Henry Clay Work
.png)
.png)
Henry Clay Work (October 1, 1832, Middletown – June 8, 1884, Hartford) was an American songwriter and composer of the mid-19th century. He is best remembered for his musical contributions to the Union in the Civil War—songs documenting the afflictions of slavery, the hardships of army life and Northern triumphs in the conflict. His sentimental ballads, some of which promoted the growing temperance movement, have also left their mark on American music. Many of Work's compositions were performed at minstrel shows and Civil War veteran reunions. Although largely forgotten nowadays, he was one of the most successful musicians of his time, comparable to Stephen Foster and George F. Root in sales and sheer influence. In songwriting, he is renowned for his perceived dexterity in African-American dialect, seriocomedy and melody.
Born to a Connecticutian family in 1832, Work's upbringing was humble. His father, Alanson, was an abolitionist who strove to free fugitive slaves, for which he was briefly imprisoned. While a youth, Henry initiated a career in printing, one that lasted his entire life. Although lacking formal music training, his passion for song manifested itself early on as he wrote poems for newspapers. Work first published a complete musical piece in 1853, "We Are Coming, Sister Mary". Its moderate success drove him to pursue songwriting further.
His career came of age at the Civil War's outbreak; willing to contribute to the Union struggle, Work started writing patriotic tunes for Chicagoan publishing firm Root & Cady. Impressed by "Kingdom Coming" (1862), Root hired him for the war's duration, during which he drove the business to prosperity and produced some of the most memorable wartime songs, most notably, "Marching Through Georgia" (1865).
After the war, Work started venturing in balladry, his first being "The Ship That Never Returned" (1865). Upon returning from a European maritime voyage, familial and financial woes demotivated him considerably, worsened by Root & Cady's closure in 1871. He quit songwriting altogether for a few years. After agreeing to collaborate with Chauncey M. Cady in 1876, his output briefly resurged, yielding one sole major hit, "Grandfather's Clock" (1876). Nonetheless, Work could not reproduce his wartime fame and fortune. He died virtually forgotten in 1884.
Early life
Henry Clay Work, named for the statesman and former House Speaker Henry Clay,[1] was born on October 1, 1832, in Middletown, Connecticut.[2] The Work family was of Scottish origin, their surname derived from Auld Wark, a significant stronghold during the Anglo-Scottish wars. To avert religious persecution, they migrated to the north of Ireland. Soon after, in 1720, Joseph Work emigrated to the United States, settling in Ashford, Connecticut.[3]
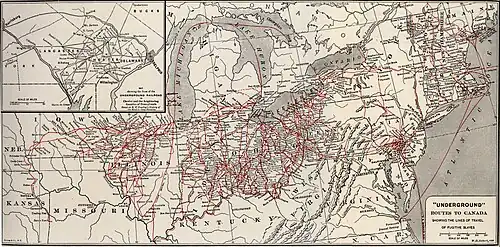
Henry Work's background was modest, "pass[ing] his boyhood days almost in want"[4] without much formal education.[5] When aged just three, his father, Alanson, resettled the family near Quincy, Illinois, to better their fortunes.[6] He was an anti-slavery advocate organizing the family home into a station of the Underground Railroad, a network for fugitive slaves to escape to freedom.[7] For aiding thousands of slaves flee from bondage,[8] Alanson was sentenced to twelve years' hard labor in Missouri in 1841. He was conditionally pardoned four years later, forced to return to Connecticut and abandon the Railroad.[9]
Having spent much time with the freed slaves, the efforts of Henry Work's father left a stirring impression on him and would come to influence his songwriting.[10] He became familiar with the African-American dialect and minstrelsy, and, above all, came to terms with slaves' routine agonies. Work grew to share his father's staunch abolitionism, manifesting itself in his later compositions, many of which were endowed with "a pronounced moralistic zeal."[11]
While in Illinois, he attended irregular Latin and Greek courses at Mission Institute.[12] These fostered an interest in philology; aged twelve, he noted his "considerable progress" in inventing two languages, "one in which English letters were used to form new words, and one that had an alphabet of its own."[13] In music, Work was largely self-taught, save for some lessons at a church singing school and exposure to camp meetings in his neighborhood.[14] He quickly grew acquainted with the principles of musical notation, devising original melodies while laboring at the family pasture.[15]
In 1845, obliged by the terms of Alanson's release from prison, the Work family migrated back to Middletown, except for Henry, who stayed a year longer.[1] Then aged fourteen, he reluctantly commenced his apprenticeship as a tailor, but his father soon allowed him to pursue a career more "congenial to his tastes" in printing, specializing in typesetting music.[16] Work never permanently strayed from this trade.[17] Typesetting granted him further insight into the English language, which would prove necessary for his future songwriting ventures.[15] In his spare time, his "everyday thought" of writing and music took effect, penning numerous poems, adapting them to melodies, and contributing them to various newspapers.[18]
Early career
Formative years
In 1853 Work composed his first song with original lyrics and melody, "We Are Coming, Sister Mary". Instead of sending it to a gazette's "poet's corner," he submitted it to Edwin P. Christy, founder of the eponymous minstrel troupe based in New York City that had initiated Stephen Foster's career.[19] Christy was "well pleased" and later performed it at his shows, received with respectable praise and some popularity.[20] He later sold it to the local publishing firm Firth, Pond & Co. for the sufficient remuneration of $25[a] he bestowed to Work.[17] This encouraged him to pursue "more ambitious efforts as a composer,"[15] publishing a comic song, "Lilly-Wily Woken", for the New York firm William Hall & Son two years later.[21]
While his career had been moderately fruitful so far, Work started doubting his songwriting capabilities. He passed the rest of the decade without publishing any music, choosing to focus exclusively on printing.[22] For this reason he migrated to Chicago in 1855, aged twenty-three, and took up a new printing job.[23] Two years later, he married the Massachusettsan Sarah Parker and bought a cottage at Hyde Park.[24][b] In March 1861, with his passion for songwriting revived, Work published a song commemorating the steamer Lady Elgin's shipwreck, "Lost on the Lady Elgin", meeting little success.[26]
Background to his Civil War career

The following month, the American Civil War broke out, laying out a new path for Work's aspirations. After the bombardment of Fort Sumter on April 12–13, President Abraham Lincoln called for 75,000 volunteers to suppress the Southern rebellion.[27] Music, which "aroused herself to meet the exigencies of the times,"[28] helped raise the Union's spirits, rallying civilians and troops, both White and Black, round their nation's cause.[29] The folk music enthusiast Irwin Silber notes, "Throughout the war, soldiers and civilians of the Union states were inspired and propagandized by a host of patriotic songs. […] a few of these songs caught the tempo and the spirit across the country carried on the lips of millions of Americans."[30] Being in such high demand, patriotic song submissions began pouring into local newspapers and music labels.[31] It is estimated that approximately two thousand were published as sheet music in 1861 alone.[32]
No firm attained as much in publishing Unionist music as Chicago's Root & Cady, "the largest of [...] the era"[33] and "most prolific producers of wartime music."[34] It was established in 1858 by Ebenezer T. Root and Chauncey M. Cady and, from 1860 onwards, principally operated by George F. Root.[35] Root was one of the most renowned composers of the Civil War era, with such tunes as "Battle Cry of Freedom" and "Tramp! Tramp! Tramp!" to his name.[36] By the war's opening weeks, his firm was receiving roughly sixty daily submissions; throughout the conflict, it published over a hundred songs.[37] In fact, it issued the very first Unionist composition, "The First Gun is Fired", in response to the attack on Fort Sumter.[38] However, the Union still lacked much antislavery vigor.[10] Having just been remotivated to write music, Work, who had witnessed the hardships of slavery firsthand, was drawn to Root & Cady, conveniently situated in his hometown of Chicago. He engaged in a successful partnership with the firm throughout the war and in subsequent years.[39]
Civil War career

Work's music "captured the spirit and struggle of the Civil War,"[40] composed with "a fiery partisanship."[41] From 1861 to 1865 he penned 27 patriotic pieces and published them for Root & Cady.[42] He is held as one of the Union's preeminent bards whose songs reflect the nation's progress and civilian struggles during the war.[43] His musical contributions to the Union are paralleled with military efforts on the battlefield itself.[44] Chief among them are "Kingdom Coming" (1861), "Grafted into the Army" (1862), "Song of a Thousand Years" (1863), "Babylon is Fallen" (1863), "Wake Nicodemus" (1864) and "Marching Through Georgia" (1865).[45] They reaped nigh unrivalled success; Work's career, as well as Root & Cady's, crested during the war.[46]
Many of Work's songs present slaves' routine undertakings on the plantation and incorporate African-American dialect, thus falling in the minstrelsy genre.[47] In Florine Thayer McCray's words, they evoke "the very atmosphere of awakening plantation life" and echo "the cottonpicker's musing hum and the roustabout's refrain."[48] However, contrary to the minstrel tradition, Work exposes the actual struggles endured by African Americans rather than stereotyping or idealizing them as most antebellum musicians had done. Having come face to face with their hardships while in the Underground Railroad, Work understood the plight of slaves.[49] He resorted to minstrelsy not for entertainment but to endorse emancipation and Black enlistment.[50]
1861
"Brave Boys Are They", a grim overview of army life, kickstarted Work's wartime career, but it was not until March that his music started leaving an impression.[51] That month, George F. Root bought out another of his Unionist compositions, "Our Captain's Last Words", amassing many sales.[52] Root met him in person a short while after as Work presented the manuscript for a new song; his autobiography recounts the encounter:
"One day early in the war a quiet and rather solemn-looking young man, poorly clad, was sent up to my room from the store with a song for me to examine. I looked at it and then at him in astonishment. It was "Kingdom Coming"—elegant in manuscript, full of bright, good sense and comical situations in its "darkey" dialect—the words fitting the melody almost as aptly and neatly as Gilbert fits Sullivan—the melody decidedly good and taking, and the whole exactly suited to the times. 'Did you write these words and music?' I asked. A gentle 'Yes' was the answer. 'What is your business, if I may inquire?' 'I am a printer.' 'Would you rather write music than set type?' 'Yes.' 'Well, if this is a specimen of what you can do, I think you may give up the printing business.'"[53]
He saw great potential in Work's "gift for composition"[54] and, in a time that "called for patriotic songs with a strong Union flavor,"[34] assigned him a songwriting post lasting until the Civil War's end.[39]
First verse and chorus
Say, darkeys, hab you seen de massa,
Wid the muffstash[c] on his face,
Go long de road some time dis mornin',
Like he gwine to leab de place?
He seen a smoke, way up de ribber,
Whar de Linkum gumboats lay;
He took his hat, an' lef' berry sudden,
An' I spec[d] he's run away!
De massa run? ha! ha!
De darkey stay? ho! ho!
It mus' be now de kingdom comin',
An' de year ob Jubilo![55]
"Kingdom Coming" and minstrelsy
"Kingdom Coming" is deemed "the first of [Work's] important songs,"[56] cementing itself as a wartime favorite of African-American troops.[57] A symbol of the war's progress, it portends the Emancipation Proclamation, the executive order effectively liberating all slaves in Confederate territory.[58] A "hypocritical and cowardly" slave owner, fearing being captured by incoming Union military forces, escapes his plantation, then taken over by his slaves who lock their overseer up as retribution for his cruelty.[59]
A staple of minstrelsy, "Kingdom Coming" reverses the antebellum tradition of denigrating the plight of slaves, instead sympathizing with them.[60] Ever since the 1830s lower-class Northern theater had been dominated by troupes of blackface performers. Dressed in extravagant costumes and armed with banjos, they acted as caricatured African Americans reminiscing about their days in the agrarian South. The romantic portrayal of Southern plantation life, with slaves and their owners residing harmoniously, gave uninformed Northern audiences a false impression of African Americans' toil in an era when slavery was growing into a dangerously divisive political issue.[61]
"Kingdom Coming" strays from the mockery of blackface minstrelsy, portraying a realistic picture of plantation life and humanizing slaves rather than presenting them as blithe, docile servants. Instead of the oppressive master reigning supreme over his subjects as generally observed in minstrel songs, these roles are inverted; the slaves take over the plantation and overcome their overseer.[60] It appealed to African-American Union troops who sang it regularly as they marched to the South.[62] The song's allure was bolstered by its employment of African-American dialect.[47]
First advertised by Edwin P. Christy in April 1862, "Kingdom Coming" quickly became a linchpin of minstrel show repertoires.[63] Root could not keep up with orders for the song, claiming it to be his firm's most profitable composition "for nearly a year and a half" and "the most successful patriotic song in the West."[64] After the Emancipation Proclamation was issued, approximately 10,000 Chicagoans gathered at Clark Street to celebrate the occasion; "Kingdom Coming", symbolizing the proclamation's outcome, was one of the abolitionist songs chanted alongside "John Brown's Body".[65] While time has not been kind with the song, up until the 19th century's close, it was reportedly as popular as "Dixie".[66]
1862
By 1862 the surge in patriotic songs witnessed the year prior had slowed down,[67] but Work's output did not decline. It includes "God Save the Nation", "Uncle Joe's Hail Columbia" and "Grafted into the Army".[68] The lattermost is described by David Ewen as "a delightful comedy tune,"[56] narrated by a widowed mother whose son was drafted into the Union army under President Lincoln's Enrollment Act.[69]
1863

In 1863 Root began issuing a periodical, the Song Messenger, with Work as its editor. They agreed that Work would be "independent and untrammeled in the expression of his views on all subjects"[70] but this promptly sparked controversy. In a June article he admonished compilers of church music books for altering traditional tunes and corrupting their sanctity, followed up by another in July denouncing one of the adapted hymns as "hardly recognizable [and] mutilated."[71] Many compilers perceived these articles as defamation and demanded an apology. While the periodical survived the dispute, Work's editing post did not; he was laid off in August.[72] Nonetheless, 1863 proved another copious year, indicated by the tunes "Sleeping for the Flag", "Song of a Thousand Years" and "Babylon is Fallen".[68]
Work published a sequel of "Kingdom Coming" in July 1863 titled "Babylon is Fallen", alluding to Revelation 14, NT: "Fallen, fallen is Babylon the great," which symbolizes the downfall of despotism.[73] Also written in vernacular, "Babylon is Fallen" aroused African Americans recruited for the Union army; their numbers had grown since the Emancipation Proclamation's passage. Also a favorite among abolitionists and soldiers, it sold more first-month copies than its prequel.[74]
1864
In 1864 Work published the patriotic songs "Wake Nicodemus", a minstrel show hit,[75] "Washington and Lincoln" and "Corporal Schnapps".[76] The last of these is a tragic yet humorous lament noted for its employment of German dialect, said to enable "the difficult fear of laughing and crying at the same time."[77]
"Come Home, Father" and temperance

Besides the Union struggle, Work devoted himself to the temperance movement, "[expressing] his passionate convictions about Prohibition" through music.[78] The movement gained much traction after the Civil War's close as many moralistic fraternities, eminently, the Women's Christian Temperance Union, called for public education on the perils of alcohol.[79]
In line with the ever-growing movement, Work composed several influential songs spotlighting the perils of alcohol consumption.[80] His most renowned is "Come Home, Father", a young girl's plea for her father, then trifling away his pay and time in a bar getting drunk, to return home while her brother is slowly dying.[81] Such was its puissance that Work received hundreds of appreciative letters from social reformers.[82]
Work wrote other temperance songs after the war, including "Lillie of the Snowstorm" (1866),[83] "King Bibler's Army" (1877), which was moderately successful,[84] and "Shadows on the Floor" (1877), an account of impoverished families' hardships,[85] although none captured the fame of "Come Home, Father".[83][76]
1865
In February Work set P. G. T. Beauregard's recent evacuation of Charleston to music; the product, "Ring the Bell, Watchman", reflected the successive toppling of Confederate cities during the war's final weeks.[86] Robert E. Lee's surrender at Appomattox Court House on April 9 marked the Civil War's end; Chicagoans paraded the streets and packed the local Court House until well into the night.[87] Work celebrated the triumph with a final wartime composition, "'Tis Finished!, or Sing Hallelujah", published in June.[88]
"Marching Through Georgia"
First verse and chorus
Bring the good old bugle boys! we'll sing another song,
Sing it with a spirit that will start the world along;
Sing it as we used to sing it fifty thousand strong,
While we were marching through Georgia.
"Hurrah! Hurrah! we bring the Jubilee!
Hurrah! Hurrah! the flag that makes you free!"
So we sang the chorus from Atlanta to the sea,
While we were marching through Georgia.[89]
Of all Work's Civil War compositions, none were as acclaimed as "Marching Through Georgia", widely regarded as "the greatest of his war songs."[90] The end of 1864 saw the March to the Sea, in which Union forces crippled Confederate resources in Georgia and took over Savannah. Work capitalized on this to write another of his topical celebratory songs, "Marching Through Georgia".[91] Published in January 1865, it was a runaway success, selling 500,000 copies in its first twelve years.[92] "Marching Through Georgia" became a staple of Civil War reunions.[93]
Later career and life
Postbellum

With the Civil War over, Work's motivation for songwriting and musical output declined considerably.[94] Turning away from patriotic songs now deemed outdated,[95] he settled into sentimental balladry.[96] His postbellum songs focus on somber themes owing to the personal tragedies engulfing his later life, as writer Dean Nelson notes in a 2008 Connecticut Explored article: "[...] in his lyrics, children die, soldiers die, ships sink, love goes unreturned, poor folks starve, and the lonely remain so."[97] Newly enriched by his war efforts, Work embarked on a tour around Europe from 1865 to 1866, during which he wrote the first of his few notable postbellum songs, "The Ship That Never Returned".[98] It narrates the departure of a ship from a harbor that never come back, with a mother and the captain's wife lamenting the loss of their loved ones on board. In 1866 Work composed another song concerning a maritime disaster, "When the 'Evening Star' Went Down", commemorating the eponymous steamer's sinking after sailing into a hurricane.[99][100]
Upon returning to the United States, Work and his brother invested most of their wealth in hundreds of acres of land in Vineland, New Jersey hoping to establishing a profitable fruit farm. Their expectations were promptly wiped out as the farm failed, bankrupting them both. This was the first of several personal tragedies to befall him.[101] "[F]orced to begin life over again," Work left Vineland and disappeared from public life.[102] In 1868 he moved to Philadelphia, living in seclusion since his wife had become insane for reasons unspecified; still, the family seemed to condemn him.[e] He was cut off from his children who were residing with Sarah in Greenwich Village, Manhattan.[104] Two years later, meanwhile having passed some time in California,[105] he resettled in Brooklyn, spending the next twelve years isolated in a boarding house.[106] A letter composed in the early 1870s to his correspondent Susie Mitchell paints a grim picture of the depression consuming his postbellum life, worsened by the loss of his son Waldo in 1871:[107]
"I think there must be a screw loose somewhere in my physical or mental organization—I am so particular about, and so much annoyed by, trifles, and lose so much time in perfecting unimportant details of plans, many of which are eventually abandoned [...] My nerves seem to be gradually gaining an ascendancy over me—the fastenings which connect the mind and body seem to be growing loose and getting detached. This is how I account for all the hallucinations previously referred to. I imagine that by-and-by my mind will be able in a clairvoyant state to leave the body temporarily—or else that I shall become insane."[108]
In the postwar years leading up to 1872, Work penned 17 songs,[f] fewer than the 27 authored during the Civil War.[42] Others include "Andy Veto" (1866), a satire of then-President Andrew Johnson's vetoing of Reconstruction legislation,[110] and "Crossing the Grand Sierras" (1870), describing a train voyage across the nation set just after the Transcontinental Railroad's completion.[111] The latter was Work's last song published for Root & Cady—personal differences between him and Root as well as the business' abrupt closure brought their once fertile collaboration to an end.[112]
Decline
Root & Cady's closure
_in_the_Great_Chicago_Fire%252C_1871.png)
In the fall of 1871, Root & Cady's firm burnt down in the Great Chicago Fire.[113] It raged on from October 8 to October 10, destroying all waterworks, banking houses and railway depots, and caused a minor depression in the national stock market.[114] All of Work's original music plates fell victim to the conflagration.[115] Root remarked in the Song Messenger: "All is gone, my musical library and the thousand useful things that I have gathered about me in so many busy years, swept in a moment."[116] Unable to continue the business in its former rendition, Root & Cady's music copyrights were all sold to Ohioan publishers S. Brainard Sons and John Church & Co. The firm filed for bankruptcy in 1872. Root continued his former teaching profession and Cady left Chicago for New York.[117] This dispirited a potential reinvigoration of Work's songwriting career; from 1872 to 1876 he published no music.[118]
Working for Cady
After Root & Cady shut down, Chauncey M. Cady also sought to reinitiate a profitable career as a music publisher. He established a business at 107 Duane Street, New York City, in 1875, lasting five years until shutting it down owing to fatigue from old age.[119] In 1876 Cady chanced to encounter Work while strolling in Broadway and, sensing a lucrative opportunity, offered him a post at his business. Eager to pick up songwriting once again, Work accepted; he published nine songs for Cady from 1876 to 1879, ending his four-year "retirement." Throughout this time, he also wrote for John Church & Co., William A. Pond & Co. and Root's firm.[120][118]
"Grandfather's Clock"
First verse and chorus
My grandfather's clock was too large for the shelf,
So it stood ninety years on the floor;
It was taller by half than the old man himself,
Though it weighed not a pennyweight more.
It was bought on the morn of the day that he was born,
And was always his treasure and pride;
But it stopped short never to go again
When the old man died.
Ninety years without slumbering (tick, tick, tick, tick)
His life seconds numbering (tick, tick, tick, tick)
It stopped short never to go again
When the old man died.[121]
Work's most profitable hit, also his last, was "Grandfather's Clock", issued by Cady in January 1876 and popularized by African-American entertainer Sam Lucas in New Haven.[122] Inspired by his sympathetic attitude toward disaffected individuals, he anthropomorphizes a clock to signify its owner; it had stood for ninety years throughout the old man's life and accompanied him.[123] The song secured over 800,000 sheet music sales.[124] It also coined the phrase "grandfather clock" to describe a longcase clock.[125] After Work sold the copyright to "Grandfather's Clock", Cady paid him a royalty of $4,000,[g] helping to lift him out of poverty.[126][h] The American music historian John T. Howard claims that "there is scarcely a school songbook" excluding "Grandfather's Clock".[41]
In 1878 Work composed a follow-up simply titled "Sequel to Grandfather's Clock", continuing the song's narrative after the grandfather's death.[129]
End
None of Work's compositions post-"Grandfather's Clock" reproduced the same success.[130] His life became mangled by boredom and depression; in an 1875 letter, he wrote: "I am no longer a printer—am now a proof-reader. Nothing to do all day, but to read and criticize, find fault or mark errors [...]"[131] Only printing, the career he held since his youth, and attendance at local church services absorbed him.[132] An unhappy marriage and family life drove him further into despair as the "last years of his life were clouded with the illness of his wife"[48] who was in a mental asylum.[133] He tried his hand at a long-distance relationship with Pennsylvanian Susie Mitchell but eventually called it off after a decade of corresponding with her.[134] Work's passion for songwriting also took another hit; following its revival in early 1876, he would only issue two compositions before another hiatus in 1879.[135] Some songs of this period are the "California Bird Song" (1878),[i] included in popular singer Emma C. Thursby's repertoire,[136] and "Mac O' Macorkity" (1877).[137]
In 1882 Work left Brooklyn for the more serene Bath in upstate New York, longing for an abode where he "could find a still nook in this still noisy world [...] engage in literary and musical work, and at the same time find repose for over-strung nerves."[138] That year, he briefly picked up composition again, penning roughly ten songs until 1883, including "The Lost Letter" and "The Prayer on the Pier", but at this point he could only "[clutch] for straws of his former fame."[139]
He died abruptly of heart disease on June 8, 1884, while visiting his mother's residence at Chestnut Street, Hartford.[140] He was survived by one of his four children, Nellie.[141] Obituaries "brushed off"[142] his legacy, often spanning a few lines and merely recognizing him as a "noted song writer and composer," citing a few famous songs and nothing more.[143] He is buried in Spring Grove Cemetery, Hartford.[144] It was not until 25 years later that a monument in his honor was erected, in the same cemetery.[145]
Personal life
Character
_-_Plymouth_Church%252C_Brooklyn%252C_NY.jpg)
One of Work's obituaries summarized his persona as an "invalid-like fellow with sadness in his voice and bearing poverty in his dress."[146] Reportedly "a man of fine appearance," he stood at about five feet ten inches, having brown hair, full whiskers and bluish-grey eyes.[147] He was "very reserved and unassuming," going as far as to refuse exposing plagiarism to his music.[148] He made few intimate friends.[115] Despite much of his life being beclouded by tragedy, Work had a sense of humor, exhibited on one occasion when someone sang "Come Home, Father" claiming he had written it; Work stood through the performance without once speaking up.[115] Practicing what his temperance songs preached, he was a committed teetotaler and Prohibitionist activist, even advocating the outlawing of tobacco.[149] Florine Thayer McCray writes: "He was of the people, in sympathy with them, and thought not of the small fame which comes from the critical sanction of a few self-instituted judges of literary and musical form."[48]
A Christian disciple and regular church-goer, while residing in Brooklyn, Work frequented services at Henry Ward Beecher's Plymouth Church; in 1871 he wrote: "One radical struck deep into the ground where Plymouth Church stands, and for months that was all that held me."[150] In fact, that year, he composed a brief oratorio dedicated to his congregation, Joy in Heaven!, or The Returning Wandering's Welcome.[151]
Family and relationship
In 1857 Work married Massachusettsan Sarah Parker.[24] He had four children with her: Waldo Franklin (1857–1871), Willie Lovejoy (1861–1862), Ellen Louisa (1863–1895) and Clara Etta (1878).[132] The Works spent a few years in Chicago and Hubbardston, Massachusetts before migrating permanently to Greenwich Village, Manhattan sometime before 1865.[152] After his wife spiraled into degeneracy, Work lived disconnected from his family.[153] They chided him, without sound grounds, for Sarah's mental instability as well as Waldo's abrupt death.[154] The only saving grace of such a tumultuous family life was his daughter Nellie, his only child to outlive him, whom he was exceedingly fond of and depended on for solace in his final years.[155] Having to endure a distressing marriage, and ruling out divorce as an option, Work hungered for a romantic relationship.[153]
In 1868, while searching for a home in Philadelphia, he came across one owned by the Mitchell family in the Ledger Residences. While greeting the family, he became enchanted by the 18-year-old Susie and soon fell in love with her.[156] Assuming she reciprocated his affection but also desperate for a gratifying relationship, Work established a correspondence with her, writing 40 lengthy letters from 1869 to 1883 which "concealed his feelings in the formal style of the day."[157] The vast majority were written in his early New York years, from 1870 to 1874.[158] While Susie invited him over several times during this period such as for Christmas, she did not share his enthusiasm.[159] In 1871 Work even dedicated a song to her, "No Letters From Home", a plea for more letters from the Mitchell family to remedy the loneliness eclipsing him.[160]
Being nearly double her age, he knew this relationship stood no chance at being fulfilled; in fact, she would get married in 1877.[161] Upon hearing of Susie's intentions to wed, Work thought it best to close off the correspondence and thereafter only wrote terse, stilted notes on occasion.[162] One of his final "long" letters, the only one in which he does not restrain his true emotions, states:[163]
"It is in the nature of things impossible that a mere transient interest or fancy springing up between persons situated as we were should go unweakened for 8 or 9 years, under adverse circumstances (absence & intermittent correspondence, to say nothing of the impossibility of consummation) without being entitled to another name. I know that you love me, and knew it (though not so well) before I went to California. But just how much I couldn't then and can't now say. [...] There is certainly a mysterious chord connecting us, and, having lasted so long, it will probably never be entirely severed. [...] Of all motives that serve as main-springs for human action, the love of a woman has ever been with me the strongest—by far the strongest. Under such influence, but rarely otherwise, I can do my best! Oh! how differently I might have been situated to-day, had such an influence, like a beacon light, shone strongly and steadily on all the years of my manhood!"[164]
Work later wrote a composition titled "Farewell, My Loved One!",[165] whose verses reflect the misery and hopelessness consuming him.[166]
Chicago

Work migrated to Chicago in 1855 to further his trade as a printer.[23] In 1859, after Paul Cornell established a new community in the city's south wing, Hyde Park, Work purchased a plot of land from him for $175.[167][j] Roughly a year later, he oversaw the construction of his residence at 5317 Dorchester Avenue, a small, humble cottage "hardly [looking] big enough to house a piano."[168] He and his wife, Sarah, devoted themselves to the Chicagoan community, being among the first organizers of the First Presbyterian Church.[169] Work even served as township clerk from 1864 to 1866.[170] In 1867 he sold the cottage and land and took up a new residence in Philadelphia, later moving to New York City.[171][153]
Pastimes
Work indulged himself in mechanical studies and experiments, and during pauses in his musical career, he was devoted "almost exclusively"[147] to them. He invented and patented a knitting machine, a walking doll and a rotary engine.[172] In 1868 he wrote a once popular seriocomic poem, The Upshot Family; its title page catalogs most of the songs he had written by then, totaling 43.[173]
Songwriting style
George F. Root said of Work's style of composition: "Mr. Work was a slow, painstaking writer, being from one to three weeks upon a song; but when the work was done it was like a piece of fine mosaic, especially in the fitting of words to music."[174] He stressed Work's perceived poetic talent and mastery of melody.[175] Another writer remarked:
"His melodies are simple and natural, but as unlike and varies as the emotions to which they give expression; but, whether grave or comic, they possess inspirational qualities that, as musical compositions, arouse the imagination and fasten themselves upon the memory of the hearer. In his songs, Mr. Work is distinguished by his use of plain Anglo-Saxon words. He discards frothy adjectives, all rant, all extravagance of language, and, like Dickens, relies upon the situation he creates. This is his source of power over the human heart."[176]
His method of composition involved devising the melody and lyrics simultaneously in his head and, after much deliberation, putting them to paper. Sometimes, he would deliberate for a short while—at other times, he would anxiously pass days on end failing to concoct a suitable idea. The finished manuscript would then be published without him once previously hearing what he had composed. In his youth, he habitually jotted down lyrics on small cards while going about his routine and then adapted them to sweet piano melodies.[177][44] Fixated on originality, Work crafted the tune for all his compositions and wrote the lyrics of all but four, actively refusing requests to put others' words to music.[178][k] He went as far as to design the title pages of his songs.[180] While a committed songwriter, he did not delight in singing, declaring: "The man who writes songs doesn't generally feel like singing them."[181]
Legacy

Work is held as one of the most celebrated American popular music songwriter of the Civil War and Reconstruction era.[182] A committed believer in moral societal causes,[183] his music brought them closer to the people. In fact, many of his songs were part and parcel of contemporary antislavery and Prohibitionist gatherings.[184] In the reformist song compilation The Musical Fountain, George F. Root declares him "the pioneer of the grand temperance awakening."[185] He is, however, best remembered for his patriotic compositions hallowing the Union in the Civil War.[43]
A Hartford monument dedicated to the composer by the then-Connecticut governor Frank B. Weeks reads, "Work rendered a service that would entitle him to be called the chief singer of the Civil War [...] whose life work did so much to keep burning brightly the flame of patriotism during the four dark years when the fate of this nation trembled in the balance."[186] An 1884 obituary encapsulates Work's legacy: "Our country has produced few song writers whose works have been more widely sung than Mr. Work. Some few of his productions have not only been on the lips of nearly every man, woman and child in America, but have been known and sung, with some variations, in every part of the world. […] His compositions were of the popular order and touched the popular heart."[187]
He was additionally one of the developers of the refined verse-chorus structure of late-19th-century popular music.[188] In 1970 Work was inducted into the Songwriters Hall of Fame.[189]
References
Notes
- ^ Roughly equating to $1,020 in 2024.
- ^ The date of Henry and Sarah's marriage is unclear. Whilst Root's concise biography of the composer gives it at 1856, Hill concludes that it "certain[ly]" took place in 1857.[25]
- ^ In Standard English, translating to "mustache."
- ^ In Standard English, translating to "expect."
- ^ In an 1871 letter to his intimate correspondent Susie Mitchell, Work writes: "Whatever the ground of complaint may be, it has in some way grown out of Sarah's derangement; for it did not exist during the nine years succeeding our marriage [from 1857 to 1866], while she was sane. There appears to be a sort of general and indefinite blame cast on me, but exactly how it was incurred, and what ought to have been done, no one has frankness enough to say."[103]
- ^ "Traveling Homeward", composed in 1872, is cataloged by Hill but Work did not recognize it. If incorporated in his list of songs, this would tally the postbellum 1865–1872 compositions up to 18.[109]
- ^ Roughly equating to $125,000 in 2024.
- ^ Cady paid Work $250 in monthly royalties for "Grandfather's Clock", amounting to $4,000 by 1879.[127] However, an 1884 issue of the Evening Capital claims that Work earned $300 a month, as opposed to $250.[128]
- ^ Also known as "Pity Me, Loo!"
- ^ Roughly equating to $6,620 in 2024.
- ^ According to Hill, the four songs with borrowed lyrics are "Little Hallie" (1861), written by J. L. Peters, "God Save the Nation" (1862), by Theodore Tilton, "Agnes by the River" (1868), by Mary J. McDermit, and "Traveling Homeward" (1872) by Cadet Otis. Additionally, the words to "Watching for Pa" (1863) and "The Picture on the Wall" (1864) were "adapted" by Work.[179]
Citations
- ^ a b Root et al. 1892, p. 6
- ^
- Root et al. 1892, p. 6
- Birdseye 1879b, p. 284
- Ewen 1962, p. 188
- Tribble 1967, p. 423
- ^
- Work, p. 6
- Birdseye 1879b, p. 284
- ^ quoted in Root et al. 1892, p. 6
- ^
- Tribble 1967, p. 423
- McWhirter 2012, p. 146
- ^
- Root et al. 1892, p. 6
- Birdseye 1879b, p. 284
- Tribble 1967, p. 423
- ^
- Birdseye 1879b, p. 284
- Ewen 1962, p. 188
- Drury 1975, p. 251
- Bailey et al. 1991, p. 197
- ^
- Ewen 1962, p. 188
- Tribble 1967, p. 423
- Bailey et al. 1991, p. 197
- Carder 2008, p. 114
- ^
- Birdseye 1879b, p. 284
- San Marcos Press 1879, p. 3
- Hill 1953a, p. 215
- ^ a b
- McWhirter 2012, p. 146
- ^
- quoted in Finson 1994, p. 56
- McCray 1898, p. 10
- Bailey et al. 1991, p. 197
- Carder 2008, p. 114
- McWhirter 2012, p. 146
- ^
- Birdseye 1879b, p. 284
- Hill 1953a, p. 215
- ^ quoted in Birdseye 1879b, pp. 284–285
- ^
- Root et al. 1892, p. 6
- Birdseye 1879b, p. 285
- Ewen 1962, p. 188
- Tribble 1967, p. 423
- ^ a b c Birdseye 1879b, p. 285
- ^
- quoted in Birdseye 1879b, p. 285
- Hill 1953a, pp. 215–216
- Ewen 1962, p. 188
- ^ a b
- Birdseye 1879b, p. 285
- Tribble 1967, p. 423
- ^
- quoted in Root et al. 1892, p. 6
- Birdseye 1879b, p. 285
- McCray 1898, p. 10
- ^
- Hill 1953a, p. 216
- Ewen 1962, p. 188
- ^
- quoted in Birdseye 1879b, p. 285
- Root et al. 1892, p. 6
- ^ Hill 1953a, pp. 213, 216
- ^
- Birdseye 1879b, p. 285
- Hill 1953a, p. 216
- ^ a b
- Root et al. 1892, p. 6
- Ewen 1962, p. 188
- Tribble 1967, p. 423
- Drury 1975, p. 251
- ^ a b
- Root et al. 1892, p. 6
- Hill 1953a, p. 218
- Drury 1975, p. 251
- ^ Hill 1953a, p. 218
- ^
- Root et al. 1892, p. 6
- Hill 1953a, pp. 213, 216
- Tribble 1967, p. 423
- ^ Carder 2008, p. 101
- ^ quoted in Saturday Evening Post 1862, p. 4
- ^
- Root et al. 1892, p. 6
- Silber 1995, p. 8
- Kelley & Snell 2004, p. 21
- McWhirter 2012, p. 15
- ^ quoted in Silber 1995, p. 7
- ^
- Tribble 1967, p. 435
- Silber 1995, pp. 7–8
- McWhirter 2012, p. 16
- ^ McWhirter 2012, p. 16
- ^
- quoted in Kelley & Snell 2004, pp. 121–122
- Epstein 1944, p. 43
- Tribble 1967, p. 425
- Carder 2008, p. 2
- ^ a b quoted in Tribble 1967, p. 425
- ^
- Root 1891, pp. 122–123
- Birdseye 1879a, p. 147
- Epstein 1944, pp. 45–46
- Howard & Bellows 1967, p. 134
- Kelley & Snell 2004, p. 5
- ^
- Birdseye 1879a, p. 148
- Epstein 1944, p. 43
- Howard & Bellows 1967, p. 134
- Carder 2008, pp. 1–2, 149
- McWhirter 2012, p. 17
- ^ McWhirter 2012, pp. 15, 17
- ^
- Root 1891, p. 132
- Silber 1995, p. 7
- Carder 2008, p. 102
- McWhirter 2012, p. 17
- ^ a b
- Hill 1953a, p. 216
- Tribble 1967, p. 425
- Carder 2008, pp. 112, 114
- ^ quoted in Song of America (b)
- ^ a b quoted in Howard & Bellows 1967, p. 135
- ^ a b
- Hill 1953a, pp. 213–214
- Kelley & Snell 2004, pp. 121–122
- ^ a b
- McCray 1898, p. 10
- Hill 1953a, p. 211
- Tribble 1967, p. 425
- Kelley & Snell 2004, p. 119
- McWhirter 2012, p. 21
- ^ a b
- McCray 1898, p. 10
- ^
- Root 1891, p. 138
- Root et al. 1892, p. 224
- Hill 1953a, pp. 213–214
- Kelley & Snell 2004, p. 121
- ^
- Birdseye 1879b, pp. 284–285
- Epstein 1944, p. 43
- Hill 1953a, p. 211
- Kelley & Snell 2004, p. 119
- ^ a b
- Birdseye 1879b, p. 288
- Bailey et al. 1991, pp. 197–198
- McWhirter 2012, pp. 146–147
- ^ a b c quoted in McCray 1898, p. 10
- ^
- McCray 1898, p. 10
- Bailey et al. 1991, p. 197
- Finson 1994, pp. 56, 210
- Carder 2008, p. 114
- McWhirter 2012, p. 146
- ^
- McWhirter 2012, pp. 20–21
- ^
- Hill 1953a, p. 213
- Carder 2008, p. 130
- ^
- Hill 1953a, p. 213
- Carder 2008, p. 112
- ^
- quoted in Root 1891, pp. 137–138
- see also: Carder 2008, p. 114
- ^ quoted in Carder 2008, p. 114
- ^
- Work, pp. 122–124
- Finson 1994, pp. 210–211
- Herder 1998, p. 190
- Cohen 2015, pp. 126–128
- ^ a b quoted in Ewen 1962, p. 188
- ^ quoted in Bailey et al. 1991, p. 197
- ^
- ^
- quoted in Hursh & Goertzen 2009, p. 174
- Bailey et al. 1991, p. 197
- Finson 1994, pp. 210–211
- ^ a b
- Finson 1994, p. 210
- Silber 1995, p. 306
- McWhirter 2012, pp. 146–147
- Cohen 2015, p. 126
- ^
- Finson 1994, pp. 176–178, 198–199
- Floyd 1995, p. 60
- Sussman 2001, pp. 79–83
- ^
- Bailey et al. 1991, p. 197
- Finson 1994, p. 210
- McWhirter 2012, p. 146
- ^
- Silber 1995, p. 306
- Carder 2008, p. 113
- Cohen 2015, p. 126
- ^
- quoted in Carder 2008, p. 133
- Carder 2008, p. 114
- ^
- Carder 2008, p. 122
- McWhirter 2012, p. 159
- ^ Hursh & Goertzen 2009, p. 174
- ^ McWhirter 2012, p. 20
- ^ a b Hill 1953a, p. 213
- ^
- Silber 1995, p. 304
- Carder 2008, p. 130
- McWhirter 2012, p. 95
- ^ quoted in Carder 2008, p. 130
- ^ quoted in Carder 2008, p. 131
- ^
- Root 1891, pp. 139–140
- Carder 2008, pp. 130–131
- ^
- Root et al. 1892, pp. 39–40
- Hill 1953a, p. 213
- Silber 1995, pp. 306–307
- Carder 2008, p. 133
- McWhirter 2012, p. 148
- ^
- Silber 1995, p. 307
- McWhirter 2012, p. 147
- Library of Congress
- ^
- Ewen 1962, pp. 188–189
- ^ a b Hill 1953a, pp. 213–214
- ^
- quoted in Carder 2008, p. 141
- Chicago Tribune 1864a, p. 4
- Silber 1995, p. 307
- ^
- quoted in Ewen 1962, p. 189
- Finson 1994, p. 130
- ^
- Ewing 1977, pp. 13, 62–63, 123–124
- Sanders 2017, p. 180
- ^
- Birdseye 1879b, p. 284
- Carder 2008, p. 166
- ^ Finson 1994, p. 57
- ^
- Birdseye 1879b, p. 286
- McCray 1898, p. 10
- ^ a b Finson 1994, p. 57
- ^
- Root et al. 1892, p. 6
- Finson 1994, p. 59
- ^
- San Marcos Press 1879, p. 3
- Birdseye 1879b, p. 287
- ^
- Hill 1953a, p. 214
- Carder 2008, p. 153
- ^ Carder 2008, p. 155
- ^
- Hill 1953a, p. 214
- ^
- Work, pp. 18–20
- Herder 1998, p. 212
- McWhirter 2012, p. 164
- ^
- quoted in Ewen 1962, p. 188
- Root et al. 1892, p. 6
- Tribble 1967, p. 426
- Silber 1995, p. 16
- McWhirter 2012, p. 169
- ^
- Howard & Bellows 1967, p. 135
- Tribble 1967, p. 426
- Carder 2008, p. 153
- McWhirter 2012, p. 169
- ^
- Tribble 1967, p. 423
- Silber 1995, p. 238
- ^
- Tribble 1967, p. 428
- McWhirter 2012, p. 186
- ^
- Hill 1953a, p. 215
- Kelley & Snell 2004, p. 122
- ^ Root 1891, p. 151
- ^ Ewen 1962, p. 189
- ^ quoted in Nelson 2008
- ^
- Root et al. 1892, p. 6
- Hill 1953a, p. 216
- ^ Edenfield
- ^
- Finson 1994, p. 116
- Shepherd 2003, p. 208
- ^
- Farmer and Mechanic 1878, p. 3
- Birdseye 1879b, p. 286
- Hill 1953a, pp. 216–217
- Tribble 1967, p. 426
- ^ quoted in Birdseye 1879b, p. 286
- ^ quoted in Hill 1953a, p. 222
- ^
- Hill 1953a, p. 224
- Hill 1953b, p. 368
- Tribble 1967, pp. 426–427
- ^ Birdseye 1879b, p. 286
- ^
- Farmer and Mechanic 1878, p. 3
- Hill 1953a, pp. 223–224
- ^
- Hill 1953a, pp. 221–222
- Hill 1953b, p. 368
- ^ quoted in Hill 1953a, p. 224
- ^ Hill 1953a, p. 214
- ^
- Hill 1953a, p. 212
- ^
- Epstein 1945, p. 98
- Carder 2008, p. 171
- Song of America (a)
- ^
- Hill 1953a, p. 214
- Kelley & Snell 2004, p. 122
- ^
- Root 1891, pp. 152–153
- Birdseye 1879b, p. 286
- San Marcos Press 1879, p. 3
- Howard & Bellows 1967, p. 134
- ^
- Nashville Union 1871, p. 1
- Epstein 1945, p. 89
- ^ a b c Work, p. 7
- ^ quoted in Carder 2008, p. 179
- ^
- Root 1891, pp. 157–158
- Birdseye 1879b, p. 286
- Epstein 1945, pp. 88–89
- Carder 2008, p. 181
- ^ a b
- Hill 1953a, p. 215
- Kelley & Snell 2004, p. 122
- ^
- Epstein 1944, pp. 58–59
- ^
- Epstein 1944, p. 58
- Hill 1953a, pp. 214–215
- Hill 1953b, p. 381
- Tribble 1967, p. 427
- ^
- Work, pp. 178–180
- Birdseye 1879b, p. 287
- Herder 1998, p. 122
- ^
- Birdseye 1879b, p. 286
- San Marcos Press 1879, p. 3
- Hill 1953a, p. 214
- Ewen 1962, p. 189
- Tribble 1967, p. 428
- Finson 1994, p. 132
- ^
- Birdseye 1879b, p. 287
- Finson 1994, p. 130
- ^
- Ewen 1962, p. 189
- Kelley & Snell 2004, pp. 122–123
- ^
- ^
- Birdseye 1879b, p. 286
- San Marcos Press 1879, p. 3
- ^
- Morning Herald 1878, p. 2
- San Marcos Press 1879, p. 3
- ^ Evening Capital 1884, p. 2
- ^
- Birdseye 1879b, p. 287
- San Marcos Press 1879, p. 3
- Finson 1994, p. 133
- ^
- Kelley & Snell 2004, pp. 122–123
- ^ quoted in Hill 1953b, p. 369
- ^ a b
- Hill 1953b, p. 368
- ^
- Hill 1953a, pp. 223–224
- Hill 1953b, p. 381
- Tribble 1967, pp. 426–427
- ^
- Hill 1953a, pp. 212, 218
- Hill 1953b, p. 381
- Tribble 1967, p. 428
- ^
- Birdseye 1879b, p. 288
- Hill 1953a, p. 215
- Hill 1953b, p. 381
- ^ Birdseye 1879b, p. 287
- ^ Hill 1953a, pp. 214–215
- ^
- quoted in Kelley & Snell 2004, p. 123
- Hill 1953b, p. 389
- Tribble 1967, p. 427
- ^
- quoted in Tribble 1967, pp. 427–428
- Root et al. 1892, p. 6
- Hill 1953a, p. 215
- ^
- New Haven Journal 1884, p. 2
- Hill 1953b, p. 390
- Ewen 1962, p. 189
- ^
- New Haven Journal 1884, p. 2
- Hill 1953b, p. 368
- ^ quoted in Hill 1953a, p. 211
- ^ see:
- Indianapolis Journal 1884, p. 2
- Rocky Mountain 1884, p. 2
- Eureka Daily 1884, p. 3
- ^
- Root et al. 1892, p. 6
- Drury 1975, p. 252
- ^
- Tribble 1967, p. 428
- Nelson 2008
- ^ quoted in Tribble 1967, p. 428
- ^ a b quoted in Birdseye 1879b, p. 288
- ^
- quoted in Birdseye 1879b, p. 288
- Work, p. 7
- ^
- Farmer and Mechanic 1878, p. 3
- Birdseye 1879b, p. 286
- ^
- quoted in Hill 1953b, p. 370
- Farmer and Mechanic 1878, p. 3
- Hill 1953b, pp. 369–370
- ^
- Evening Star 1881, p. 3
- Hill 1953a, p. 215
- Hill 1953b, pp. 369–370
- ^
- Hill 1953b, p. 368
- Drury 1975, pp. 250–252
- ^ a b c Hill 1953a, pp. 223–224
- ^ Hill 1953a, p. 222
- ^
- Farmer and Mechanic 1878, p. 3
- New Haven Journal 1884, p. 2
- Hill 1953a, p. 224
- ^
- Hill 1953a, p. 217
- Tribble 1967, p. 427
- ^
- quoted in Tribble 1967, p. 427
- Hill 1953a, pp. 212, 218
- ^
- Hill 1953a, p. 220
- Tribble 1967, p. 427
- ^
- Hill 1953a, pp. 219–220
- Hill 1953b, p. 380
- ^ Hill 1953a, p. 220
- ^
- Hill 1953a, pp. 218, 220
- Hill 1953b, p. 383
- Tribble 1967, p. 426
- ^ Hill 1953b, pp. 388–389
- ^
- Hill 1953b, p. 385
- Tribble 1967, p. 427
- ^ quoted in Hill 1953b, pp. 389–390
- ^
- Hill 1953a, p. 215
- Hill 1953b, p. 389
- ^ Hill 1953b, p. 389
- ^ Drury 1975, p. 250
- ^ quoted in Drury 1975, p. 250
- ^
- Andreas 1884, p. 529
- Drury 1975, p. 251
- ^
- Andreas 1884, p. 514
- Drury 1975, p. 252
- ^ Drury 1975, p. 252
- ^
- Birdseye 1879b, p. 288
- Hill 1953b, pp. 374–375
- Tribble 1967, p. 427
- ^
- Hill 1953a, p. 212
- Drury 1975, p. 252
- ^ quoted in Root 1891, p. 138
- ^ Root 1891, p. 139
- ^ quoted in Birdseye 1879b, pp. 287–288
- ^ Evening Star 1881, p. 3
- ^
- Birdseye 1879b, p. 287
- Hill 1953a, pp. 213–215
- ^ Hill 1953a, pp. 213–215
- ^
- Birdseye 1879b, p. 287
- San Marcos Press 1879, p. 3
- ^ quoted in Willimantic Journal 1879, p. 7
- ^ see:
- McCray 1898, p. 10
- Silber 1995, p. 56
- ^ quoted in Finson 1994, p. 130
- ^
- Birdseye 1879b, p. 285
- Ewen 1962, p. 189
- Ewing 1977, pp. 16, 219
- Finson 1994, pp. 56–57
- ^ quoted in Carder 2008, p. 166
- ^ quoted in Nelson 2008
- ^
- Quoted in New Haven Journal 1884, p. 2
- see also: Kelley & Snell 2004, p. 122
- ^ Sadie & Tyrrell 2001, p. 568
- ^ Songwriters Hall of Fame
Bibliography
Books
Primary sources
- Root, George F. (1891). The Story of a Musical Life: An Autobiography by Geo F. Root. Cincinnati, Ohio: The John Church Co. ISBN 978-1-4047-8329-4.
{{cite book}}: ISBN / Date incompatibility (help) - Root, George F.; Sawyer, Charles C.; Work, Henry C., eds. (1892). Our National War Songs (2 ed.). Chicago: The S. Brainard's Sons Co.
- Work, Henry C. (n.d.). Work, Bertram G. (ed.). Songs of Henry Clay Work. New York City: Little & Ives.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: year (link)
Secondary sources
- Andreas, Alfred T. (1884). History of Cook County Illinois: From the Earliest Period to the Present Time. Chicago.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Bailey, Guy; Natalie, Maynor; Cukor-Avila, Patricia (1991). The Emergence of Black English: Text and Commentary. Philadelphia: John Benjamins Publishing Company. ISBN 1-55619-161-8.
- Carder, P. H. (2008). George F. Root, Civil War Songwriter: A Biography. Jefferson, NC: McFarland & Company, Inc. ISBN 978-0-7864-3374-2.
- Cohen, Michael C. (2015). The Social Lives of Poems in Nineteenth-Century America. Philadelphia: The University of Pennsylvania Press. ISBN 978-0-8122-4708-4.
- Cohen, Norm (2000). Long Steel Rail: The Railroad in American Folksong (2nd ed.). Chicago: University of Illinois Press. ISBN 0-252-06881-5.
- Drury, John (1975). Old Chicago Houses. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. ISBN 0-226-16555-8.
- Ewen, David (1962). Popular American Composers from Revolutionary Times to the Present: A Biographical and Critical Guide. New York City: H. W. Wilson Company, Inc. ISBN 978-0824200404.
{{cite book}}: ISBN / Date incompatibility (help) - Ewing, George W. (1977). The Well-Tempered Lyre: Songs and Verse of the Temperance Movements. Dallas: Southern Methodist University Press. ISBN 0-870-740-008.
- Finson, Jon W. (1994). The Voices That Are Gone: Themes in Nineteenth-Century American Popular Song. New York City: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-505750-3.
- Floyd, Samuel A. (1995). The Power of Black Music: Interpreting Its History from Africa to the United States. New York City: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-508235-4.
- Herder, Ronald (1998). 500 Best-Loved Song Lyrics. Mineola, NY: Dover Publications, Inc. ISBN 0-486-29725-X.
- Howard, John Tasker; Bellows, George Kent (1967). A Short History of Music in America. New York City: McFarland & Company, Inc. ISBN 0-8152-0162-1.
- Hursh, David; Goertzen, Chris (2009). Good Medicine and Good Music: A Biography of Mrs. Joe Person, Patent Remedy Entrepreneur and Musician, Including the Complete Text of Her 1903 Autobiography. Jefferson, NC: McFarland & Company, Inc. ISBN 978-0-7864-3459-6.
- Kelley, Bruce C.; Snell, Mark A. (2004). Bugle Resounding: Music and Musicians of the Civil War Era. Columbia: University of Missouri Press. ISBN 0-8262-1538-6.
- McWhirter, Christian (2012). Battle Hymns: The Power and Popularity of Music in the Civil War. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press. ISBN 978-0-8078-3550-0.
- Merriam-Webster, Inc., ed. (2000). Merriam-Webster's Collegiate Dictionary (3rd ed.). Springfield, Massachusetts. ISBN 978-0-87779-807-1.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Shepherd, John (2003). Continuum Encyclopedia of Popular Music of the World. Vol. 1. New York City: Continuum International Publishing Group. ISBN 0-8264-6321-5.
- Silber, Irwin (1995). Songs of the Civil War. Mineola, NY: Dover Publications. ISBN 0-486-28438-7.
- Sadie, Stanley; Tyrrell, John, eds. (2001). The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians. Vol. 27 (2nd ed.). New York City: Macmillan Publishers. ISBN 1-56159-239-0.
Studies and journals
- Birdseye, George (1879). "America's Song Composers: II. George F. Root". Potter's American Monthly. 12 (86): 145–148 – via Internet Archive.
- Birdseye, George (1879). "America's Song Composers: IV. Henry Clay Work". Potter's American Monthly. 12 (88): 284–288 – via Internet Archive.
- Epstein, Dena J. (1944). "Music Publishing in Chicago before 1871: The Firm of Root & Cady, 1858–1871". Notes. 1 (4): 43–59. doi:10.2307/891291. JSTOR 891291.
- Epstein, Dena J. (1945). "Music Publishing in Chicago before 1871: Chapter VI, the End of the Firm, 1868–1871". Notes. 3 (1): 80–98, 101–109. doi:10.2307/891291. JSTOR 891291.
- Hill, Richard S. (1953). "The Mysterious Chord of Henry Clay Work". Notes. 10 (2): 211–225. doi:10.2307/892874. JSTOR 892874.
- Hill, Richard S. (1953). "The Mysterious Chord of Henry Clay Work (Conclusion)". Notes. 10 (3): 367–390. doi:10.2307/892162. JSTOR 892162.
- Sanders, Paul D. (2017). "Temperance Songs in American School Songbooks, 1865–1899". Journal of Historical Research in Music Education. 38 (2): 178–208. doi:10.1177/1536600616667602. JSTOR 26376931.
- Sussman, Rachel (2001). "The Carnavalizing of Race". Etnofoor. 14 (2): 79–88. JSTOR 41396391.
- Tribble, Edwin (1967). "Marching Through Georgia". The Georgia Review. 21 (4): 423–429. JSTOR 41396391.
Newspaper articles
- McCray, Florine Thayer (January 19, 1898). "About Henry Clay Work". New Haven Morning Journal and Courier. p. 10. Retrieved June 29, 2024.
- "Dies Iræ!: Another Fearful Fire at Chicago". Nashville Union and American. October 10, 1871. p. 1. Retrieved July 1, 2024.
- "Flue Dust: Scraps from the Note-book of the Sentinel's Reporter". Eureka Daily Sentinel. July 14, 1884. p. 3. Retrieved June 29, 2024.
- "General News". Rocky Mountain Husbandman. June 12, 1884. p. 2. Retrieved June 29, 2024.
- "Hawk-Eyetems". The Willimantic Journal. February 28, 1879. p. 7. Retrieved July 17, 2024.
- "Henry C. Work: A Popular Song Writer, and His Method of Composing". Evening Star. May 28, 1881. p. 3. Retrieved July 17, 2024.
- "Henry Clay Work: The Famous Song Writer Ends His Life in Hartford". New Haven Morning Journal and Courier. June 10, 1884. p. 2. Retrieved June 29, 2024.
- "Herald Notes". The Morning Herald. November 4, 1878. p. 3. Retrieved June 29, 2024.
- "My Grandfather's Clock: A Song that was Suddenly Made Popular—Henry C. Work's Melodies". San Marcos Free Press. January 25, 1879. p. 3. Retrieved June 29, 2024.
- "Obituary: Henry C. Work". Indianapolis Journal. June 9, 1884. p. 2. Retrieved June 29, 2024.
- "Page 2". Evening Capital. July 18, 1884. p. 2. Retrieved June 29, 2024.
- "Songs for the Million". The Saturday Evening Post. April 12, 1862. p. 4. Retrieved June 29, 2024.
- "The Author of "Grandfather's Clock"". The Farmer and Mechanic. Vol. 3, no. 7. November 28, 1878. p. 3. Retrieved July 17, 2024.
- "The City: Corporal Schnapps". Chicago Tribune. April 17, 1864. p. 4. Retrieved July 15, 2024.
Websites
- Edenfield, Gray. "The Wreck of the Evening Star". Florida History Network. Retrieved August 22, 2025.
- Nelson, Dean (2008). "Marching with Henry C. Work". Museum of Connecticut History. Retrieved July 18, 2024.
- Webster, Ian. "CPI Inflation Calculator". officialdata.org. Retrieved July 15, 2024.
- "African-American Soldiers During the Civil War". Library of Congress. Retrieved July 16, 2024.
- "Crossing the Grand Sierras". Song of America. Retrieved July 16, 2024.
- "The Emancipation Proclamation". National Archives. January 28, 2022. Retrieved July 15, 2024.
- "Grandfather clock". Oxford English Dictionary. September 2015. Retrieved July 15, 2024.
- "Henry C. Work". Songwriters Hall of Fame. Retrieved July 15, 2024.
- "Henry Clay Work". Song of America. Retrieved July 15, 2024.
External links
General
- Work's profile on Song of America
- Sheet music of Work's compositions in his nephew's biography
- Newspaper archives courtesy of the Library of Congress featuring content on Work
- His poem The Upshot Family on the Library of Congress
Recordings of Work's songs
- "Kingdom Coming" by the 2nd South Carolina String Band on their 2000 album Hard Road
- "Grafted into the Army" by The Lansdowne Orchestra on their 1960 album The Blue and the Grey
- "God Save the Nation" by Bobby Horton on his 1991 album Homespun Songs of the Union Army, Volume 3
- "Babylon is Fallen" by the 97th Regimental String Band on their 1999 album Brass Mounted Army: Civil War Era Songs, Vol. VII
- "Come Home, Father" by Jerry Silverman on the 1990 album The Songs of the American Civil War (1861-1865: Chants de la Guerre Sécession)
- "Marching Through Georgia" by Tennessee Ernie Ford on his 1961 album Songs of the Civil War
- "The Ship That Never Returned" by Sara and Maybelle Carter on their 1966 album An Historic Union
- "Grandfather's Clock" by Johnny Cash on his 1959 album Songs of Our Soil
- "Sequel to Grandfather's Clock" by Tom Roush on his album Americana