. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2006.10526.x. S2CID 13971499.
- ^ a b c d Uytterhoeven, K.; Willems, B.; Lefever, K.; Aerts, C.; Telting, J. H.; Kolb, U. (2004). "Interpretation of the variability of the β Cephei star λ Scorpii". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 427 (2): 581–592. Bibcode:2004A&A...427..581U. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20041223. hdl:2066/60554.
- ^ a b Hamdy, M. A.; Abo Elazm, M. S.; Saad, S. M. (1993). "A catalogue of spectral classification and photometric data of B-type stars". Astrophysics and Space Science. 203 (1): 53–107. Bibcode:1993Ap&SS.203...53H. doi:10.1007/BF00659414. S2CID 122459090.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Handler, G.; Schwarzenberg-Czerny, A. (2013). "Time-resolved multicolour photometry of bright B-type variable stars in Scorpius". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 557: A1. arXiv:1307.2733. Bibcode:2013A&A...557A...1H. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201321886. S2CID 56403146.
- ^ "Lambda Sco". International Variable Star Index. AAVSO.
{{cite web}}: Text "access-date-2025-08-20" ignored (help) - ^ Gontcharov, G. A. (2006). "Pulkovo Compilation of Radial Velocities for 35 495 Hipparcos stars in a common system". Astronomy Letters. 32 (11): 759–771. arXiv:1606.08053. Bibcode:2006AstL...32..759G. doi:10.1134/S1063773706110065. S2CID 119231169.
- ^ Balona, L. A.; Feast, M. W. (1975). "The luminosities of the beta Canis Majoris variables, the zero age main sequence and the distance of the Sco-Cen association". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 172 (1): 191–203. Bibcode:1975MNRAS.172..191B. doi:10.1093/mnras/172.1.191.
- ^ a b Tokovinin, Andrei (2018-03-01). "The Updated Multiple Star Catalog". The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series. 235 (1): 6. arXiv:1712.04750. Bibcode:2018ApJS..235....6T. doi:10.3847/1538-4365/aaa1a5. ISSN 0067-0049. S2CID 119047709.
- ^ "IAU Working Group on Star Names (WGSN)". Archived from the original on 15 July 2018. Retrieved 22 May 2016.
- ^ "Bulletin of the IAU Working Group on Star Names, No. 1" (PDF). Retrieved 28 July 2016.
- ^ (in Chinese) 中國星座神話, written by 陳久金. Published by 台灣書房出版有限公司, 2005, ISBN 978-986-7332-25-7.
- ^ (in Chinese) 香港太空館 - 研究資源 - 亮星中英對照表 Archived 2008-10-25 at the Wayback Machine, Hong Kong Space Museum. Accessed on line November 23, 2010.
- ^ Rogers, J. H. (February 1998). "Origins of the ancient constellations: I. The Mesopotamian traditions". Journal of the British Astronomical Association. 108 (1): 9–28. Bibcode:1998JBAA..108....9R.
- ^ Robert Burnham (1978). Burnham's Celestial Handbook: An Observer's Guide to the Universe Beyond the Solar System. New York: Courier Corporation. p. 1678. ISBN 978-0-486-23673-5.
- ^ Hamacher, Duane W.; Frew, David J. (2010). "An Aboriginal Australian Record of the Great Eruption of Eta Carinae". Journal of Astronomical History and Heritage. 13 (3): 220–34. arXiv:1010.4610. Bibcode:2010JAHH...13..220H. doi:10.3724/SP.J.1440-2807.2010.03.06. S2CID 118454721.
- ^ Stanbridge, William Edward (1857). "On the astronomy and mythology of the Aborigines of Victoria". Proceedings of the Philosophical Institute of Victoria. 2: 137. Bibcode:1857PPIVT...2..137S.
- ^ "MAST: Barbara A. Mikulski Archive for Space Telescopes". Space Telescope Science Institute. Retrieved 8 December 2021.
- ^ Vallenari, A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (2023). "Gaia Data Release 3. Summary of the content and survey properties". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 674: A1. arXiv:2208.00211. Bibcode:2023A&A...674A...1G. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202243940. S2CID 244398875. Gaia DR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ^ Vallenari, A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (2023). "Gaia Data Release 3. Summary of the content and survey properties". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 674: A1. arXiv:2208.00211. Bibcode:2023A&A...674A...1G. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202243940. S2CID 244398875. Gaia DR3 record for this source at VizieR.
