INT-777
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
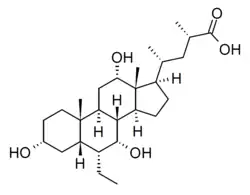
| Formula | C27H46O5 |
| Molar mass | 450.660 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
INT-777 is an experimental drug which acts as a potent and selective agonist for the G protein-coupled bile acid receptor (GPBAR1/TGR5). It has antiinflammatory effects and has been researched for various conditions including diabetes and pulmonary arterial hypertension.[1][2][3][4]
References
- ^ Holst JJ, McGill MA (2012). "Potential New Approaches to Modifying Intestinal GLP-1 Secretion in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus". Clinical Drug Investigation. 32 (1): 1–14. doi:10.2165/11595370-000000000-00000. PMID 27933595.
- ^ Comeglio P, Morelli A, Adorini L, Maggi M, Vignozzi L (November 2017). "Beneficial effects of bile acid receptor agonists in pulmonary disease models". Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs. 26 (11): 1215–1228. doi:10.1080/13543784.2017.1385760. PMID 28949776.
- ^ Qi Y, Duan G, Wei D, Zhao C, Ma Y (August 2022). "The Bile Acid Membrane Receptor TGR5 in Cancer: Friend or Foe?". Molecules. 27 (16). Basel, Switzerland: 5292. doi:10.3390/molecules27165292. PMC 9416356. PMID 36014536.
- ^ Romero-Ramírez L, Mey J (August 2024). "Emerging Roles of Bile Acids and TGR5 in the Central Nervous System: Molecular Functions and Therapeutic Implications". International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 25 (17): 9279. doi:10.3390/ijms25179279. PMC 11395147. PMID 39273226.