Kz 8 cm GrW 42
| kurzer 8 cm Granatwerfer 42 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | Mortar |
| Place of origin | Nazi Germany |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1943 – 1945 |
| Used by | |
| Wars | World War II |
| Production history | |
| Designed | 1940 – 1941 |
| Manufacturer | Rheinmetall |
| Developed from | 8 cm Gr.W. 34 |
| Produced | 1941 – 1945 |
| No. built | 1,591[1] |
| Specifications | |
| Mass |
|
| Barrel length | 747 mm (29.4 in) |
| Crew | 5 |
| Shell | HE / Smoke |
| Shell weight | 3.5 kg (7 lb 11 oz) |
| Caliber | 81.4 mm (3.20 in) |
| Elevation | +40° / +90° |
| Traverse | 14° / 34° |
| Rate of fire | 15−25 rounds/min |
| Maximum firing range | 1.1 km (0.68 mi) |
| References | [2] |
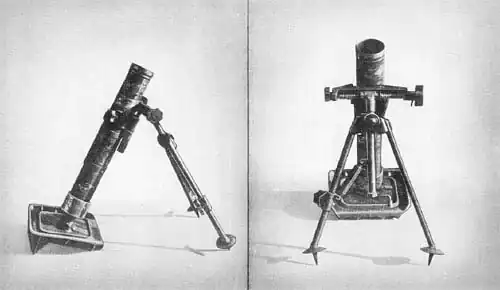
The kurzer 8 cm Granatwerfer 42 (kz 8 cm GrW 42) was a mortar used by Germany during World War II. Nicknamed the "Stummelwerfer" (Stump-Thrower),[3] it was developed as a lightened version of the standard German 8 cm GrW 34 medium mortar with a shorter barrel for use by paratroopers, but replaced the ineffective 5 cm leGrW 36 as that weapon's shortcomings became apparent.
History and use
At the start of World War II, the 5 cm Granatwerfer 36 was the standard light mortar of the German Army. Its performance was considered lackluster, specially given the overly complicated design, which included a telescopic sight (eventually dropped) and levelling and elevation controls. After 1942, the GrW 36 was gradually withdrawn from frontline service with the Army and Waffen SS in favor of the GrW 42, which was originally intended for use by Fallschirmjäger and special forces.[2][4]
Design
The GrW 42 was a shorter and lighter version of the 8 cm Granatwerfer 34, which fired 8 cm (3.1 in) ammunition and was based on the Stokes mortar with a few modifications.[5] While the short barrel inevitably decreased range, the heavier bomb provided extra firepower in comparison to the 5 cm (2.0 in) mortar. It could be broken down in three loads. The GrW 42 was normally drop fired, but a lanyard-operated mechanism could be fitted over the muzzle, allowing crews to take cover or fire the weapon from ambush positions. Minimum fire range was 50 m (160 ft) while the maximum range was 1,100 m (1,200 yd),[6] about half of the 8 cm GrW 34.[7]
According to military historian Ian V. Hogg, the GrW 42 was about the smallest size that a medium mortar could be reduced while still being able to fire a standard-sized bomb.[7] According to Rottman, the mortar nominal caliber was 8 cm, it actually fired 81 mm (3.2 in) bombs and could fire US ammunition.[3]
References
Ciations
- ^ "Lexikon der Wehrmacht - Granatwerfer der Wehrmacht". www.lexikon-der-wehrmacht.de.
- ^ a b Merriam 1999, p. 6.
- ^ a b Rottman 2011, p. 266.
- ^ Chamberlain & Gander 1975, pp. 6, 8.
- ^ Hogg 1977, p. 111.
- ^ Chamberlain & Gander 1975, p. 8.
- ^ a b Hogg 1983, p. 534.
Main sources
- Chamberlain, Peter; Gander, Terry (1975). Mortars and Rockets. New York, NY: Arco Pub. Co. ISBN 978-0-668-03817-1.
- Hogg, Ian V. (1977). The Encyclopedia of Infantry Weapons of World War II. New York, NY: Crowell. ISBN 978-0-690-01447-1.
- Hogg, Ian V, ed. (1983). Jane’s Infantry Weapons 1983−84 (9th ed.). London: Jane’s Publishing Company Limited. ISBN 978-0-7106-0775-1.
- Merriam, Ray, ed. (1999). Gebirgsjaeger: Germany's Mountain Troops. Merriam Press. ISBN 978-1-57638-163-2.
- Rottman, Gordon L. (2011). FUBAR F***ed Up Beyond All Recognition: Soldier Slang of World War II. Bloomsbury Publishing. ISBN 978-1-84908-653-0.
Secondary sources
- "Granatwerfer 42 (kurz)". quartermastersection.com. Retrieved August 1, 2025.