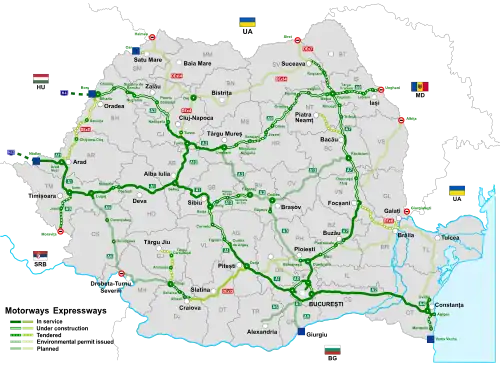
Highways in Romania
.svg.png)
Controlled-access highways in Romania are dual carriageways, grade separated with controlled-access, designed for high speeds. There are two types of highways, motorways (Romanian: Autostrăzi, sing. Autostradă) and expressways (Romanian: Drumuri expres, sing. Drum expres), with the main difference being that motorways have emergency lanes and slightly wider lanes. The maximum allowed speed limit for motorways is 130 km/h (81 mph), while for expressways the limit is 120 km/h (75 mph). There are no toll roads, but a road vignette is required.
The first construction works began in 1967, and the first highway segment was opened in 1972. However, extension of the high-speed road network lagged behind until after EU accession in 2007, when improved utilization of the allocated EU funds enabled Romania to speed up the expansion of its highway network.
Only A2, A10 and DEx12 are completed, while A1 is mostly completed with all its remaining sections currently being built. A3 has five segments that are currently in use, with most of the remaining ones being in various stages of construction or tendering. A4, A6, A11 and DEx4 currently have only small segments in use. DEx12 was the first expressway to be opened in 2022. Construction contracts for part of A0, A7, A8, A9, A13, DEx6, DEx11 and DEx14 are in various stages of execution or tendering.
As of 31 July 2025, there are 1,325.735 km of highways in service (of which 1,187.982 km motorways and 137.753 km expressways),[1] with another 741.247 km with signed contracts in various stages of execution, and another 669.3 km being tendered (29 May 2025).[2][3]
Legislation


In 2012, legislation amendments defined two types of highways: motorways (Romanian: Autostrăzi) and expressways (Romanian: Drumuri expres). Motorways are identified by A followed by a number while expressways are identified by DEx followed by a number.
There are almost no tolls for using roads in Romania, with exception of large bridges. There is one at the Giurgeni – Vadu Oii Bridge over the river Danube on highway DN2A at Vadu Oii and one at the Cernavodă Bridge, on the A2 motorway. Nevertheless, every owner of a car that uses a motorway (A), an expressway (DEx) or a national road (DN) in Romania must purchase a vignette (rovinietă) from any of the main petrol stations or at any post office throughout the country.[4]
The main differences are that motorways have wide emergency lanes (3 m) and slightly wider traffic lanes (by 3.75 versus 3.5 m).[5] Expressways only have a narrow 1.5 m gravel roadside on the right side, added to the 0.5 m asphalted road edges, and may not have acceleration and deceleration lanes in mountainous areas.[6] The maximum allowed speed limit is 130 km/h (81 mph) (80 km/h (50 mph) during poor conditions), while expressways have a maximum speed limit of 120 km/h (75 mph).[7][8] Generally, feasibility studies for motorways have a minimum projected speed of 100 km/h, while for expressways, it is reduced to 80 km/h.[9]
History
| Year | Opened (km) |
Total (km) |
|---|---|---|
| 1972 | 95.5 | 95.5 |
| 1987 | 17.5 | 113.1 |
| 2004 | 97.3 | 210.4 |
| 2007 | 50.2 | 260.6 |
| 2009 | 41.5 | 302 |
| 2010 | 27.8 | 329.8 |
| 2011 | 55.3 | 385.1 |
| 2012 | 139.5 | 524.6 |
| 2013 | 107.7 | 632.3 |
| 2014 | 50.9 | 683.1 |
| 2015 | 46 | 729.1 |
| 2017 | 15.4 | 744.6 |
| 2018 | 59.5 | 804.1 |
| 2019 | 43.3 | 847.4 |
| 2020 | 61.3 | 908.7 |
| 2021 | 30.3 | 938.9 |
| 2022 | 53 | 991.9 |
| 2023 | 80.5 | 1,072.5 |
| 2024 | 199.4 | 1,271.8 |
| 2025 | 53.9 | 1,325.7 |
First projects

The construction of the first motorway in Romania began in 1967, and the first segment of the A1 motorway, from Pitești to the capital Bucharest was opened in 1972 with a total length of 96 km. During the building of this motorway, a general plan was released in 1969, detailing the building of motorways in the incoming years, however, due to low volumes of traffic, the communist regime focused on improving current roads instead. Until the collapse of the communist regime in 1989, the building of a second motorway between Bucharest and Constanța had been planned, but only an 18 km long segment of A2 from Fetești to Cernavodă opened in 1987.
In the 1990s, the transition from a centralized economy to a market economy severely limited investment into infrastructure projects, and the entire motorway network totaled 113 km for many years until the construction project of A2 was resumed in 1998. Actual construction began in 2001, and three segments were finally opened in 2004 (Bucharest – Fundulea – Lehliu – Drajna) and another in 2007 (Drajna – Fetești) totaling around 130 km. The A1 motorway was extended also in 2007 with the Pitești bypass. A large sector of A3, termed "Transylvania Motorway", was awarded controversially in 2004 without bidding to the American Bechtel Corporation. Large cost overruns and delays ensued for this project, and after political controversies, most of the contracts were cancelled, and only some 50 km of the Cluj bypass (Gilău – Turda – Câmpia Turzii) were opened between 2009 and 2010, at much larger costs than initially signed in the contract.
Accessing EU funds
After joining the European Union in 2007, Romania was able to access funds for infrastructure development more easily, especially for those part of the Pan-European Corridor IV overlapping with A1 and A2 motorways. Many segments of the A1 motorway were started, and by the end of 2011 around 85 km were partially or fully opened: A1 segments Timișoara – Arad and Sibiu bypass; A2 segment Murfatlar – Constanța; A4 Constanța bypass and A11 Arad bypass.[10] In 2012 more segments were opened on A1 (Deva – Simeria), A2 (Cernavodă – Murfatlar), A4, and the first A3 segment not built by Bechtel (Bucharest – Ploiești). More segments were opened over the next few years: on A1 (part of Lugoj – Deva, Sibiu – Orăștie – Simeria, Arad – Nădlac, Timișoara – Lugoj), A6 (Balinț – Lugoj), and A4. A total of 726.6 km of motorways were in use in Romania in December 2015.
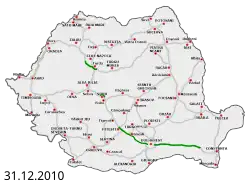
Political debates and changes in priorities of left-leaning parties after 2014 greatly slowed down motorway projects.[11] With no new openings in 2016, a small segment part of Lugoj – Deva opening in 2017,[12] almost half of the A10 (Aiud – Turda), and part of A3 (Ungheni – Iernut, Gilău – Nădășelu, and the entrance into Bucharest[13]) brought the total to over 800 km at the end of 2018. Two more segments of the A1 opened in 2019 (between Coșevița and Deva), providing an almost fully opened motorway (excluding a segment of 13.5 km) between the border with Hungary and Sibiu.[14][15] In 2020, more segments were opened, on A3 (Biharia − Borș, Iernut − Chețani, Râșnov − Cristian),[16][17][18] on A10 (Sebeș – Alba Iulia), and the first segment of A7 (Bacău bypass)[19] bringing the total to over 900 km of highways.[20] In 2021, A10 completely opened (Alba Iulia – Aiud) and a segment of A3 (Târgu Mureș – Ungheni) opened to traffic.[21][22] In 2022 the first segment of an expressway-class road in Romania open for traffic, the DEx12 expressway: between Balș and Slatina (16.0 km),[23] and Slatina bypass.[24]
Current projects
.jpg)
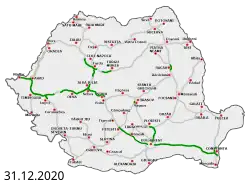
As of December 2023, over 750 km of controlled-access roads have contracted for construction. These contracts include: part of the A3 (some 68.6 km), all segments of the A1 between Sibiu – Pitești (122.9 km), almost all of the Bucharest Ring Motorway (91.4 km), a section of the A8 (29.9 km), as well as most segments of the A7 (319 km).
Currently the only completed motorways are A2 and A10. The unfinished segments of A1 and A3 are in various stages of tendering and construction, with multiple segments likely to finish by 2024-2028.[25]
A few more motorways have received active discussion, including the termed A0 Bucharest Motorway Ring Road as an outer ring to the Bucharest Ring Road, with construction contracts signed or tendered for all of its 100 km length. The A7 motorway, between Ploiești and the border with Ukraine, has been planned to be part of the Pan-European Corridor IX, but so far only the Bacău bypass has been built. However, PNRR funding is ensured for most of its segments, with tendering contracts existing for its first 320 km till Pașcani. Beyond Pașcani, the Corridor IX is envisioned to be covered by the A8 (the East–West Motorway, a link between Moldavia and Transylvania), with the first construction contract signed in 2023. Highways crossing the Carpathian Mountains have been delayed due to large costs, with debates on whether to build the A3 (through long-term concession contracts) or the A1 (EU funds would cover most of the cost). The A13 motorway is planned to serve as an alternative to link the A1 and the A3, then to the A7, with the first 68 km currently being under construction.
A9 is planned to link A1 to Serbia, with plans to sign the first construction contracts not earlier than 2023. Expressways extending the current A11 as well as the DEx6 linking Galați and Brăila are currently being constructed. Plans to extend the current network with expressways exist for A4, A5 (planned to link to Bulgaria), A6, and A14 corridors, as well as several other smaller ones.[25][26]
Future timeline
Contracted segments with estimated openings:[27][28][29][30]
- 2025
 Ploiești (Dumbrava) - Buzău, sections 2 and 3 between Mizil (Baba Ana) - Spătaru (DN2) (31.0 km) (Q3)
Ploiești (Dumbrava) - Buzău, sections 2 and 3 between Mizil (Baba Ana) - Spătaru (DN2) (31.0 km) (Q3) Bucharest North Ring, section 3 Afumați overpass (DN2) (1.8 km) (Q3)
Bucharest North Ring, section 3 Afumați overpass (DN2) (1.8 km) (Q3) Bucharest South Ring, section 3 between Ciorogârla (A1) - Bâcu (DJ601A) (2.5 km) (Q3)
Bucharest South Ring, section 3 between Ciorogârla (A1) - Bâcu (DJ601A) (2.5 km) (Q3) Topa Mică - Suplacu de Barcău (3B), section 3B2 between Sutoru - Poarta Sălajului (12.24 km) (Q3)
Topa Mică - Suplacu de Barcău (3B), section 3B2 between Sutoru - Poarta Sălajului (12.24 km) (Q3) Brăila - Galați (10.77 km) (Q4)
Brăila - Galați (10.77 km) (Q4) Focșani (Petrești) - Bacău, sections 1 and 2 between Focșani (Petrești) - Domnești Târg (35.6 km) and Domnești Târg - Răcăciuni (38.78 km) (Q4)
Focșani (Petrești) - Bacău, sections 1 and 2 between Focșani (Petrești) - Domnești Târg (35.6 km) and Domnești Târg - Răcăciuni (38.78 km) (Q4) Bucharest North Ring, section 4 between Pantelimon (DN3) - Căldăraru (A2) (4.47 km) (Q4)
Bucharest North Ring, section 4 between Pantelimon (DN3) - Căldăraru (A2) (4.47 km) (Q4) Ploiești (Dumbrava) - Buzău, section 3 between Spătaru (DN2) - Buzău (DN2B) (10.9 km) (Q4)
Ploiești (Dumbrava) - Buzău, section 3 between Spătaru (DN2) - Buzău (DN2B) (10.9 km) (Q4)
Total: 148.06 km
- 2026
 Bucharest North Ring, section 3 between Afumați (DN2) - Pantelimon (DN3) (6.6 km)
Bucharest North Ring, section 3 between Afumați (DN2) - Pantelimon (DN3) (6.6 km) Bucharest North Ring, section 1 between Bâcu (DJ601A) - Corbeanca (Cherry Park) (17.5 km) [+2.4 km A0-North 2]
Bucharest North Ring, section 1 between Bâcu (DJ601A) - Corbeanca (Cherry Park) (17.5 km) [+2.4 km A0-North 2] Deva - Lugoj, section 2E between Holdea - Margina (9.13 km)
Deva - Lugoj, section 2E between Holdea - Margina (9.13 km) Pitești - Sibiu, section 4 between Curtea de Argeș - Tigveni (9.861 km)
Pitești - Sibiu, section 4 between Curtea de Argeș - Tigveni (9.861 km) Suplacu de Barcău - Borș (3C), section 3C1 between Suplacu de Barcău - Chiribiș (26.35 km)
Suplacu de Barcău - Borș (3C), section 3C1 between Suplacu de Barcău - Chiribiș (26.35 km) Gilău - Topa Mică (3A), section 3A2 between Nădășelu - Topa Mică (16.8 km); Topa Mică - Suplacu de Barcău (3B), section 3B1 between Topa Mică - Sutoru (13.26 km)
Gilău - Topa Mică (3A), section 3A2 between Nădășelu - Topa Mică (16.8 km); Topa Mică - Suplacu de Barcău (3B), section 3B1 between Topa Mică - Sutoru (13.26 km) Focșani (Petrești) - Bacău, section 3 between Răcăciuni - Bacău (21.522 km)
Focșani (Petrești) - Bacău, section 3 between Răcăciuni - Bacău (21.522 km) Bacău - Pașcani, sections 1, 2, and 3 between Bacău - Trifești (30.3 km), Trifești - Mircești (19.0 km), and Mircești - Pașcani (28.094 km)
Bacău - Pașcani, sections 1, 2, and 3 between Bacău - Trifești (30.3 km), Trifești - Mircești (19.0 km), and Mircești - Pașcani (28.094 km) Târgu Mureș - Ditrău, section 1A between Gheorge Doja (A3) - Miercurea Nirajului (DJ135) (24.39 km)
Târgu Mureș - Ditrău, section 1A between Gheorge Doja (A3) - Miercurea Nirajului (DJ135) (24.39 km) Ditrău - Târgu Neamț, section 2D between Vânători-Neamț (DN15B) - Boureni (DN2) (29.912 km)
Ditrău - Târgu Neamț, section 2D between Vânători-Neamț (DN15B) - Boureni (DN2) (29.912 km)
Total: 255.119 km
- 2027
 Pitești - Sibiu, section 3 Tigveni - Copăceni (37.4 km)
Pitești - Sibiu, section 3 Tigveni - Copăceni (37.4 km) Suplacu de Barcău - Borș (3C), section 3C2 between Chiribiș - Biharia (28.55 km)
Suplacu de Barcău - Borș (3C), section 3C2 between Chiribiș - Biharia (28.55 km) Târgu Mureș - Ditrău, section 1B between Miercurea Nirajului (DJ135) - Sărățeni (DN13A) (23.40 km)
Târgu Mureș - Ditrău, section 1B between Miercurea Nirajului (DJ135) - Sărățeni (DN13A) (23.40 km) Boița (A1) - Făgăraș, sections 3 and 4 between, Arpașu de Jos (DN1) - Sâmbăta de Sus (DJ105B) (17.61 km), and Sâmbăta de Sus (DJ105B) - Făgăraș (DC67) (16.265 km)
Boița (A1) - Făgăraș, sections 3 and 4 between, Arpașu de Jos (DN1) - Sâmbăta de Sus (DJ105B) (17.61 km), and Sâmbăta de Sus (DJ105B) - Făgăraș (DC67) (16.265 km) Arad - Oradea, section 1 between Oradea - Salonta (33.7 km)
Arad - Oradea, section 1 between Oradea - Salonta (33.7 km)
Total: 156.65 km
- 2028
 Pitești - Sibiu, section 2 between Copăceni - Boița (31.33 km)
Pitești - Sibiu, section 2 between Copăceni - Boița (31.33 km) Boița (A1) - Făgăraș, sections 1 and 2 between Boița (A1) - Mârșa (DJ105G) (14.253 km), Mârșa (DJ105G) - Arpașu de Jos (DN1) (19.922 km)
Boița (A1) - Făgăraș, sections 1 and 2 between Boița (A1) - Mârșa (DJ105G) (14.253 km), Mârșa (DJ105G) - Arpașu de Jos (DN1) (19.922 km) Pucioasa - Fieni (12.68 km)
Pucioasa - Fieni (12.68 km)
Total: 78.185 km
- 2029
 Ditrău - Târgu Neamț, section 2A between Ditrău (DN12) - Grințieș (DN15) (37.9 km)
Ditrău - Târgu Neamț, section 2A between Ditrău (DN12) - Grințieș (DN15) (37.9 km) Ditrău - Târgu Neamț, section 2C between Pipirig (DN15B) - Vânători Neamț (DN15B) (19.30 km)
Ditrău - Târgu Neamț, section 2C between Pipirig (DN15B) - Vânători Neamț (DN15B) (19.30 km)
Total: 57.2 km
- 2031
 Mihăiești - Suplacu de Barcău (3B), section 3B2 between Poarta Sălajului - Zalău (15.14 km)
Mihăiești - Suplacu de Barcău (3B), section 3B2 between Poarta Sălajului - Zalău (15.14 km) Mihăiești - Suplacu de Barcău (3B), section 3B3 between Zalău - Nușfalău (25.84 km)
Mihăiești - Suplacu de Barcău (3B), section 3B3 between Zalău - Nușfalău (25.84 km)
Total: 40.98 km
In total, some 748 km of highways and expressways are currently contracted with builder after tenders and appeals, to be built by 2031.
Motorways in Romania
| Motorway (A) |
Map | Route[1] | Total length (km) |
In service | Under construction (km) |
Tendered (km) |
Years of construction | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sign | E-roads | Name | From | Via | To | (km) | % | |||||
| Bucharest Ring Road |
|
Bucharest | Bucharest | 100.765 | 72.495 | 71,94% | 28.27 | – | 2020 - | |||
| Transcarpathian | 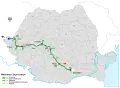
|
Bucharest |
Nădlac |
581.04 | 486.66 | 83,75% | 91.84 | – | 1967 - | |||
| Sun | 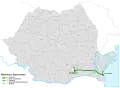
|
Bucharest |
Fetești – Cernavodă – |
Constanța | 202.75 | 202.75 | 100% | – | – | 1983 - 2012 | ||
| Transilvania | 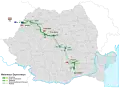
|
Bucharest |
Borș |
603 | 203.44 | 33,70% | 138.18 | – | 2004 - | |||
| Constanța Bypass |
Agigea | Ovidiu | 21.8 | 21.8 | 100% | – | – | 2009 - 2013 | ||||
| Vlasia | Bucharest |
Giurgiu |
55 (version) |
0 | under feasibility studies | / | ||||||
| Lugoj | Balinț |
Lugoj | 10.518 | 10.518 | 100% | – | – | 2011 - 2013 | ||||
| Moldova | 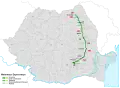
|
Dumbrava |
Buzău – Focșani – |
Suceava |
397.224 | 119.709 | 30,13% | 215.545 | 61.971 | 2022 - | ||
| Union | 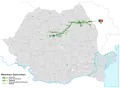
|
Târgu Mureș |
Sovata – Ditrău – Târgu Neamț – |
Podu Jijiei |
309.077 | 0 | – | 134.912 | 174.165 | 2024 - | ||
| Banat | 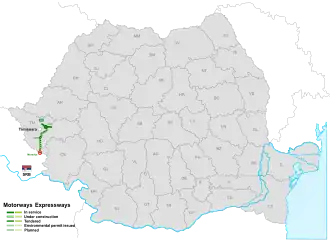
|
Izvin |
Voiteg | Moravița |
72.93 | 0 | – | – | 69.16 | / | ||
| Mihai Viteazu | Sebeș |
Alba Iulia – Aiud | Turda |
70.00 | 70.00 | 100% | – | – | 2013 - 2021 | |||
| Arad Bypass |
Arad |
Arad |
3.5 | 3.5 | 100% | – | – | 2011 - 2011 | ||||
| Alexandru Ioan Cuza | Boița |
Făgăraș – Codlea |
Răcăciuni |
280 (version) |
0 | – | 68.05 | – | 2024 - | |||
| Northern | Suceava |
Vatra Dornei – Bistrița – |
Baia Mare | 370 (version) |
0 | under feasibility studies | / | |||||
| A- | Southern | Bucharest |
Alexandria - Craiova | Calafat |
293 (version) |
0 | under feasibility studies | / | ||||
| A- | Jiu | Craiova |
Filiași | 51.503 | 0 | – | – | 51.503 | / | |||
| A- | Coast | Constanța |
23 August – Mangalia | Vama Veche |
50 (version) |
0 | – | – | 30.59 | / | ||
| Total | 3527.749 | 1,187.984 | 33,76% | 676.797 | 387.389 | |||||||
Expressways in Romania
| Expressway (DEx) |
Route | Total length (km) |
In service | Under construction (km) |
Tendered (km) |
Years of construction | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sign | E-roads | Name | From | Via | To | (km) | % | ||||
| DEx1 | Bessarabia | Mărășești |
Bârlad – Vaslui | Albița |
160 | 0 | under planning | / | |||
| Someș | Turda (Petreștii de Jos) |
Cluj-Napoca – Gherla | Dej |
75 (version) |
4.957 | 6,60% | under planning | 2023 - 2025 | |||
| Danube | Brăila | Galați | 10.77 | 0 | – | 10.77 | – | 2021 - | |||
| Bukovina | Suceava |
Siret |
55.7 | 0 | under feasibility studies | / | |||||
| Dobruja | Ovidiu |
Tulcea | 112.5 | 0 | under planning | / | |||||
| Crișana | Arad |
Chisineu-Cris – Salonta → |
Oradea |
120.47 | 0 | – | 33.7 | 86.77 | 2025 - | ||
| Oltenia | Oarja |
Slatina – Balș – |
Craiova | 121.115 | 121.115 | 100% | – | – | 2018 - 2025 | ||
| Horea, Cloșca and Crișan | Satu Mare | Oar |
10.9 | 0 | – | – | 10.9 | / | |||
| Oradea Bypass |
Biharia |
Oradea |
11.636 | 11.636 | 100% | – | – | 2022 - 2024 | |||
| Danubius | Filiași | Drobeta-Turnu Severin – Domașnea – Caransebeș | Lugoj |
224 (version) | 0 | under feasibility studies | / | ||||
| Ardeal | Târgu Secuiesc |
Bixad – Odorheiu Secuiesc – Cristuru Secuiesc – Sighișoara |
Ungheni |
203 (version) |
0 | under planning | / | ||||
| Muntenia | Buzău |
Făurei | Brăila |
111.661 | 0 | under feasibility studies | / | ||||
| Milcovia | Focșani |
Brăila | 73.524 | 0 | – | – | 73.524 | / | |||
| Severin | Caransebeș | Reșița – Bocșa | Voiteg |
104 (version) | 0 | under feasibility studies | / | ||||
| Tulcea | Jijila | Cataloi |
61.63 | 0 | under planning | / | |||||
| Vlad Țepeș | Găești |
Târgoviște | Ploiești |
76 | 0 | under feasibility studies | / | ||||
| Valahia | Bucharest Ring Road |
Târgoviște | 62.21 | 0 | under feasibility studies | / | |||||
| Bistrița | Bacău |
Piatra Neamț | 52.12 | 0 | – | – | 52.12 | / | |||
| Avram Iancu | Românași |
Jibou | 20 | 0 | under planning | / | |||||
| Jiu | Filiași | Târgu Jiu | 58.597 | 0 | – | – | 58.597 | / | |||
| Maramureș | Baia Mare |
Satu Mare (Bypass) | 55 | 0 | under planning | / | |||||
| Mihai Eminescu | Suceava |
Botoșani | 26 | 0 | under planning | / | |||||
| Dacia | Pitești |
Mioveni | 10.3 | 0 | under planning | / | |||||
| Pucioasa | Fieni | 12.68 | 0 | – | 12.68 | – | 2025 - | ||||
| Total | 1,321.134 | 137.751 | 10,42% | 57.15 | 281.911 | ||||||
Gallery
-
 A1 motorway between Bucharest and Pitești, the first Romanian motorway
A1 motorway between Bucharest and Pitești, the first Romanian motorway -
.jpg) A1 motorway at Pitești bypass
A1 motorway at Pitești bypass -
 A1 motorway at Sibiu bypass, opened in 2010.
A1 motorway at Sibiu bypass, opened in 2010. -
A1 motorway near Timișoara
-
 A2 motorway at Cernavodă, opened 1987
A2 motorway at Cernavodă, opened 1987 -
 A2 motorway near Constanța at a junction with the A4 motorway
A2 motorway near Constanța at a junction with the A4 motorway -
 A2 motorway between Bucharest and Fetești
A2 motorway between Bucharest and Fetești -
.jpg) A3 motorway between Bucharest and Ploiești
A3 motorway between Bucharest and Ploiești -

-
.jpg) A4 motorway (Constanța bypass)
A4 motorway (Constanța bypass) -
 A7 motorway at Bacău bypass
A7 motorway at Bacău bypass -
 A11 motorway (Arad bypass)
A11 motorway (Arad bypass)
See also
- Transport in Romania
- Roads in Romania
- List of controlled-access highway systems
- Evolution of motorway construction in European nations
- European routes
- List of roads and highways
References
- ^ a b c 1,319.035 Km (2025-07-31) [A0 → 6.7 Km are not yet in use] (2025-08-04). "Motorway (A) and Expressway (DEx) in use [Rețea în trafic - Autostrăzi și Drumuri Expres]" (PDF). www.cnadnr.ro (in Romanian). Ministry of Transportation - Romania (CNAIR). Retrieved 2025-08-07.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "Highways in service". www.forum.peundemerg.ro (in Romanian). Peundemerg.ro. Retrieved 21 December 2023.
- ^ "Lista proiectelor de autostrazi din Romania". www.130km.ro (in Romanian). 130km.ro. Retrieved 21 December 2023.
- ^ "Rovinietă 2012 Taxa de Drum și Tarife Rovinietă 2012". Ghidtransport.ro. Retrieved 8 October 2012.
- ^ "Ministerul Transporturilor cere creşterea limitei de viteză de la 100 km/H la 120 km/H pe Drumurile Expres, respectiv de la 130 la 140 km/H pe autostradă. Legătura între limita maximă de viteză şi finanţarea europeană/Drulă a depus un proiect de lege pentru şosele mai rapide". 17 October 2021.
- ^ "Ce este un drum expres si care este diferenta fata de o autostrada".
- ^ "Ce este un drum expres și cum se aseamănă sau se deosebește de o autostradă" (in Romanian). Hotnews.ro. 30 September 2014.
- ^ "Limita maximă de viteză în afara localităţilor pe drumurile expres, 120 km/h - lege promulgată". monitorizari.hotnews.ro (in Romanian). Retrieved 2022-08-31.
- ^ "Vitezele de proiectare pentru diferite clase tehnice ale drumurilor publice | Normă tehnică actualizat 2023".
- ^ "Autostrada spre litoral este de 20 de ani în construcție, dar va fi finalizată abia în 2011".
- ^ "Cum va arăta HARTA AUTOSTRĂZILOR din România. Strategia de dezvoltare până în 2018. Proiectul Guvernului".
- ^ "Prezentarea generală a rețelei de drumuri". CNADNR. Archived from the original on 11 February 2010. Retrieved 17 February 2010.
- ^ "VIDEO. Cum arată cei trei km de autostradă "urbană", dați în folosință după cinci amânări". 15 December 2018.
- ^ "Se deschide circulația pe lotul 4 din Autostrada Lugoj-Deva: 22 de kilometri de la Ilia la Șoimuș". Tion (in Romanian). 14 August 2019.
- ^ "VIDEO Lotul 3 al Autostrăzii Lugoj – Deva a fost deschis". G4Media (in Romanian). 23 December 2019.
- ^ "Prima inaugurare de autostradă din acest an: România deschide astăzi traficul pe 5 km din Autostrada Transilvania, de la granița cu Ungaria". G4Media (in Romanian). 4 September 2020.
- ^ "18 kilometri de autostradă se deschid azi circulației. Iohannis și Orban participă la inaugurare". Digi24 (in Romanian). 18 September 2020.
- ^ "S-a tăiat panglica pentru încă un "ciot" de autostradă. Lotul de 10 km dintre Râșnov și Cristian a fost dat în trafic". 17 December 2020.
- ^ "Centura Bacăului, realizată in regim de autostradă, inaugurată de Orban și Iohannis, după ce a fost terminată cu un an înainte de termen". Ziare.com (in Romanian). Retrieved 2021-04-02.
- ^ "Autostrada Sebeș - Turda: S-a deschis circulația pe lotul 1 Update FOTO VIDEO". 3 December 2020.
- ^ VIDEO| Se CIRCULĂ pe TOATĂ autostrada A10 Sebeș-Turda: Alba Iulia, legată de Cluj, Sibiu și Deva prin drumuri de mare viteză
- ^ Un nou ciot de 4,5 km de autostradă, deschis în România. Grindeanu: Rezultate concrete, nu festivism
- ^ "VIDEO Primul tronaon de drum expres din România se deschide azi: Cum arată DEx12 de lângă Balș cu câteva ore înainte de inaugurare". www.hotnews.ro (in Romanian). Retrieved 2022-04-21.
- ^ "S-a deschis Centura Slatina, pe Drumul Expres Craiova - Pitești. Cum se circulă pe cei 21 de km de drum de mare viteză". www.digi24.ro (in Romanian). 28 July 2022. Retrieved 2022-08-03.
- ^ a b "Articol 130km.ro: Review proiecte autostrăzi în Trimestrul I 2018".
- ^ "Autostrăzi in pregătire".
- ^ "Harta proiectelor de infrastructură (Motorway/Expressway)". www.cnadnr.ro (in Romanian). CNAIR.
- ^ "Calendarul finalizării proiectelor de autostrăzi în România".
- ^ "ANEXA NR.1 OBIECTIVE DE INVESTIȚII ÎN SECTORUL RUTIER, Proiecte noi de autostrăzi și drumuri expres, Pg.146-147 (2020-2027)" (PDF). www.gov.ro (in Romanian). Guvernul României. April 2020.
- ^ "Pe hârtie totul este perfect: Lista autostrăzilor și drumurilor expres pe care România vrea să le construiască până în 2036".













