Fresnel's physical optics
The French civil engineer and physicist Augustin-Jean Fresnel (1788–1827) made contributions to several areas of physical optics, including to diffraction, polarization, and double refraction.
Historical context: From Newton to Biot
The appreciation of Fresnel's reconstruction of physical optics might be assisted by an overview of the fragmented state in which he found the subject. In this subsection, optical phenomena that were unexplained or whose explanations were disputed are named in bold type.
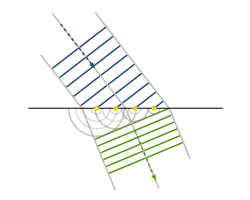
The corpuscular theory of light explained rectilinear propagation: the corpuscles obviously moved very fast, so that their paths were very nearly straight. The wave theory, as developed by Christiaan Huygens in his Treatise on Light (1690), explained rectilinear propagation on the assumption that each point crossed by a traveling wavefront becomes the source of a secondary wavefront. Given the initial position of a traveling wavefront, any later position (according to Huygens) was the common tangent surface (envelope) of the secondary wavefronts emitted from the earlier position.[1] As the extent of the common tangent was limited by the extent of the initial wavefront, the repeated application of Huygens's construction to a plane wavefront of limited extent (in a uniform medium) gave a straight, parallel beam. While this construction indeed predicted rectilinear propagation, it was difficult to reconcile with the common observation that wavefronts on the surface of water can bend around obstructions, and with the similar behavior of sound waves—causing Newton to maintain, to the end of his life, that if light consisted of waves it would "bend and spread every way" into the shadows.[2]
Huygens's theory neatly explained the law of ordinary reflection and the law of ordinary refraction ("Snell's law"), provided that the secondary waves traveled slower in denser media (those of higher refractive index).[3] The corpuscular theory, with the hypothesis that the corpuscles were subject to forces acting perpendicular to surfaces, explained the same laws equally well,[4] albeit with the implication that light traveled faster in denser media; that implication was wrong, but could not be directly disproven with the technology of Newton's time or even Fresnel's time ().
Similarly inconclusive was stellar aberration—that is, the apparent change in the position of a star due to the velocity of the earth across the line of sight (not to be confused with stellar parallax, which is due to the displacement of the earth across the line of sight). Identified by James Bradley in 1728, stellar aberration was widely taken as confirmation of the corpuscular theory. But it was equally compatible with the wave theory, as Euler noted in 1746—tacitly assuming that the aether (the supposed wave-bearing medium) near the earth was not disturbed by the motion of the earth.[5]
The outstanding strength of Huygens's theory was his explanation of the birefringence (double refraction) of "Iceland crystal" (transparent calcite), on the assumption that the secondary waves are spherical for the ordinary refraction (which satisfies Snell's law) and spheroidal for the extraordinary refraction (which does not).[6] In general, Huygens's common-tangent construction implies that rays are paths of least time between successive positions of the wavefront, in accordance with Fermat's principle.[7][8] In the special case of isotropic media, the secondary wavefronts must be spherical, and Huygens's construction then implies that the rays are perpendicular to the wavefront; indeed, the law of ordinary refraction can be separately derived from that premise, as Ignace-Gaston Pardies did before Huygens.[9]
Although Newton rejected the wave theory, he noticed its potential to explain colors, including the colors of "thin plates" (e.g., "Newton's rings", and the colors of skylight reflected in soap bubbles), on the assumption that light consists of periodic waves, with the lowest frequencies (longest wavelengths) at the red end of the spectrum, and the highest frequencies (shortest wavelengths) at the violet end. In 1672 he published a heavy hint to that effect,[10][11]: 5088–5089 but contemporary supporters of the wave theory failed to act on it: Robert Hooke treated light as a periodic sequence of pulses but did not use frequency as the criterion of color,[12] while Huygens treated the waves as individual pulses without any periodicity;[13] and Pardies died young in 1673. Newton himself tried to explain colors of thin plates using the corpuscular theory, by supposing that his corpuscles had the wavelike property of alternating between "fits of easy transmission" and "fits of easy reflection",[14][15] the distance between like "fits" depending on the color and the medium [16] and, awkwardly, on the angle of refraction or reflection into that medium.[17][18]: 1144 More awkwardly still, this theory required thin plates to reflect only at the back surface, although thick plates manifestly reflected also at the front surface.[19] It was not until 1801 that Thomas Young, in the Bakerian Lecture for that year, cited Newton's hint,[20]: 18–19 and accounted for the colors of a thin plate as the combined effect of the front and back reflections, which reinforce or cancel each other according to the wavelength and the thickness.[20]: 37–39 Young similarly explained the colors of "striated surfaces" (e.g., gratings) as the wavelength-dependent reinforcement or cancellation of reflections from adjacent lines.[20]: 35–37 He described this reinforcement or cancellation as interference.
.jpg)
Huygens noticed something: when light passes through two similarly oriented calcite crystals at normal incidence, the ordinary ray emerging from the first crystal suffers only the ordinary refraction in the second, while the extraordinary ray emerging from the first suffers only the extraordinary refraction in the second; but when the second crystal is rotated 90° about the incident rays, the roles are interchanged, so that the ordinary ray emerging from the first crystal suffers only the extraordinary refraction in the second, and vice versa.[21] This discovery gave Newton another reason to reject the wave theory: rays of light evidently had "sides".[22] Corpuscles could have sides [23] (or poles, as they would later be called); but waves of light could not,[24] because (so it seemed) any such waves would need to be longitudinal (with vibrations in the direction of propagation). Newton offered an alternative "Rule" for the extraordinary refraction,[25] which rode on his authority through the 18th century, although he made "no known attempt to deduce it from any principles of optics, corpuscular or otherwise". [26]: 327

In 1808, the extraordinary refraction of calcite was investigated experimentally by Étienne-Louis Malus, and found to be consistent with Huygens's spheroid construction, not Newton's "Rule".[26] Malus, encouraged by Pierre-Simon Laplace,[18]: 1146 then sought to explain this law in corpuscular terms: from the known relation between the incident and refracted ray directions, Malus derived the corpuscular velocity (as a function of direction) that would satisfy Maupertuis's "least action" principle. But, as Young pointed out, the existence of such a velocity law was guaranteed by Huygens's spheroid, because Huygens's construction leads to Fermat's principle, which becomes Maupertuis's principle if the ray speed is replaced by the reciprocal of the particle speed! The corpuscularists had not found a force law that would yield the alleged velocity law, except by a circular argument in which a force acting at the surface of the crystal inexplicably depended on the direction of the (possibly subsequent) velocity within the crystal. Worse, it was doubtful that any such force would satisfy the conditions of Maupertuis's principle.[27] In contrast, Young proceeded to show that "a medium more easily compressible in one direction than in any direction perpendicular to it, as if it consisted of an infinite number of parallel plates connected by a substance somewhat less elastic" admits spheroidal longitudinal wavefronts, as Huygens supposed.[28][29]

Malus noticed, when a ray of light is reflected off a non-metallic surface at the appropriate angle, it behaves like one of the two rays emerging from a calcite crystal.[30][31] It was Malus who coined the term polarization to describe this behavior, although the polarizing angle became known as Brewster's angle after its dependence on the refractive index was determined experimentally by David Brewster in 1815.[32] Malus also introduced the term plane of polarization. In the case of polarization by reflection, his "plane of polarization" was the plane of the incident and reflected rays; in modern terms, this is the plane normal to the electric vibration. In 1809, Malus further discovered that the intensity of light passing through two polarizers is proportional to the squared cosine of the angle between their planes of polarization (Malus's law),[33][34] whether the polarizers work by reflection or double refraction, and that all birefringent crystals produce both extraordinary refraction and polarization.[35] As the corpuscularists started trying to explain these things in terms of polar "molecules" of light, the wave-theorists had no working hypothesis on the nature of polarization, prompting Young to remark that Malus's observations "present greater difficulties to the advocates of the undulatory theory than any other facts with which we are acquainted". [36]
In August 1811, François Arago reported that if a thin plate of mica was viewed against a white polarized backlight through a calcite crystal, the two images of the mica were of complementary colors (the overlap having the same color as the background). The light emerging from the mica was "depolarized" in the sense that there was no orientation of the calcite that made one image disappear; yet it was not ordinary ("unpolarized") light, for which the two images would be of the same color. Rotating the calcite around the line of sight changed the colors, though they remained complementary. Rotating the mica changed the saturation (not the hue) of the colors. This phenomenon became known as chromatic polarization. Replacing the mica with a much thicker plate of quartz, with its faces perpendicular to the optic axis (the axis of Huygens's spheroid or Malus's velocity function), produced a similar effect, except that rotating the quartz made no difference. Arago tried to explain his observations in corpuscular terms.[37][38]

In 1812, Jean-Baptiste Biot reworked the same ground using a gypsum lamina in place of the mica, and found empirical formulae for the intensities of the ordinary and extraordinary images. The formulae contained two coefficients, supposedly representing colors of rays "affected" and "unaffected" by the plate—the "affected" rays being of the same color mix as those reflected by amorphous thin plates of proportional, but lesser, thickness.[39]

Arago protested, declaring that he had made some of the same discoveries but had not had time to write them up. In fact the overlap between Arago's work and Biot's was minimal, Arago's being only qualitative and wider in scope (attempting to include polarization by reflection). But the dispute triggered a notorious falling-out between the two men.[40][41][42]
Later that year, Biot tried to explain the observations as an oscillation of the alignment of the "affected" corpuscles at a frequency proportional to that of Newton's "fits", due to forces depending on the alignment. This theory became known as mobile polarization. To reconcile his results with a sinusoidal oscillation, Biot had to suppose that the corpuscles emerged with one of two permitted orientations, namely the extremes of the oscillation, with probabilities depending on the phase of the oscillation.[43][44][45] Corpuscular optics was becoming expensive on assumptions. But in 1813, Biot reported that the case of quartz was simpler: the observable phenomenon (now called optical rotation or optical activity or sometimes rotary polarization) was a gradual rotation of the polarization direction with distance, and could be explained by a corresponding rotation (not oscillation) of the corpuscles.[46][47]
Early in 1814, Young noted that the periodicity of the color as a function of the plate thickness—including the factor by which the period exceeded that for a reflective thin plate, and even the effect of obliquity of the plate (but not the role of polarization)—could be explained by the wave theory in terms of the different propagation times of the ordinary and extraordinary waves through the plate.[48] But Young was then the only public defender of the wave theory.[49]
In summary, in the spring of 1814, as Fresnel tried in vain to guess what polarization was, the corpuscularists thought that they knew, while the wave-theorists (if we may use the plural) literally had no idea. Both theories claimed to explain rectilinear propagation, but the wave explanation was overwhelmingly regarded as unconvincing. The corpuscular theory could not rigorously link double refraction to surface forces; the wave theory could not yet link it to polarization. The corpuscular theory was weak on thin plates and silent on gratings;[Note 1] the wave theory was strong on both, but under-appreciated. Concerning diffraction, the corpuscular theory did not yield quantitative predictions, while the wave theory had begun to do so by considering diffraction as a manifestation of interference, but had only considered two rays at a time. Only the corpuscular theory gave even a vague insight into Brewster's angle, Malus's law, or optical rotation. Concerning chromatic polarization, the wave theory explained the periodicity far better than the corpuscular theory, but had nothing to say about the role of polarization; and its explanation of the periodicity was largely ignored.[50] And Arago had founded the study of chromatic polarization, only to lose the lead, controversially, to Biot. Such were the circumstances in which Arago first heard of Fresnel's interest in optics.
Rêveries

Fresnel's letters from later in 1814 reveal his interest in the wave theory, including his awareness that it explained the constancy of the speed of light and was at least compatible with stellar aberration. Eventually he compiled what he called his rêveries (musings) into an essay and submitted it via Léonor Mérimée to André-Marie Ampère, who did not respond directly. But on 19 December, Mérimée dined with Ampère and Arago, with whom he was acquainted through the École Polytechnique; and Arago promised to look at Fresnel's essay.[52][53][54][55][Note 2]
In mid 1815, on his way home to Mathieu to serve his suspension, Fresnel met Arago in Paris and spoke of the wave theory and stellar aberration. He was informed that he was trying to break down open doors ("il enfonçait des portes ouvertes"), and directed to classical works on optics.[56]
Diffraction
First attempt (1815)
On 12 July 1815, as Fresnel was about to leave Paris, Arago left him a note on a new topic:
I do not know of any book that contains all the experiments that physicists are doing on the diffraction of light. M'sieur Fresnel will only be able to get to know this part of the optics by reading the work by Grimaldi, the one by Newton, the English treatise by Jordan,[57] and the memoirs of Brougham and Young, which are part of the collection of the Philosophical Transactions.[58]
Fresnel would not have ready access to these works outside Paris, and could not read English.[59] But, in Mathieu—with a point-source of light made by focusing sunlight with a drop of honey, a crude micrometer of his own construction, and supporting apparatus made by a local locksmith—he began his own experiments.[60] His technique was novel: whereas earlier investigators had projected the fringes onto a screen, Fresnel soon abandoned the screen and observed the fringes in space, through a lens with the micrometer at its focus, allowing more accurate measurements while requiring less light.[61][62]
Later in July, after Napoleon's final defeat, Fresnel was reinstated with the advantage of having backed the winning side. He requested a two-month leave of absence, which was readily granted because roadworks were in abeyance.[63]
On 23 September he wrote to Arago, beginning "I think I have found the explanation and the law of colored fringes which one notices in the shadows of bodies illuminated by a luminous point." In the same paragraph, however, Fresnel implicitly acknowledged doubt about the novelty of his work: noting that he would need to incur some expense in order to improve his measurements, he wanted to know "whether this is not useless, and whether the law of diffraction has not already been established by sufficiently exact experiments". [64][65] He explained that he had not yet had a chance to acquire the items on his reading lists,[59] with the apparent exception of "Young's book", which he could not understand without his brother's help.[66][67][Note 3] Not surprisingly, he had retraced many of Young's steps.
In a memoir sent to the institute on 15 October 1815, Fresnel mapped the external and internal fringes in the shadow of a wire. He noticed, like Young before him, that the internal fringes disappeared when the light from one side was blocked, and concluded that "the vibrations of two rays that cross each other under a very small angle can contradict each other ..." [68] But, whereas Young took the disappearance of the internal fringes as confirmation of the principle of interference, Fresnel reported that it was the internal fringes that first drew his attention to the principle. To explain the diffraction pattern, Fresnel constructed the internal fringes by considering the intersections of circular wavefronts emitted from the two edges of the obstruction, and the external fringes by considering the intersections between direct waves and waves reflected off the nearer edge. For the external fringes, to obtain tolerable agreement with observation, he had to suppose that the reflected wave was inverted; and he noted that the predicted paths of the fringes were hyperbolic. In the part of the memoir that most clearly surpassed Young, Fresnel explained the ordinary laws of reflection and refraction in terms of interference, noting that if two parallel rays were reflected or refracted at other than the prescribed angle, they would no longer have the same phase in a common perpendicular plane, and every vibration would be cancelled by a nearby vibration. He noted that his explanation was valid provided that the surface irregularities were much smaller than the wavelength.[69][70][71]
On 10 November, Fresnel sent a supplementary note dealing with Newton's rings and with gratings,[72] including, for the first time, transmission gratings—although in that case the interfering rays were still assumed to be "inflected", and the experimental verification was inadequate because it used only two threads.[73][74]
As Fresnel was not a member of the institute, the fate of his memoir depended heavily on the report of a single member. The reporter for Fresnel's memoir turned out to be Arago (with Poinsot as the other reviewer).[75][76] On 8 November, Arago wrote to Fresnel:
I have been instructed by the Institute to examine your memoir on the diffraction of light; I have studied it carefully, and found many interesting experiments, some of which had already been done by Dr. Thomas Young, who in general regards this phenomenon in a manner rather analogous to the one you have adopted. But what neither he nor anyone had seen before you is that the external colored bands do not travel in a straight line as one moves away from the opaque body. The results you have achieved in this regard seem to me very important; perhaps they can serve to prove the truth of the undulatory system, so often and so feebly combated by physicists who have not bothered to understand it.[77]
Fresnel was troubled, wanting to know more precisely where he had collided with Young.[78] Concerning the curved paths of the "colored bands", Young had noted the hyperbolic paths of the fringes in the two-source interference pattern, corresponding roughly to Fresnel's internal fringes, and had described the hyperbolic fringes that appear on the screen within rectangular shadows.[79][80] He had not mentioned the curved paths of the external fringes of a shadow; but, as he later explained,[81] that was because Newton had already done so.[82] Newton evidently thought the fringes were caustics. Thus Arago erred in his belief that the curved paths of the fringes were fundamentally incompatible with the corpuscular theory.[83]
Arago's letter went on to request more data on the external fringes. Fresnel complied, until he exhausted his leave and was assigned to Rennes in the département of Ille-et-Vilaine. At this point Arago interceded with Gaspard de Prony, head of the École des Ponts, who wrote to Louis-Mathieu Molé, head of the Corps des Ponts, suggesting that the progress of science and the prestige of the Corps would be enhanced if Fresnel could come to Paris for a time. He arrived in March 1816, and his leave was subsequently extended through the middle of the year.[84][75][85][86]
Meanwhile, in an experiment reported on 26 February 1816, Arago verified Fresnel's prediction that the internal fringes were shifted if the rays on one side of the obstacle passed through a thin glass lamina. Fresnel correctly attributed this phenomenon to the lower wave velocity in the glass.[87][88][89] Arago later used a similar argument to explain the colors in the scintillation of stars.[Note 4]
Fresnel's updated memoir [90] was eventually published in the March 1816 issue of Annales de Chimie et de Physique, of which Arago had recently become co-editor.[72][91] That issue did not actually appear until May.[92] In March, Fresnel already had competition: Biot read a memoir on diffraction by himself and his student Claude Pouillet, containing copious data and arguing that the regularity of diffraction fringes, like the regularity of Newton's rings, must be linked to Newton's "fits". But the new link was not rigorous, and Pouillet himself would become a distinguished early adopter of the wave theory.[93][94]
"Efficacious ray", double-mirror experiment (1816)
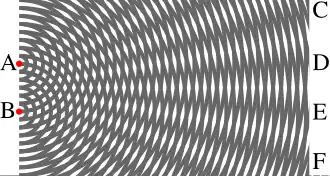
On 24 May 1816, Fresnel wrote to Young (in French), acknowledging how little of his own memoir was new.[96] But in a "supplement" signed on 14 July and read the next day,[97] Fresnel noted that the internal fringes were more accurately predicted by supposing that the two interfering rays came from some distance outside the edges of the obstacle. To explain this, he divided the incident wavefront at the obstacle into what we now call Fresnel zones, such that the secondary waves from each zone were spread over half a cycle when they arrived at the observation point. The zones on one side of the obstacle largely canceled out in pairs, except the first zone, which was represented by an "efficacious ray". This approach worked for the internal fringes, but the superposition of the efficacious ray and the direct ray did not work for the external fringes.[98][99]
The contribution from the "efficacious ray" was thought to be only partly canceled, for reasons involving the dynamics of the medium: where the wavefront was continuous, symmetry forbade oblique vibrations; but near the obstacle that truncated the wavefront, the asymmetry allowed some sideways vibration towards the geometric shadow. This argument showed that Fresnel had not (yet) fully accepted Huygens's principle, which would have permitted oblique radiation from all portions of the front.[100][101]
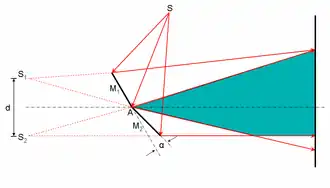
In the same supplement, Fresnel described his well-known double mirror, comprising two flat mirrors joined at an angle of slightly less than 180°, with which he produced a two-slit interference pattern from two virtual images of the same slit. A conventional double-slit experiment required a preliminary single slit to ensure that the light falling on the double slit was coherent (synchronized). In Fresnel's version, the preliminary single slit was retained, and the double slit was replaced by the double mirror—which bore no physical resemblance to the double slit and yet performed the same function. This result (which had been announced by Arago in the March issue of the Annales) made it hard to believe that the two-slit pattern had anything to do with corpuscles being deflected as they passed near the edges of the slits.[102][103][104][85][105]
But 1816 was the "Year Without a Summer": crops failed; hungry farming families lined the streets of Rennes; the central government organized "charity workhouses" for the needy; and in October, Fresnel was sent back to Ille-et-Vilaine to supervise charity workers in addition to his regular road crew.[106][107] According to Arago,
with Fresnel conscientiousness was always the foremost part of his character, and he constantly performed his duties as an engineer with the most rigorous scrupulousness. The mission to defend the revenues of the state, to obtain for them the best employment possible, appeared to his eyes in the light of a question of honour. The functionary, whatever might be his rank, who submitted to him an ambiguous account, became at once the object of his profound contempt. ... Under such circumstances the habitual gentleness of his manners disappeared ...[108]
Fresnel's letters from December 1816 reveal his consequent anxiety. To Arago he complained of being "tormented by the worries of surveillance, and the need to reprimand ...". And to Mérimée he wrote: "I find nothing more tiresome than having to manage other men, and I admit that I have no idea what I'm doing."[109]
Prize memoir (1818) and sequel
On 17 March 1817, the Académie des Sciences announced that diffraction would be the topic for the biannual physics Grand Prix to be awarded in 1819.[110][111][112][113] The deadline for entries was set at 1 August 1818 to allow time for replication of experiments. Although the wording of the problem referred to rays and inflection and did not invite wave-based solutions, Arago and Ampère encouraged Fresnel to enter.[114][115][116][117]
In the fall of 1817, Fresnel, supported by de Prony, obtained a leave of absence from the new head of the Corp des Ponts, Louis Becquey, and returned to Paris.[118][112] He resumed his engineering duties in the spring of 1818; but from then on he was based in Paris,[119][91] first on the Canal de l'Ourcq,[120][121][122] and then (from May 1819) with the cadastre of the pavements.[123][124]: 486
On 15 January 1818, in a different context (revisited below), Fresnel showed that the addition of sinusoidal functions of the same frequency but different phases is analogous to the addition of forces with different directions.[125] His method was similar to the phasor representation, except that the "forces" were plane vectors rather than complex numbers; they could be added, and multiplied by scalars, but not (yet) multiplied and divided by each other. The explanation was algebraic rather than geometric.
Knowledge of this method was assumed in a preliminary note on diffraction,[126] dated 19 April 1818 and deposited on 20 April, in which Fresnel outlined the elementary theory of diffraction as found in modern textbooks. He restated Huygens's principle in combination with the superposition principle, saying that the vibration at each point on a wavefront is the sum of the vibrations that would be sent to it at that moment by all the elements of the wavefront in any of its previous positions, all elements acting separately (). For a wavefront partly obstructed in a previous position, the summation was to be carried out over the unobstructed portion. In directions other than the normal to the primary wavefront, the secondary waves were weakened due to obliquity, but weakened much more by destructive interference, so that the effect of obliquity alone could be ignored.[127] For diffraction by a straight edge, the intensity as a function of distance from the geometric shadow could then be expressed with sufficient accuracy in terms of what are now called the normalized Fresnel integrals:
.svg.png)
These are special cases of the Faddeeva function [128] – the real and imaginary parts of its value on the line in the complex plane.
The same note included a table of the integrals, for an upper limit ranging from 0 to 5.1 in steps of 0.1, computed with a mean error of 0.0003,[129][130] plus a smaller table of maxima and minima of the resulting intensity.
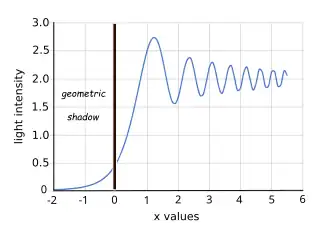
In his final "Memoir on the diffraction of light",[131] deposited on 29 July [132] and bearing the Latin epigraph "Natura simplex et fecunda" ("Nature simple and fertile"),[133][134][135] Fresnel slightly expanded the two tables without changing the existing figures, except for a correction to the first minimum of intensity. For completeness, he repeated his solution to "the problem of interference", whereby sinusoidal functions are added like vectors. He acknowledged the directionality of the secondary sources and the variation in their distances from the observation point, chiefly to explain why these things make negligible difference in the context, provided of course that the secondary sources do not radiate in the retrograde direction. Then, applying his theory of interference to the secondary waves, he expressed the intensity of light diffracted by a single straight edge (half-plane) in terms of integrals which involved the dimensions of the problem, but which could be converted to the normalized forms above. With reference to the integrals, he explained the calculation of the maxima and minima of the intensity (external fringes), and noted that the calculated intensity falls very rapidly as one moves into the geometric shadow.[136] The last result, as Olivier Darrigol says, "amounts to a proof of the rectilinear propagation of light in the wave theory, indeed the first proof that a modern physicist would still accept". [137]
For the experimental testing of his calculations, Fresnel used red light with a wavelength of 638 nm, which he deduced from the diffraction pattern in the simple case in which light incident on a single slit was focused by a cylindrical lens. For a variety of distances from the source to the obstacle and from the obstacle to the field point, he compared the calculated and observed positions of the fringes for diffraction by a half-plane, a slit, and a narrow strip—concentrating on the minima, which were visually sharper than the maxima. For the slit and the strip, he could not use the previously computed table of maxima and minima; for each combination of dimensions, the intensity had to be expressed in terms of sums or differences of Fresnel integrals and calculated from the table of integrals, and the extrema had to be calculated anew.[138][139] The agreement between calculation and measurement was better than 1.5% in almost every case.[140]
Near the end of the memoir, Fresnel summed up the difference between Huygens's use of secondary waves and his own: whereas Huygens says there is light only where the secondary waves exactly agree, Fresnel says there is complete darkness only where the secondary waves exactly cancel out.[141]

The judging committee comprised Laplace, Biot, and Poisson (all corpuscularists), Gay-Lussac (uncommitted), and Arago, who eventually wrote the committee's report.[142][143][144][145] Although entries in the competition were supposed to be anonymous to the judges, Fresnel's must have been recognizable by the content.[135] There was only one other entry, of which neither the manuscript nor any record of the author has survived.[146][147] That entry (identified as "no. 1") was mentioned only in the last paragraph of the judges' report,[148] noting that the author had shown ignorance of the relevant earlier works of Young and Fresnel, used insufficiently precise methods of observation, overlooked known phenomena, and made obvious errors. In the words of John Worrall, "The competition facing Fresnel could hardly have been less stiff." [149] We may infer that the committee had only two options: award the prize to Fresnel ("no. 2"), or withhold it.[150]

The committee deliberated into the new year.[151]: 144 Then Poisson, exploiting a case in which Fresnel's theory gave easy integrals, predicted that if a circular obstacle were illuminated by a point-source, there should be (according to the theory) a bright spot in the center of the shadow, illuminated as brightly as the exterior. This seems to have been intended as a reductio ad absurdum. Arago, undeterred, assembled an experiment with an obstacle 2 mm in diameter—and there, in the center of the shadow, was Poisson's spot.[152][142]
The unanimous [142][153] report of the committee,[154] read at the meeting of the Académie on 15 March 1819,[155][156][157] awarded the prize to "the memoir marked no. 2, and bearing as epigraph: Natura simplex et fecunda". [158][159] At the same meeting,[160]: 427 after the judgment was delivered, the president of the Académie opened a sealed note accompanying the memoir, revealing the author as Fresnel.[161] The award was announced at the public meeting of the Académie a week later, on 22 March.[160]: 432
Arago's verification of Poisson's counter-intuitive prediction passed into folklore as if it had decided the prize.[162][163] That view, however, is not supported by the judges' report, which gave the matter only two sentences in the penultimate paragraph.[164] Neither did Fresnel's triumph immediately convert Laplace, Biot, and Poisson to the wave theory,[165] for at least four reasons. First, although the professionalization of science in France had established common standards, it was one thing to acknowledge a piece of research as meeting those standards, and another thing to regard it as conclusive.[49] Second, it was possible to interpret Fresnel's integrals as rules for combining rays. Arago even encouraged that interpretation, presumably in order to minimize resistance to Fresnel's ideas.[166][152] Even Biot began teaching the Huygens-Fresnel principle without committing himself to a wave basis.[167][168] Third, Fresnel's theory did not adequately explain the mechanism of generation of secondary waves or why they had any significant angular spread; this issue particularly bothered Poisson.[169][170][163] Fourth, the question that most exercised optical physicists at that time was not diffraction, but polarization—on which Fresnel had been working, but was yet to make his critical breakthrough.
Polarization
Background: Emissionism and selectionism
An emission theory of light was one that regarded the propagation of light as the transport of some kind of matter. While the corpuscular theory was obviously an emission theory, the converse did not follow: in principle, one could be an emissionist without being a corpuscularist. This was convenient because, beyond the ordinary laws of reflection and refraction, emissionists never managed to make testable quantitative predictions from a theory of forces acting on corpuscles of light. But they did make quantitative predictions from the premises that rays were countable objects, which were conserved in their interactions with matter (except absorbent media), and which had particular orientations with respect to their directions of propagation. According to this framework, polarization and the related phenomena of double refraction and partial reflection involved altering the orientations of the rays and/or selecting them according to orientation, and the state of polarization of a beam (a bundle of rays) was a question of how many rays were in what orientations: in a fully polarized beam, the orientations were all the same. This approach, which Jed Buchwald has called selectionism, was pioneered by Malus and diligently pursued by Biot.[171][172][42]: 110–113
Fresnel, in contrast, decided to introduce polarization into interference experiments.
Interference of polarized light, chromatic polarization (1816–21)
In July or August 1816, Fresnel discovered that when a birefringent crystal produced two images of a single slit, he could not obtain the usual two-slit interference pattern, even if he compensated for the different propagation times. A more general experiment, suggested by Arago, found that if the two beams of a double-slit device were separately polarized, the interference pattern appeared and disappeared as the polarization of one beam was rotated, giving full interference for parallel polarizations, but no interference for perpendicular polarizations ().[173][174][175] These experiments, among others, were eventually reported in a brief memoir published in 1819 and later translated into English.[176]
In a memoir drafted on 30 August 1816 and revised on 6 October, Fresnel reported an experiment in which he placed two matching thin laminae in a double-slit apparatus—one over each slit, with their optic axes perpendicular—and obtained two interference patterns offset in opposite directions, with perpendicular polarizations. This, in combination with the previous findings, meant that each lamina split the incident light into perpendicularly polarized components with different velocities—just like a normal (thick) birefringent crystal, and contrary to Biot's "mobile polarization" hypothesis.[177][178]
Accordingly, in the same memoir, Fresnel offered his first attempt at a wave theory of chromatic polarization. When polarized light passed through a crystal lamina, it was split into ordinary and extraordinary waves (with intensities described by Malus's law), and these were perpendicularly polarized and therefore did not interfere, so that no colors were produced (yet). But if they then passed through an analyzer (second polarizer), their polarizations were brought into alignment (with intensities again modified according to Malus's law), and they would interfere.[174] This explanation, by itself, predicts that if the analyzer is rotated 90°, the ordinary and extraordinary waves simply switch roles, so that if the analyzer takes the form of a calcite crystal, the two images of the lamina should be of the same hue (this issue is revisited below). But in fact, as Arago and Biot had found, they are of complementary colors. To correct the prediction, Fresnel proposed a phase-inversion rule whereby one of the constituent waves of one of the two images suffered an additional 180° phase shift on its way through the lamina. This inversion was a weakness in the theory relative to Biot's, as Fresnel acknowledged,[179] although the rule specified which of the two images had the inverted wave.[180] Moreover, Fresnel could deal only with special cases, because he had not yet solved the problem of superposing sinusoidal functions with arbitrary phase differences due to propagation at different velocities through the lamina.[181]
He solved that problem in a "supplement" signed on 15 January 1818 [125] (mentioned above). In the same document, he accommodated Malus's law by proposing an underlying law: that if polarized light is incident on a birefringent crystal with its optic axis at an angle θ to the "plane of polarization", the ordinary and extraordinary vibrations (as functions of time) are scaled by the factors cos θ and sin θ, respectively. Although modern readers easily interpret these factors in terms of perpendicular components of a transverse oscillation, Fresnel did not (yet) explain them that way. Hence he still needed the phase-inversion rule. He applied all these principles to a case of chromatic polarization not covered by Biot's formulae, involving two successive laminae with axes separated by 45°, and obtained predictions that disagreed with Biot's experiments (except in special cases) but agreed with his own.[182][183]
Fresnel applied the same principles to the standard case of chromatic polarization, in which one birefringent lamina was sliced parallel to its axis and placed between a polarizer and an analyzer. If the analyzer took the form of a thick calcite crystal with its axis in the plane of polarization, Fresnel predicted that the intensities of the ordinary and extraordinary images of the lamina were respectively proportional to
where is the angle from the initial plane of polarization to the optic axis of the lamina, is the angle from the initial plane of polarization to the plane of polarization of the final ordinary image, and is the phase lag of the extraordinary wave relative to the ordinary wave due to the difference in propagation times through the lamina. The terms in are the frequency-dependent terms and explain why the lamina must be thin in order to produce discernible colors: if the lamina is too thick, will pass through too many cycles as the frequency varies through the visible range, and the eye (which divides the visible spectrum into only three bands) will not be able to resolve the cycles.
From these equations it is easily verified that for all , so that the colors are complementary. Without the phase-inversion rule, there would be a plus sign in front of the last term in the second equation, so that the -dependent term would be the same in both equations, implying (incorrectly) that the colors were of the same hue.
These equations were included in an undated note that Fresnel gave to Biot,[184] to which Biot added a few lines of his own. If we substitute
- and
then Fresnel's formulae can be rewritten as
which are none other than Biot's empirical formulae of 1812,[185][186] except that Biot interpreted and as the "unaffected" and "affected" selections of the rays incident on the lamina. If Biot's substitutions were accurate, they would imply that his experimental results were more fully explained by Fresnel's theory than by his own.
Arago delayed reporting on Fresnel's works on chromatic polarization until June 1821, when he used them in a broad attack on Biot's theory. In his written response, Biot protested that Arago's attack went beyond the proper scope of a report on the nominated works of Fresnel. But Biot also claimed that the substitutions for and , and therefore Fresnel's expressions for and , were empirically wrong because when Fresnel's intensities of spectral colors were mixed according to Newton's rules, the squared cosine and sine functions varied too smoothly to account for the observed sequence of colors. That claim drew a written reply from Fresnel,[187] who disputed whether the colors changed as abruptly as Biot claimed,[188] and whether the human eye could judge color with sufficient objectivity for the purpose. On the latter question, Fresnel pointed out that different observers may give different names to the same color. Furthermore, he said, a single observer can only compare colors side by side; and even if they are judged to be the same, the identity is of sensation, not necessarily of composition.[189] Fresnel's oldest and strongest point—that thin crystals were subject to the same laws as thick ones and did not need or allow a separate theory—Biot left unanswered. Arago and Fresnel were seen to have won the debate.[190][191][192]
Moreover, by this time Fresnel had a new, simpler explanation of his equations on chromatic polarization.
Breakthrough: Pure transverse waves (1821)

In the draft memoir of 30 August 1816, Fresnel mentioned two hypotheses—one of which he attributed to Ampère—by which the non-interference of orthogonally polarized beams could be explained if polarized light waves were partly transverse. But Fresnel could not develop either of these ideas into a comprehensive theory. As early as September 1816, according to his later account,[193] he realized that the non-interference of orthogonally polarized beams, together with the phase-inversion rule in chromatic polarization, would be most easily explained if the waves were purely transverse, and Ampère "had the same thought" on the phase-inversion rule. But that would raise a new difficulty: as natural light seemed to be unpolarized and its waves were therefore presumed to be longitudinal, one would need to explain how the longitudinal component of vibration disappeared on polarization, and why it did not reappear when polarized light was reflected or refracted obliquely by a glass plate.[194][193][195][196]
Independently, on 12 January 1817, Young wrote to Arago (in English) noting that a transverse vibration would constitute a polarization, and that if two longitudinal waves crossed at a significant angle, they could not cancel without leaving a residual transverse vibration.[197] Young repeated this idea in an article published in a supplement to the Encyclopædia Britannica in February 1818, in which he added that Malus's law would be explained if polarization consisted in a transverse motion.[198]: 333–335
Thus Fresnel, by his own testimony, may not have been the first person to suspect that light waves could have a transverse component, or that polarized waves were exclusively transverse. And it was Young, not Fresnel, who first published the idea that polarization depends on the orientation of a transverse vibration. But these incomplete theories had not reconciled the nature of polarization with the apparent existence of unpolarized light; that achievement was to be Fresnel's alone.
In a note that Buchwald dates in the summer of 1818, Fresnel entertained the idea that unpolarized waves could have vibrations of the same energy and obliquity, with their orientations distributed uniformly about the wave-normal, and that the degree of polarization was the degree of non-uniformity in the distribution. Two pages later he noted, apparently for the first time in writing, that his phase-inversion rule and the non-interference of orthogonally polarized beams would be easily explained if the vibrations of fully polarized waves were "perpendicular to the normal to the wave"—that is, purely transverse.[199][200]
But if he could account for lack of polarization by averaging out the transverse component, he did not also need to assume a longitudinal component. It was enough to suppose that light waves are purely transverse, hence always polarized in the sense of having a particular transverse orientation, and that the "unpolarized" state of natural or "direct" light is due to rapid and random variations in that orientation, in which case two coherent portions of "unpolarized" light will still interfere because their orientations will be synchronized.
It is not known exactly when Fresnel made this last step, because there is no relevant documentation from 1820 or early 1821 [201] (perhaps because he was too busy working on lighthouse-lens prototypes; ). But he first published the idea in a paper on "Calcul des teintes ..." ("calculation of the tints ..."), serialized in Arago's Annales for May, June, and July 1821.[202] In the first installment, Fresnel described "direct" (unpolarized) light as "the rapid succession of systems of waves polarized in all directions",[203][204] and gave what is essentially the modern explanation of chromatic polarization, albeit in terms of the analogy between polarization and the resolution of forces in a plane, mentioning transverse waves only in a footnote. The introduction of transverse waves into the main argument was delayed to the second installment, in which he revealed the suspicion that he and Ampère had harbored since 1816, and the difficulty it raised.[205][193] He continued:
It has only been for a few months that in meditating more attentively on this subject, I have realized that it was very probable that the oscillatory movements of light waves were executed solely along the plane of these waves, for direct light as well as for polarized light.[206][Note 5]
According to this new view, he wrote, "the act of polarization consists not in creating these transverse movements, but in decomposing them into two fixed perpendicular directions and in separating the two components."[207]
While selectionists could insist on interpreting Fresnel's diffraction integrals in terms of discrete, countable rays, they could not do the same with his theory of polarization. For a selectionist, the state of polarization of a beam concerned the distribution of orientations over the population of rays, and that distribution was presumed to be static. For Fresnel, the state of polarization of a beam concerned the variation of a displacement over time. That displacement might be constrained but was not static, and rays were geometric constructions, not countable objects. The conceptual gap between the wave theory and selectionism had become unbridgeable.[208]
The other difficulty posed by pure transverse waves, of course, was the apparent implication that the aether was an elastic solid, except that, unlike other elastic solids, it was incapable of transmitting longitudinal waves.[Note 6] The wave theory was cheap on assumptions, but its latest assumption was expensive on credulity.[209] If that assumption was to be widely entertained, its explanatory power would need to be impressive.
Partial reflection (1821)
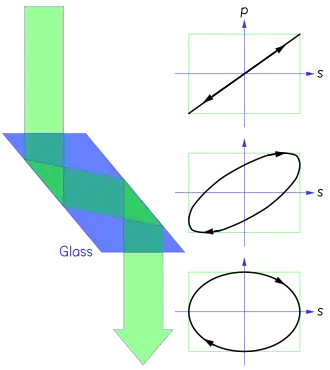
In the second installment of "Calcul des teintes" (June 1821), Fresnel supposed, by analogy with sound waves, that the density of the aether in a refractive medium was inversely proportional to the square of the wave velocity, and therefore directly proportional to the square of the refractive index. For reflection and refraction at the surface between two isotropic media of different indices, Fresnel decomposed the transverse vibrations into two perpendicular components, now known as the s and p components, which are parallel to the surface and the plane of incidence, respectively; in other words, the s and p components are respectively square and parallel to the plane of incidence.[Note 7] For the s component, Fresnel supposed that the interaction between the two media was analogous to an elastic collision, and obtained a formula for what we now call the reflectivity: the ratio of the reflected intensity to the incident intensity. The predicted reflectivity was non-zero at all angles.[210][211]
The third installment (July 1821) was a short "postscript" in which Fresnel announced that he had found, by a "mechanical solution", a formula for the reflectivity of the p component, which predicted that the reflectivity was zero at the Brewster angle. So polarization by reflection had been accounted for—but with the proviso that the direction of vibration in Fresnel's model was perpendicular to the plane of polarization as defined by Malus. (On the ensuing controversy, see Plane of polarization.) The technology of the time did not allow the s and p reflectivities to be measured accurately enough to test Fresnel's formulae at arbitrary angles of incidence. But the formulae could be rewritten in terms of what we now call the reflection coefficient: the signed ratio of the reflected amplitude to the incident amplitude. Then, if the plane of polarization of the incident ray was at 45° to the plane of incidence, the tangent of the corresponding angle for the reflected ray was obtainable from the ratio of the two reflection coefficients, and this angle could be measured. Fresnel had measured it for a range of angles of incidence, for glass and water, and the agreement between the calculated and measured angles was better than 1.5° in all cases.[212][213]
Fresnel gave details of the "mechanical solution" in a memoir read to the Académie des Sciences on 7 January 1823.[214] Conservation of energy was combined with continuity of the tangential vibration at the interface.[215][216] The resulting formulae for the reflection coefficients and reflectivities became known as the Fresnel equations. The reflection coefficients for the s and p polarizations are most succinctly expressed as
- and
where and are the angles of incidence and refraction; these equations are known respectively as Fresnel's sine law and Fresnel's tangent law.[217][218][219] By allowing the coefficients to be complex, Fresnel even accounted for the different phase shifts of the s and p components due to total internal reflection.[220][221][222]
This success inspired James MacCullagh and Augustin-Louis Cauchy, beginning in 1836, to analyze reflection from metals by using the Fresnel equations with a complex refractive index.[223][224] The same technique is applicable to non-metallic opaque media. With these generalizations, the Fresnel equations can predict the appearance of a wide variety of objects under illumination—for example, in computer graphics ().
Circular and elliptical polarization, optical rotation (1822)

In a memoir dated 9 December 1822,[225] Fresnel coined the terms linear polarization (French: polarisation rectiligne) for the simple case in which the perpendicular components of vibration are in phase or 180° out of phase, circular polarization for the case in which they are of equal magnitude and a quarter-cycle (±90°) out of phase, and elliptical polarization for other cases in which the two components have a fixed amplitude ratio and a fixed phase difference. He then explained how optical rotation could be understood as a species of birefringence. Linearly polarized light could be resolved into two circularly polarized components rotating in opposite directions. If these components propagated at slightly different speeds, the phase difference between them—and therefore the direction of their linearly polarized resultant—would vary continuously with distance.[226]
These concepts called for a redefinition of the distinction between polarized and unpolarized light. Before Fresnel, it was thought that polarization could vary in direction, and in degree (e.g., due to variation in the angle of reflection off a transparent body), and that it could be a function of color (chromatic polarization), but not that it could vary in kind. Hence it was thought that the degree of polarization was the degree to which the light could be suppressed by an analyzer with the appropriate orientation. Light that had been converted from linear to elliptical or circular polarization (e.g., by passage through a crystal lamina, or by total internal reflection) was described as partly or fully "depolarized" because of its behavior in an analyzer. After Fresnel, the defining feature of polarized light was that the perpendicular components of vibration had a fixed ratio of amplitudes and a fixed difference in phase. By that definition, elliptically or circularly polarized light is fully polarized although it cannot be fully suppressed by an analyzer alone.[227] The conceptual gap between the wave theory and selectionism had widened again.
Total internal reflection (1817–23)
By 1817 it had been discovered by Brewster,[228] but not adequately reported,[229][198]: 324 that plane-polarized light was partly depolarized by total internal reflection if initially polarized at an acute angle to the plane of incidence. Fresnel rediscovered this effect and investigated it by including total internal reflection in a chromatic-polarization experiment. With the aid of his first theory of chromatic polarization, he found that the apparently depolarized light was a mixture of components polarized parallel and perpendicular to the plane of incidence, and that the total reflection introduced a phase difference between them.[177] Choosing an appropriate angle of incidence (not yet exactly specified) gave a phase difference of 1/8 of a cycle (45°). Two such reflections from the "parallel faces" of "two coupled prisms" gave a phase difference of 1/4 of a cycle (90°). These findings were contained in a memoir submitted to the Académie on 10 November 1817 and read a fortnight later. An undated marginal note indicates that the two coupled prisms were later replaced by a single "parallelepiped in glass"—now known as a Fresnel rhomb.[230]
This was the memoir whose "supplement",[125] dated January 1818, contained the method of superposing sinusoidal functions and the restatement of Malus's law in terms of amplitudes. In the same supplement, Fresnel reported his discovery that optical rotation could be emulated by passing the polarized light through a Fresnel rhomb (still in the form of "coupled prisms"), followed by an ordinary birefringent lamina sliced parallel to its axis, with the axis at 45° to the plane of reflection of the Fresnel rhomb, followed by a second Fresnel rhomb at 90° to the first.[231] In a further memoir read on 30 March,[232] Fresnel reported that if polarized light was fully "depolarized" by a Fresnel rhomb—now described as a parallelepiped—its properties were not further modified by a subsequent passage through an optically rotating medium or device.
The connection between optical rotation and birefringence was further explained in 1822, in the memoir on elliptical and circular polarization.[225] This was followed by the memoir on reflection, read in January 1823, in which Fresnel quantified the phase shifts in total internal reflection, and thence calculated the precise angle at which a Fresnel rhomb should be cut in order to convert linear polarization to circular polarization. For a refractive index of 1.51, there were two solutions: about 48.6° and 54.6°.[214]: 760
Double refraction
Background: Uniaxial and biaxial crystals; Biot's laws
When light passes through a slice of calcite cut perpendicular to its optic axis, the difference between the propagation times of the ordinary and extraordinary waves has a second-order dependence on the angle of incidence. If the slice is observed in a highly convergent cone of light, that dependence becomes significant, so that a chromatic-polarization experiment will show a pattern of concentric rings. But most minerals, when observed in this manner, show a more complicated pattern of rings involving two foci and a lemniscate curve, as if they had two optic axes.[233][234] The two classes of minerals naturally become known as uniaxal and biaxal—or, in later literature, uniaxial and biaxial.
In 1813, Brewster observed the simple concentric pattern in "beryl, emerald, ruby &c." The same pattern was later observed in calcite by Wollaston, Biot, and Seebeck. Biot, assuming that the concentric pattern was the general case, tried to calculate the colors with his theory of chromatic polarization, and succeeded better for some minerals than for others. In 1818, Brewster belatedly explained why: seven of the twelve minerals employed by Biot had the lemniscate pattern, which Brewster had observed as early as 1812; and the minerals with the more complicated rings also had a more complicated law of refraction.[235]
In a uniform crystal, according to Huygens's theory, the secondary wavefront that expands from the origin in unit time is the ray-velocity surface—that is, the surface whose "distance" from the origin in any direction is the ray velocity in that direction. In calcite, this surface is two-sheeted, consisting of a sphere (for the ordinary wave) and an oblate spheroid (for the extraordinary wave) touching each other at opposite points of a common axis—touching at the north and south poles, if we may use a geographic analogy. But according to Malus's corpuscular theory of double refraction, the ray velocity was proportional to the reciprocal of that given by Huygens's theory, in which case the velocity law was of the form
where and were the ordinary and extraordinary ray velocities according to the corpuscular theory, and was the angle between the ray and the optic axis.[236] By Malus's definition, the plane of polarization of a ray was the plane of the ray and the optic axis if the ray was ordinary, or the perpendicular plane (containing the ray) if the ray was extraordinary. In Fresnel's model, the direction of vibration was normal to the plane of polarization. Hence, for the sphere (the ordinary wave), the vibration was along the lines of latitude (continuing the geographic analogy); and for the spheroid (the extraordinary wave), the vibration was along the lines of longitude.
On 29 March 1819,[237] Biot presented a memoir in which he proposed simple generalizations of Malus's rules for a crystal with two axes, and reported that both generalizations seemed to be confirmed by experiment. For the velocity law, the squared sine was replaced by the product of the sines of the angles from the ray to the two axes (Biot's sine law). And for the polarization of the ordinary ray, the plane of the ray and the axis was replaced by the plane bisecting the dihedral angle between the two planes each of which contained the ray and one axis (Biot's dihedral law).[238][239] Biot's laws meant that a biaxial crystal with axes at a small angle, cleaved in the plane of those axes, behaved nearly like a uniaxial crystal at near-normal incidence; this was fortunate because gypsum, which had been used in chromatic-polarization experiments, is biaxial.[240]
First memoir and supplements (1821–22)
Until Fresnel turned his attention to biaxial birefringence, it was assumed that one of the two refractions was ordinary, even in biaxial crystals.[241] But, in a memoir submitted [Note 8] on 19 November 1821,[242] Fresnel reported two experiments on topaz showing that neither refraction was ordinary in the sense of satisfying Snell's law; that is, neither ray was the product of spherical secondary waves.[243]
The same memoir contained Fresnel's first attempt at the biaxial velocity law. For calcite, if we interchange the equatorial and polar radii of Huygens's oblate spheroid while preserving the polar direction, we obtain a prolate spheroid touching the sphere at the equator. A plane through the center/origin cuts this prolate spheroid in an ellipse whose major and minor semi-axes give the magnitudes of the extraordinary and ordinary ray velocities in the direction normal to the plane, and (said Fresnel) the directions of their respective vibrations. The direction of the optic axis is the normal to the plane for which the ellipse of intersection reduces to a circle. So, for the biaxial case, Fresnel simply replaced the prolate spheroid with a triaxial ellipsoid,[244] which was to be sectioned by a plane in the same way. In general there would be two planes passing through the center of the ellipsoid and cutting it in a circle, and the normals to these planes would give two optic axes. From the geometry, Fresnel deduced Biot's sine law (with the ray velocities replaced by their reciprocals).[245][246]
The ellipsoid indeed gave the correct ray velocities (although the initial experimental verification was only approximate). But it did not give the correct directions of vibration, for the biaxial case or even for the uniaxial case, because the vibrations in Fresnel's model were tangential to the wavefront—which, for an extraordinary ray, is not generally normal to the ray. This error (which is small if, as in most cases, the birefringence is weak) was corrected in an "extract" that Fresnel read to the Académie a week later, on 26 November. Starting with Huygens's spheroid, Fresnel obtained a 4th-degree surface which, when sectioned by a plane as above, would yield the wave-normal velocities for a wavefront in that plane, together with their vibration directions. For the biaxial case, he generalized the equation to obtain a surface with three unequal principal dimensions; this he subsequently called the "surface of elasticity". But he retained the earlier ellipsoid as an approximation, from which he deduced Biot's dihedral law.[247]
Fresnel's initial derivation of the surface of elasticity had been purely geometric, and not deductively rigorous. His first attempt at a mechanical derivation, contained in a "supplement" dated 13 January 1822, assumed that (i) there were three mutually perpendicular directions in which a displacement produced a reaction in the same direction, (ii) the reaction was otherwise a linear function of the displacement, and (iii) the radius of the surface in any direction was the square root of the component, in that direction, of the reaction to a unit displacement in that direction. The last assumption recognized the requirement that if a wave was to maintain a fixed direction of propagation and a fixed direction of vibration, the reaction must not be outside the plane of those two directions.[248]
In the same supplement, Fresnel considered how he might find, for the biaxial case, the secondary wavefront that expands from the origin in unit time—that is, the surface that reduces to Huygens's sphere and spheroid in the uniaxial case. He noted that this "wave surface" (surface de l'onde)[249] is tangential to all possible plane wavefronts that could have crossed the origin one unit of time ago, and he listed the mathematical conditions that it must satisfy. But he doubted the feasibility of deriving the surface from those conditions.[250][251][252]
In a "second supplement",[253] Fresnel eventually exploited two related facts: (i) the "wave surface" was also the ray-velocity surface, which could be obtained by sectioning the ellipsoid that he had initially mistaken for the surface of elasticity, and (ii) the "wave surface" intersected each plane of symmetry of the ellipsoid in two curves: a circle and an ellipse. Thus he found that the "wave surface" is described by the 4th-degree equation
where and are the propagation speeds in directions normal to the coordinate axes for vibrations along the axes (the ray and wave-normal speeds being the same in those special cases).[254][255][256] Later commentators[257]: 19 put the equation in the more compact and memorable form
Earlier in the "second supplement", Fresnel modeled the medium as an array of point-masses and found that the force-displacement relation was described by a symmetric matrix, confirming the existence of three mutually perpendicular axes on which the displacement produced a parallel force.[258][259] Later in the document, he noted that in a biaxial crystal, unlike a uniaxial crystal, the directions in which there is only one wave-normal velocity are not the same as those in which there is only one ray velocity.[260][261] Nowadays we refer to the former directions as the optic axes or binormal axes, and the latter as the ray axes or biradial axes ().[262]
Fresnel's "second supplement" was signed on 31 March 1822 and submitted the next day—less than a year after the publication of his pure-transverse-wave hypothesis, and just less than a year after the demonstration of his prototype eight-panel lighthouse lens ().
Second memoir (1822–26)
Having presented the pieces of his theory in roughly the order of discovery, Fresnel needed to rearrange the material so as to emphasize the mechanical foundations;[263][264][265] and he still needed a rigorous treatment of Biot's dihedral law.[266] He attended to these matters in his "second memoir" on double refraction,[267] published in the Recueils of the Académie des Sciences for 1824; this was not actually printed until late 1827, a few months after his death.[268] In this work, having established the three perpendicular axes on which a displacement produces a parallel reaction,[269] and thence constructed the surface of elasticity,[270] he showed that Biot's dihedral law is exact provided that the binormals are taken as the optic axes, and the wave-normal direction as the direction of propagation.[271][272]
As early as 1822, Fresnel discussed his perpendicular axes with Cauchy. Acknowledging Fresnel's influence, Cauchy went on to develop the first rigorous theory of elasticity of non-isotropic solids (1827), hence the first rigorous theory of transverse waves therein (1830)—which he promptly tried to apply to optics.[273][274][275] The ensuing difficulties drove a long competitive effort to find an accurate mechanical model of the aether.[276][277][278] Fresnel's own model was not dynamically rigorous; for example, it deduced the reaction to a shear strain by considering the displacement of one particle while all others were fixed, and it assumed that the stiffness determined the wave velocity as in a stretched string, whatever the direction of the wave-normal. But it was enough to enable the wave theory to do what selectionist theory could not: generate testable formulae covering a comprehensive range of optical phenomena, from mechanical assumptions.[279][280][281]
Photoelasticity, multiple-prism experiments (1822)

In 1815, Brewster reported that colors appear when a slice of isotropic material, placed between crossed polarizers, is mechanically stressed. Brewster himself immediately and correctly attributed this phenomenon to stress-induced birefringence [282][283]—now known as photoelasticity.
In a memoir read in September 1822, Fresnel announced that he had verified Brewster's diagnosis more directly, by compressing a combination of glass prisms so severely that one could actually see a double image through it. In his experiment, Fresnel lined up seven 45°–90°–45° prisms, short side to short side, with their 90° angles pointing in alternating directions. Two half-prisms were added at the ends to make the whole assembly rectangular. The prisms were separated by thin films of turpentine (térébenthine) to suppress internal reflections, allowing a clear line of sight along the row. When the four prisms with similar orientations were compressed in a vise across the line of sight, an object viewed through the assembly produced two images with perpendicular polarizations, with an apparent spacing of 1.5 mm at one metre.[284][285]
At the end of that memoir, Fresnel predicted that if the compressed prisms were replaced by (unstressed) monocrystalline quartz prisms with matching directions of optical rotation, and with their optic axes aligned along the row, an object seen by looking along the common optic axis would give two images, which would seem unpolarized when viewed through an analyzer but, when viewed through a Fresnel rhomb, would be polarized at ±45° to the plane of reflection of the rhomb (indicating that they were initially circularly polarized in opposite directions). This would show directly that optical rotation is a form of birefringence. In the memoir of December 1822, in which he introduced the term circular polarization, he reported that he had confirmed this prediction using only one 14°–152°–14° prism and two glass half-prisms. But he obtained a wider separation of the images by replacing the glass half-prism with quartz half-prisms whose rotation was opposite to that of the 14°–152°–14° prism. He added in passing that one could further increase the separation by increasing the number of prisms.[286]
Reception
For the supplement to Riffault's translation of Thomson's System of Chemistry, Fresnel was chosen to contribute the article on light. The resulting 137-page essay, titled De la Lumière (On Light),[287] was apparently finished in June 1821 and published by February 1822.[288] With sections covering the nature of light, diffraction, thin-film interference, reflection and refraction, double refraction and polarization, chromatic polarization, and modification of polarization by reflection, it made a comprehensive case for the wave theory to a readership that was not restricted to physicists.[289]
To examine Fresnel's first memoir and supplements on double refraction, the Académie des Sciences appointed Ampère, Arago, Fourier, and Poisson.[290] Their report,[291] of which Arago was clearly the main author,[281] was delivered at the meeting of 19 August 1822. Then, in the words of Émile Verdet, as translated by Ivor Grattan-Guinness:
Immediately after the reading of the report, Laplace took the floor, and ... proclaimed the exceptional importance of the work which had just been reported: he congratulated the author on his steadfastness and his sagacity which had led him to discover a law which had escaped the cleverest, and, anticipating somewhat the judgement of posterity, declared that he placed these researches above everything that had been communicated to the Académie for a long time.[292][293]
Whether Laplace was announcing his conversion to the wave theory—at the age of 73—is uncertain. Grattan-Guinness entertained the idea.[294] Buchwald, noting that Arago failed to explain that the "ellipsoid of elasticity" did not give the correct planes of polarization, suggests that Laplace may have merely regarded Fresnel's theory as a successful generalization of Malus's ray-velocity law, embracing Biot's laws.[295]

In the following year, Poisson, who did not sign Arago's report, disputed the possibility of transverse waves in the aether. Starting from assumed equations of motion of a fluid medium, he noted that they did not give the correct results for partial reflection and double refraction—as if that were Fresnel's problem rather than his own—and that the predicted waves, even if they were initially transverse, became more longitudinal as they propagated. In reply Fresnel noted, inter alia, that the equations in which Poisson put so much faith did not even predict viscosity. The implication was clear: given that the behavior of light had not been satisfactorily explained except by transverse waves, it was not the responsibility of the wave-theorists to abandon transverse waves in deference to pre-conceived notions about the aether; rather, it was the responsibility of the aether modelers to produce a model that accommodated transverse waves.[296][297] According to Robert H. Silliman, Poisson eventually accepted the wave theory shortly before his death in 1840.[298]
Among the French, Poisson's reluctance was an exception. According to Eugene Frankel, "in Paris no debate on the issue seems to have taken place after 1825. Indeed, almost the entire generation of physicists and mathematicians who came to maturity in the 1820s—Pouillet, Savart, Lamé, Navier, Liouville, Cauchy—seem to have adopted the theory immediately." Fresnel's other prominent French opponent, Biot, appeared to take a neutral position in 1830, and eventually accepted the wave theory—possibly by 1846 and certainly by 1858.[299]
In 1826, the British astronomer John Herschel, who was working on a book-length article on light for the Encyclopædia Metropolitana, addressed three questions to Fresnel concerning double refraction, partial reflection, and their relation to polarization. The resulting article,[300] titled simply "Light", was highly sympathetic to the wave theory, although not entirely free of selectionist language. It was circulating privately by 1828 and was published in 1830.[301][302] Meanwhile, Young's translation of Fresnel's De la Lumière was published in installments from 1827 to 1829.[303][304] George Biddell Airy, the former Lucasian Professor at Cambridge and future Astronomer Royal, unreservedly accepted the wave theory by 1831.[305] In 1834, he famously calculated the diffraction pattern of a circular aperture from the wave theory,[306] thereby explaining the limited angular resolution of a perfect telescope (). By the end of the 1830s, the only prominent British physicist who held out against the wave theory was Brewster, whose objections included the difficulty of explaining photochemical effects and (in his opinion) dispersion.[307]
A German translation of De la Lumière was published in installments in 1825 and 1828. The wave theory was adopted by Fraunhofer in the early 1820s and by Franz Ernst Neumann in the 1830s, and then began to find favor in German textbooks.[308][309]
The economy of assumptions under the wave theory was emphasized by William Whewell in his History of the Inductive Sciences, first published in 1837. In the corpuscular system, "every new class of facts requires a new supposition", whereas in the wave system, a hypothesis devised in order to explain one phenomenon is then found to explain or predict others. In the corpuscular system there is "no unexpected success, no happy coincidence, no convergence of principles from remote quarters"; but in the wave system, "all tends to unity and simplicity". [310]
Hence, in 1850, when Foucault and Fizeau found by experiment that light travels more slowly in water than in air, in accordance with the wave explanation of refraction and contrary to the corpuscular explanation, the result came as no surprise.[311][312][313]
Notes
- ^ Newton (1730) observed feathers acting as reflection gratings and as a transmission gratings, but classified the former case under thin plates (p. 252), and the latter, more vaguely, under inflection (p. 322). In retrospect, the latter experiment (p. 322, end of Obs. 2) is dangerous to eyesight and should not be repeated as written.
- ^ The story that Ampère lost the essay (propagated from Boutry 1948, p. 593?) is implicitly contradicted by Darrigol (2012, p. 198), Buchwald (1989, p. 117), Mérimée's letter to Fresnel dated 20 December 1814 (in Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 2, pp. 830–831), and two footnotes in Fresnel's collected works (Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, pp. xxix–xxx, note 4, and p. 6n).
- ^ "Young's book", which Fresnel distinguished from the Philosophical Transactions, is presumably A Course of Lectures on Natural Philosophy and the Mechanical Arts (2 volumes, 1807). In vol. 1, the relevant illustrations are Plate XX (facing p. 777), including the famous two-source interference pattern (Fig. 267), and Plate XXX (facing p. 787), including the hyperbolic paths of the fringes in that pattern (Fig. 442) followed by sketches of other diffraction patterns and thin-plate patterns, with no visual hints on their physical causes. In vol. 2, which includes the Bakerian lectures from the Philosophical Transactions, Fig. 108 (p. 632) shows just one case of an undeviated direct ray intersecting a reflected ray.
- ^ Silliman (1967, p. 163) and Frankel (1976, p. 156) give the date of Arago's note on scintillation as 1814; but the sequence of events implies 1816, in agreement with Darrigol (2012, pp. 201, 290). Kipnis (1991, pp. 202–203, 206) proves the later date and explains the origin and propagation of the incorrect earlier date.
- ^ In the same installment, Fresnel acknowledged a letter from Young to Arago, dated 29 April 1818 (and lost before 1866), in which Young suggested that light waves could be analogous to waves on stretched strings. But Fresnel was dissatisfied with the analogy because it suggested both transverse and longitudinal modes of propagation and was hard to reconcile with a fluid medium (Silliman 1967, pp. 214–215; Fresnel, 1821a, §13).
- ^ Fresnel, in an effort to show that transverse waves were not absurd, suggested that the aether was a fluid comprising a lattice of molecules, adjacent layers of which would resist a sliding displacement up to a certain point, beyond which they would gravitate towards a new equilibrium. Such a medium, he thought, would behave as a solid for sufficiently small deformations, but as a perfect liquid for larger deformations. Concerning the lack of longitudinal waves, he further suggested that the layers offered incomparably greater resistance to a change of spacing than to a sliding motion (Silliman 1967, pp. 216–218; Fresnel, 1821a, §§ 11–12; cf. Fresnel, 1827, tr. Hobson, pp. 258–262).
- ^ The s originally comes from the German senkrecht, meaning perpendicular (to the plane of incidence).
- ^ In Fresnel's collected works (1866–70), a paper is said to have been "presented" ("présenté") if it was merely delivered to the Permanent Secretary of the Académie for witnessing or processing (cf. vol. 1, p. 487; vol. 2, pp. 261,308). In such cases this article prefers the generic word "submitted", to avoid the impression that the paper had a formal reading.
References
- ^ Huygens, 1690, tr. Thompson, pp. 20–21.
- ^ Newton, 1730, p. 362.
- ^ Huygens, 1690, tr. Thompson, pp. 22–38.
- ^ Darrigol 2012, pp. 93–94, 103.
- ^ Darrigol 2012, pp. 129–130, 258.
- ^ Huygens, 1690, tr. Thompson, pp. 52–105.
- ^ de Witte, A. J. (1 May 1959). "Equivalence of Huygens' Principle and Fermat's Principle in Ray Geometry". American Journal of Physics. 27 (5): 293–301. Bibcode:1959AmJPh..27..293D. doi:10.1119/1.1934839. ISSN 0002-9505.Erratum: In Fig. 7(b), each instance of "ray" should be "normal" (noted in vol. 27, no. 6, p. 387).
- ^ Young 1855, pp. 225–226, 229.
- ^ Darrigol 2012, pp. 62–64.
- ^ Darrigol 2012, p. 87.
- ^ Newton, Isaac (18 November 1672). "Mr. Isaac Newtons answer to some considerations upon his doctrine of light and colors; which doctrine was printed in Numb. 80 of these tracts". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. 7 (88): 5084–5103. doi:10.1098/rstl.1672.0051. ISSN 0261-0523. JSTOR 100964.
- ^ Darrigol 2012, pp. 53–56.
- ^ Huygens, 1690, tr. Thompson, p. 17.
- ^ Darrigol 2012, pp. 98–100.
- ^ Newton, 1730, p. 281.
- ^ Newton, 1730, p. 284.
- ^ Newton, 1730, pp. 283,287.
- ^ a b N. Kipnis, "Physical optics", in I. Grattan-Guinness (ed.), Companion Encyclopedia of the History and Philosophy of the Mathematical Sciences, JHU Press, 2003, vol. 2, pp. 1143–1152.
- ^ Newton, 1730, pp. 279, 281–282.
- ^ a b c T. Young, "On the Theory of Light and Colours" (Bakerian Lecture), Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society, vol. 92 (1802), pp. 12–48, read 12 November 1801.
- ^ Huygens, 1690, tr. Thompson, pp. 92–94. For simplicity, the above text describes a special case; Huygens's description has greater generality.
- ^ Newton, 1730, pp. 358–361.
- ^ Newton, 1730, pp. 373–374.
- ^ Newton, 1730, p. 363.
- ^ Newton, 1730, p. 356.
- ^ a b Buchwald, Jed Z. (1 December 1980). "Experimental investigations of double refraction from Huygens to Malus". Archive for History of Exact Sciences. 21 (4): 311–373. doi:10.1007/BF00595375. ISSN 1432-0657. As the author notes, alternative rules for the extraordinary refraction were offered by La Hire in 1710 and by Haüy in 1788 (see pp. 332–334, 335–337, respectively).
- ^ Frankel (1974) and Young (1855, pp. 225–228) debunk Laplace's claim to have established the existence of such a force. Fresnel (1827, tr. Hobson, pp. 239–241) more comprehensively addresses the mechanical difficulties of this claim. Admittedly, the particular statement that he attributes to Laplace is not found in the relevant passage from Laplace's writings (appended to Fresnel's memoir by the translator), which is similar to the passage previously demolished by Young; however, an equivalent statement is found in the works of Malus (Mémoires de Physique et de Chimie, de la Société d'Arcueil, vol. 2, 1809, p. 266, quoted in translation by Silliman 1967, p. 131).
- ^ Young 1855, pp. 228–232.
- ^ cf. Whewell 1857, p. 329
- ^ Darrigol 2012, pp. 191–192.
- ^ Silliman 1967, pp. 125–127.
- ^ Brewster, David (31 December 1815). "IX. On the laws which regulate the polarisation of light by reflexion from transparent bodies". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. 105: 125–159. doi:10.1098/rstl.1815.0010. ISSN 0261-0523. JSTOR 107362.
- ^ Darrigol 2012, p. 192.
- ^ Silliman 1967, p. 128.
- ^ Young 1855, pp. 249–250.
- ^ Young 1855, p. 233.
- ^ Levitt 2009, p. 37.
- ^ Darrigol 2012, pp. 193–194, 290.
- ^ Darrigol 2012, pp. 194–195 (ordinary intensity); Frankel 1976, p. 148 (both intensities).
- ^ Buchwald 1989, pp. 79–88.
- ^ Levitt 2009, pp. 33–54.
- ^ a b Buchwald, J Z (May 1989). "The battle between Arago and Biot over Fresnel". Journal of Optics. 20 (3): 109–117. Bibcode:1989JOpt...20..109B. doi:10.1088/0150-536X/20/3/002. ISSN 0150-536X.
- ^ Frankel 1976, pp. 149–150.
- ^ Buchwald 1989, pp. 99–103.
- ^ Darrigol 2012, pp. 195–196.
- ^ Frankel 1976, pp. 151–152.
- ^ Darrigol 2012, p. 196.
- ^ Young 1855, pp. 269–272.
- ^ a b Frankel, 1976, p. 176; cf. Silliman 1967, pp. 142–143.
- ^ Frankel 1976, p. 155.
- ^ 'martan' (author), "Eure (27)", Guide National des Maisons Natales, 30 May 2014.
- ^ Buchwald 1989, pp. 116–117.
- ^ Silliman 1967, pp. 40–45.
- ^ Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 2, p. 831.
- ^ Levitt 2009, p. 49.
- ^ Boutry 1948, pp. 594–595.
- ^ Presumably G.W. Jordan, The Observations of Newton Concerning the Inflections of Light; Accompanied by Other Observations Differing from His; and Appearing to Lead to a Change of His Theory of Light and Colours (also cited as New Observations concerning the Inflections of Light), London: T. Cadell Jr. & W. Davies, 1799; reviewed in T.G. Smollett (ed.), The Critical Review, Or, Annals of Literature (London), vol. 34, pp. 436–443 (April 1802).
- ^ Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, p. 6n; Kipnis 1991, p. 167; emphasis added.
- ^ a b Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, pp. 6–7.
- ^ Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, pp. xxxi (micrometer, locksmith [serrurier], supports), 6n (locksmith); Buchwald 1989, pp. 122 (honey drop), 125–126 (micrometer, with diagram); Boutry 1948, p. 595 and Levitt 2013, p. 40 (locksmith, honey drop, micrometer); Darrigol 2012, pp. 198–199 (locksmith, honey drop).
- ^ Buchwald 1989, pp. 122, 126.
- ^ Silliman 1967, pp. 147–149.
- ^ Levitt 2013, pp. 39, 239.
- ^ Kipnis 1991, p. 167.
- ^ Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, pp. 5–6.
- ^ Darrigol 2012, p. 198.
- ^ Silliman (1967, p. 146) identifies the brother as Fulgence, then in Paris; cf. Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, p. 7n.
- ^ Darrigol 2012, p. 199.
- ^ Buchwald 1989, pp. 119, 131–132.
- ^ Darrigol 2012, pp. 199–201.
- ^ Kipnis 1991, pp. 175–176.
- ^ a b Darrigol 2012, p. 201.
- ^ Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, pp. 48–49
- ^ Kipnis 1991, pp. 176–178.
- ^ a b Frankel 1976, p. 158.
- ^ Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, p. 9n.
- ^ Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, p. 38; italics added.
- ^ Buchwald 1989, pp. 137–139.
- ^ Young, 1807, vol. 1, p. 787 & Figs. 442,445.
- ^ Young 1855, pp. 180–181, 184.
- ^ Young to Arago (in English), 12 January 1817, in Young 1855, pp. 380–384, at p. 381; quoted in Silliman 1967, p. 171.
- ^ Newton, 1730, p. 321, Fig. 1, where the straight rays DG, EH, FI contribute to the curved path of a fringe, so that the same fringe is made by different rays at different distances from the obstacle (cf. Darrigol 2012, p. 101, Fig. 3.11 – where, in the caption, "1904" should be "1704" and "CFG" should be "CFI").
- ^ Kipnis 1991, pp. 204–205.
- ^ Silliman 1967, pp. 163–164.
- ^ a b Boutry 1948, p. 597.
- ^ Levitt 2013, pp. 41–43, 239.
- ^ Silliman 1967, pp. 165–166.
- ^ Buchwald 1989, p. 137.
- ^ Kipnis 1991, pp. 178, 207, 213.
- ^ Fresnel, 1816.
- ^ a b Frankel 1976, p. 159.
- ^ Kipnis 1991, pp. 166n, 214n.
- ^ Kipnis 1991, pp. 212–214.
- ^ Frankel 1976, pp. 159–160, 173.
- ^ Cf. Young, 1807, vol. 1, p. 777 & Fig. 267.
- ^ Darrigol 2012, p. 201; the letter is printed in Young 1855, pp. 376–378, and its conclusion is translated by Silliman (1967, p. 170).
- ^ Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, pp. 129–170.
- ^ Silliman 1967, pp. 177–179.
- ^ Darrigol 2012, pp. 201–203.
- ^ Buchwald 1989, pp. 134–135, 144–145.
- ^ Silliman 1967, pp. 176–177.
- ^ Silliman 1967, pp. 173–175.
- ^ Buchwald 1989, pp. 137–138.
- ^ Darrigol 2012, pp. 201–202.
- ^ Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, pp. 123–128 (Arago's announcement).
- ^ Levitt 2013, p. 43.
- ^ Boutry 1948, p. 599.
- ^ Arago, 1857, pp. 404–405.
- ^ Levitt 2013, pp. 28, 237.
- ^ Kipnis 1991, p. 218.
- ^ Buchwald & Fox 2013, p. 453.
- ^ a b Levitt 2013, p. 44.
- ^ Frankel (1976, pp. 160–161) and Grattan-Guinness (1990, p. 867) note that the topic was first proposed on 10 February 1817. Darrigol (2012, p. 203) alone says that the competition was "opened" on 17 March 1818. Prizes were offered in odd-numbered years for physics and in even-numbered years for mathematics (Frankel 1974, p. 224n).
- ^ Buchwald 1989, pp. 169–171.
- ^ Frankel 1976, p. 161.
- ^ Silliman 1967, pp. 183–184.
- ^ Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, pp. xxxvi–xxxvii.
- ^ Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, p. xxxv.
- ^ Silliman 2008, p. 166.
- ^ Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, pp. xxxv, xcvi.
- ^ Boutry 1948, pp. 599, 601.
- ^ Silliman (1967, p. 180) gives the starting date as 1 May 1818.
- ^ Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, p. xcvi; Arago, 1857, p. 466.
- ^ G. Ripley and C.A. Dana (eds.), "Fresnel, Augustin Jean", American Cyclopædia, 1879, vol. 7, pp. 486–489. Contrary to this entry (p. 486), calcite and quartz were not the only doubly refractive crystals known before Fresnel; see (e.g.) Young 1855, pp. 250 (written 1810) and pp. 262,266,277 (written 1814), and Lloyd 1834, pp. 376–377.
- ^ a b c A. Fresnel, "Supplément au Mémoire sur les modifications que la réflexion imprime à la lumière polarisée" ("Supplement to the Memoir on the modifications that reflection impresses on polarized light"), signed 15 January 1818, submitted for witnessing 19 January 1818; printed in Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, pp. 487–508.
- ^ Printed in Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, pp. 171–181.
- ^ Cf. Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, pp. 174–175; Buchwald 1989, pp. 157–158.
- ^ Abramowitz, Milton; Stegun, Irene, eds. (1972). "7 Error Function and Fresnel Integrals". Handbook of Mathematical Functions with Formulas, Graphs, and Mathematical Tables. National Bureau of Standards. Applied Mathematics Series 55. U.S. Department of Commerce.
- ^ Buchwald 1989, p. 167.
- ^ Buchwald & Fox 2013, p. 454.
- ^ Fresnel, 1818b.
- ^ See Fresnel, 1818b, in Mémoires de l'Académie Royale des Sciences ..., vol. V, p. 339n, and in Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, p. 247, note 1.
- ^ Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, p. 247.
- ^ Crew 1900, p. 79.
- ^ a b Levitt 2013, p. 46.
- ^ Crew 1900, pp. 101–108 (vector-like representation), 109 (no retrograde radiation), 110–111 (directionality and distance), 118–122 (derivation of integrals), 124–125 (maxima & minima), 129–131 (geometric shadow).
- ^ Darrigol 2012, pp. 204–205.
- ^ Crew 1900, pp. 127–128 (wavelength), 129–131 (half-plane), 132–135 (extrema, slit).
- ^ Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, pp. 350–355 (narrow strip).
- ^ Buchwald 1989, pp. 179–182.
- ^ Crew 1900, p. 144.
- ^ a b c Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, p. xlii.
- ^ Worrall 1989, p. 136.
- ^ Buchwald 1989, pp. 171, 183.
- ^ Levitt 2013, pp. 45–46.
- ^ Frankel 1976, p. 162.
- ^ However, Kipnis (1991, pp. 222–224) offers evidence that the unsuccessful entrant was Honoré Flaugergues (1755–1830?) and that the essence of his entry is contained in a "supplement" published in Journal de Physique, vol. 89 (September 1819), pp. 161–186.
- ^ Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, pp. 236–237.
- ^ Worrall 1989, pp. 139–140.
- ^ Cf. Worrall 1989, p. 141
- ^ B. Watson, Light: A Radiant History from Creation to the Quantum Age, New York: Bloomsbury, 2016.
- ^ a b Darrigol 2012, p. 205.
- ^ Worrall 1989, p. 141.
- ^ Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, pp. 229–246.
- ^ Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, p. 229, note 1.
- ^ Grattan-Guinness 1990, p. 867.
- ^ Levitt 2013, p. 47.
- ^ Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, p. 237.
- ^ Worrall 1989, p. 140.
- ^ a b Académie des Sciences, Proces-verbaux des séances de l'Académie tenues depuis la fondation de l'Institut jusqu'au mois d'août 1835, vol. VI (for 1816–19), Hendaye, Basses Pyrénées: Imprimerie de l'Observatoire d'Abbadia, 1915.
- ^ Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, p. 230n.
- ^ Worrall 1989, pp. 135–138.
- ^ a b Kipnis 1991, p. 220.
- ^ Worrall 1989, pp. 143–145. The printed version of the report also refers to a note (E), but this note concerns further investigations that took place after the prize was decided (Worrall 1989, pp. 145–146; Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, pp. 236, 245–246). According to Kipnis (1991, pp. 221–222), the real significance of Poisson's spot and its complement (at the center of the disk of light cast by a circular aperture) was that they concerned the intensities of fringes, whereas Fresnel's measurements had concerned only the positions of fringes; but, as Kipnis also notes, this issue was pursued only after the prize was decided.
- ^ Concerning their later views, see §Reception.
- ^ Buchwald 1989, pp. 183–184.
- ^ Kipnis 1991, pp. 219–220, 224, 232–233.
- ^ Grattan-Guinness 1990, p. 870.
- ^ Buchwald 1989, pp. 186–198.
- ^ Darrigol 2012, pp. 205–206.
- ^ Buchwald 1989, pp. 50–51, 63–65, 103–104.
- ^ Buchwald & Fox 2013, pp. 448–449.
- ^ Buchwald 1989, pp. 203, 205.
- ^ a b Darrigol 2012, p. 206.
- ^ Silliman 1967, pp. 203–205.
- ^ Arago & Fresnel, 1819.
- ^ a b Darrigol 2012, p. 207.
- ^ Frankel 1976, pp. 163–164, 182.
- ^ Frankel 1976, p. 164.
- ^ Buchwald 1989, p. 386.
- ^ Buchwald 1989, pp. 216, 384.
- ^ Buchwald 1989, pp. 333–336.
- ^ Darrigol 2012, pp. 207–208. (Darrigol gives the date as 1817, but the page numbers in his footnote 95 fit his reference "1818b", not "1817".)
- ^ Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, pp. 533–537. On the provenance of the note, see p. 523. In the above text, φ is an abbreviation for Fresnel's 2π(e − o), where e and o are the numbers of cycles taken by the extraordinary and ordinary waves to travel through the lamina.
- ^ Buchwald 1989, p. 97.
- ^ Frankel 1976, p. 148.
- ^ Fresnel, 1821b.
- ^ Fresnel, 1821b, §3.
- ^ Fresnel, 1821b, §1 & footnotes.
- ^ Buchwald 1989, pp. 237–251.
- ^ Frankel 1976, pp. 165–168.
- ^ Darrigol 2012, pp. 208–209.
- ^ a b c Fresnel, 1821a, §10.
- ^ Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, p. 394n.
- ^ Silliman 1967, pp. 209–210.
- ^ Buchwald 1989, pp. 205–206, 208, 212, 218–219.
- ^ Young 1855, p. 383.
- ^ a b T. Young, "Chromatics" (written Sep.– Oct. 1817), Supplement to the Fourth, Fifth, and Sixth Editions of the Encyclopædia Britannica, vol. 3 (issued February 1818), reprinted in Young 1855, pp. 279–342.
- ^ Buchwald 1989, pp. 225–226.
- ^ Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, pp. 526–527, 529.
- ^ Buchwald 1989, p. 226.
- ^ Fresnel, 1821a.
- ^ Buchwald 1989, p. 227.
- ^ Fresnel, 1821a, §1.
- ^ Buchwald 1989, p. 212.
- ^ Fresnel, 1821a, §10; emphasis added.
- ^ Fresnel, 1821a, §13; cf. Buchwald 1989, p. 228
- ^ Cf. Buchwald 1989, p. 230.
- ^ "This hypothesis of Mr. Fresnel is at least very ingenious, and may lead us to some satisfactory computations: but it is attended by one circumstance which is perfectly appalling in its consequences. The substances on which Mr. Savart made his experiments were solids only; and it is only to solids that such a lateral resistance has ever been attributed: so that if we adopted the distinctions laid down by the reviver of the undulatory system himself, in his Lectures, it might be inferred that the luminiferous ether, pervading all space, and penetrating almost all substances, is not only highly elastic, but absolutely solid!!!" — Thomas Young (written January 1823), Sect. XIII in "Refraction, double, and polarisation of light", Supplement to the Fourth, Fifth, and Sixth Editions of the Encyclopædia Britannica, vol. 6 (1824), at p. 862, reprinted in Young 1855, p. 415 (italics and exclamation marks in the original). The "Lectures" that Young quotes next are his own (Young, 1807, vol. 1, p. 627).
- ^ Buchwald 1989, pp. 388–390.
- ^ Fresnel, 1821a, §18.
- ^ Buchwald 1989, pp. 390–391.
- ^ Fresnel, 1821a, §§ 20–22.
- ^ a b A. Fresnel, "Mémoire sur la loi des modifications que la réflexion imprime à la lumière polarisée" ("Memoir on the law of the modifications that reflection impresses on polarized light"), read 7 January 1823; reprinted in Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, pp. 767–799 (full text, published 1831), pp. 753–762 (extract, published 1823). See especially pp. 773 (sine law), 757 (tangent law), 760–761 and 792–796 (angles of total internal reflection for given phase differences).
- ^ Buchwald 1989, pp. 391–393.
- ^ Whittaker 1910, pp. 133–135.
- ^ Whittaker 1910, p. 134.
- ^ Darrigol 2012, p. 213.
- ^ Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, pp. 773,757.
- ^ Buchwald 1989, pp. 393–394.
- ^ Whittaker 1910, pp. 135–136.
- ^ Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, pp. 760–761, 792–796.
- ^ Whittaker 1910, pp. 177–179.
- ^ Buchwald & Fox 2013, p. 467.
- ^ a b A. Fresnel, "Mémoire sur la double réfraction que les rayons lumineux éprouvent en traversant les aiguilles de cristal de roche suivant les directions parallèles à l'axe" ("Memoir on the double refraction that light rays undergo in traversing the needles of rock crystal [quartz] in directions parallel to the axis"), read 9 December 1822; printed in Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, pp. 731–751 (full text), pp. 719–29 (extract, first published in Bulletin de la Société philomathique for 1822, pp. 191–198).
- ^ Buchwald 1989, pp. 230–232, 442.
- ^ Cf. Buchwald 1989, p. 232.
- ^ Item re Brewster, "On a new species of moveable polarization", [Quarterly] Journal of Science and the Arts, vol. 2, no. 3, 1817, p. 213.
- ^ Lloyd 1834, p. 368.
- ^ A. Fresnel, "Mémoire sur les modifications que la réflexion imprime à la lumière polarisée" ("Memoir on the modifications that reflection impresses on polarized light"), signed & submitted 10 November 1817, read 24 November 1817; printed in Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, pp. 441–485, including pp. 452 (rediscovery of depolarization by total internal reflection), 455 (two reflections, "coupled prisms", "parallelepiped in glass"), 467–8 (phase difference per reflection); see also p. 487, note 1 (date of reading). Kipnis (1991, p. 217n) confirms the reading and adds that the paper was published in 1821.
- ^ Buchwald 1989, pp. 223, 336; on the latter page, a "prism" means a Fresnel rhomb or equivalent. A footnote in the 1817 memoir (Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, p. 460, note 2) described the emulator more briefly, and not in a self-contained manner.
- ^ Fresnel, 1818a, especially pp. 47–49.
- ^ Jenkins & White 1976, pp. 576–579, (§ 27.9, esp. Fig. 27M).
- ^ For illustrations see J.M. Derochette, "Conoscopy of biaxial minerals (1)", www.jm-derochette.be, 2004; archived 1 May 2017.
- ^ Buchwald 1989, pp. 254–255, 402.
- ^ Cf. Buchwald 1989, p. 269.
- ^ Grattan-Guinness 1990, p. 885.
- ^ Buchwald 1989, pp. 269, 418.
- ^ J.-B. Biot, "Mémoire sur les lois générales de la double réfraction et de la polarisation, dans les corps régulièrement cristallisés" (read 29 March 1819), Mémoires de l'Académie Royale des Sciences ..., vol. III (for 1818 [sic], printed 1820), pp. 177–384; "Extrait d'un Mémoire sur les lois de la double réfraction et de la polarisation dans les corps régulièrement cristallisés", Bulletin des Sciences par la Société Philomathique de Paris, 1820, pp. 12–16, including pp. 13–14 (sine law), 15–16 (dihedral law).
- ^ Cf. Fresnel, 1822a, tr. Young, in Quarterly Journal of Science, Literature, and Art, Jul–Dec 1828, at pp. 178–179.
- ^ Buchwald 1989, p. 260.
- ^ Printed in Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 2, pp. 261–308.
- ^ Silliman 1967, pp. 243–246 (first experiment); Buchwald 1989, pp. 261–267 (both experiments). The first experiment was briefly reported earlier in Fresnel, 1821c.
- ^ Buchwald (1989, pp. 267–272) and Grattan-Guinness (1990, pp. 893–894) call it the "ellipsoid of elasticity".
- ^ Buchwald 1989, pp. 267–272.
- ^ Grattan-Guinness 1990, pp. 885–887.
- ^ Buchwald 1989, pp. 274–279.
- ^ Buchwald 1989, pp. 279–280.
- ^ Literally "surface of the wave"—as in Hobson's translation of Fresnel 1827.
- ^ Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 2, pp. 340, 361–363.
- ^ Buchwald 1989, pp. 281–283.
- ^ The derivation of the "wave surface" from its tangent planes was eventually accomplished by Ampère in 1828 (Lloyd 1834, pp. 386–387; Darrigol 2012, p. 218; Buchwald 1989, pp. 281, 457).
- ^ Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 2, pp. 369–442.
- ^ Buchwald 1989, pp. 283–285.
- ^ Darrigol 2012, pp. 217–218.
- ^ Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 2, pp. 386–388.
- ^ W.N. Griffin, The Theory of Double Refraction, Cambridge: T. Stevenson, 1842.
- ^ Grattan-Guinness 1990, pp. 891–892.
- ^ Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 2, pp. 371–379.
- ^ Buchwald 1989, pp. 285–286.
- ^ Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 2, p. 396.
- ^ Lunney, James G.; Weaire, Denis (1 May 2006). "The ins and outs of conical refraction". Europhysics News. 37 (3): 26–29. Bibcode:2006ENews..37c..26L. doi:10.1051/epn:2006305. ISSN 0531-7479.
- ^ Grattan-Guinness 1990, pp. 896–897.
- ^ Silliman 1967, pp. 262–263.
- ^ Silliman 2008, p. 170.
- ^ Buchwald 1989, pp. 286–287, 447.
- ^ Fresnel, 1827.
- ^ Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 2, p. 800n. Although the original publication (Fresnel, 1827) shows the year "1824" in selected page footers, it is known that Fresnel, slowed down by illness, did not finish the memoir until 1826 (Buchwald 1989, pp. 289, 447, citing Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 2, p. 776n).
- ^ Fresnel, 1827, tr. Hobson, pp. 266–273.
- ^ Fresnel, 1827, tr. Hobson, pp. 281–285.
- ^ Fresnel, 1827, tr. Hobson, pp. 320–322.
- ^ Buchwald 1989, p. 447.
- ^ Grattan-Guinness 1990, pp. 1003–1009, 1034–1040, 1043. Grattan-Guinness offers evidence against any earlier dating of Cauchy's theories.
- ^ Whittaker 1910, pp. 143–145.
- ^ Darrigol 2012, p. 228.
- ^ Whittaker 1910, chapter V.
- ^ Darrigol 2012, ch. 6.
- ^ Buchwald & Fox 2013, pp. 460–464.
- ^ Fresnel, 1827, tr. Hobson, pp. 273–281.
- ^ Silliman 1967, p. 268n.
- ^ a b Buchwald 1989, p. 288.
- ^ Brewster, David (31 December 1815). "V. On the effects of simple pressure in producing that species of crystallization which forms two oppositely polarised images, and exhibits the complementary colours by polarised light". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. 105: 60–64. doi:10.1098/rstl.1815.0006. ISSN 0261-0523. JSTOR 107358.
- ^ Brewster, David (31 December 1816). "X. On the communication of the structure of doubly refracting crystals to glass, muriate of soda, fluor spar, and other substances, by mechanical compression and dilatation". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. 106: 156–178. doi:10.1098/rstl.1816.0011. ISSN 0261-0523. JSTOR 107522.
- ^ A. Fresnel, "Note sur la double réfraction du verre comprimé" ("Note on the double refraction of compressed glass"), read 16 September 1822, published 1822; reprinted in Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, pp. 713–718, at pp. 715–717.
- ^ Whewell 1857, pp. 355–356.
- ^ Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, pp. 737–739 (§4). Cf. Whewell 1857, pp. 356–358; Jenkins & White 1976, pp. 589–590.
- ^ Fresnel, 1822a.
- ^ Grattan-Guinness 1990, p. 884.
- ^ Cf. Frankel 1976, p. 169
- ^ Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 2, pp. 261n,369n.
- ^ Printed in Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 2, pp. 459–464.
- ^ Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, pp. lxxxvi–lxxxvii.
- ^ Grattan-Guinness 1990, p. 896.
- ^ Grattan-Guinness 1990, p. 898.
- ^ Buchwald 1989, pp. 289–390.
- ^ Frankel 1976, pp. 170–171.
- ^ cf. Fresnel, 1827, tr. Hobson, pp. 243–244, 262.
- ^ Silliman 1967, pp. 284–285, citing Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, p. lxxxix, note 2. Frankel (1976, p. 173) agrees. Worrall (1989, p. 140) is skeptical.
- ^ Frankel 1976, pp. 173–174.
- ^ J.F.W. Herschel, "Light", Encyclopædia Metropolitana, vol. 4 (London, 1845; re-issued 1849), pp. 341–586; reprinted (with original page numbers and appended plates) in J.F.W. Herschel, Treatises on Physical Astronomy, Light and Sound, contributed to the Encyclopædia Metropolitana, London and Glasgow: R. Griffin & Co. (undated).
- ^ Buchwald 1989, pp. 291–296.
- ^ Darrigol 2012, pp. 220–221, 303.
- ^ Fresnel, 1822a
- ^ Kipnis 1991, pp. 227–228.
- ^ Buchwald 1989, p. 296.
- ^ G.B. Airy, "On the diffraction of an object-glass with circular aperture", Transactions of the Cambridge Philosophical Society, vol. V, part III (1835), pp. 283–291 (read 24 November 1834).
- ^ Darrigol 2012, pp. 222–223, 248.
- ^ Kipnis 1991, pp. 225, 227.
- ^ Darrigol 2012, pp. 223, 245.
- ^ Whewell 1857, pp. 340–341; the quoted paragraphs date from the 1st Ed. (1837).
- ^ Whewell 1857, pp. 482–483.
- ^ Whittaker 1910, p. 136.
- ^ Darrigol 2012, p. 223.
Sources
General and cited references
- D.F.J. Arago (tr. B. Powell), 1857, "Fresnel" (elegy read at the Public Meeting of the Academy of Sciences, 26 July 1830), in D.F.J. Arago (tr. W.H. Smyth, B. Powell, and R. Grant), Biographies of Distinguished Scientific Men (single-volume edition), London: Longman, Brown, Green, Longmans, & Roberts, 1857, pp. 399–471. (On the translator's identity, see pp. 425n,452n.) Erratum: In the translator's note on p. 413, a plane tangent to the outer sphere at point t should intersect the refractive surface (assumed flat); then, through that intersection, tangent planes should be drawn to the inner sphere and spheroid (cf. Mach, 1926, p. 263).
- D.F.J. Arago and A. Fresnel, 1819, "Mémoire sur l'action que les rayons de lumière polarisée exercent les uns sur les autres", Annales de Chimie et de Physique, Ser. 2, vol. 10, pp. 288–305, March 1819; reprinted in Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, pp. 509–522; translated as "On the action of rays of polarized light upon each other", in Crew 1900, pp. 145–155
- Boutry, G.-A. (October 1948), "Augustin Fresnel: His time, life and work, 1788–1827", Science Progress, 36 (144): 587–604, JSTOR 43413515
- Buchwald, J.Z. (1989), The Rise of the Wave Theory of Light: Optical Theory and Experiment in the Early Nineteenth Century, University of Chicago Press, ISBN 0-226-07886-8
- Buchwald, J.Z.; Fox, R., eds. (2013), "Optics in the Nineteenth Century", The Oxford Handbook of the History of Physics, Oxford, pp. 445–472, ISBN 978-0-19-969625-3
- Crew, H., ed. (1900), The Wave Theory of Light: Memoirs by Huygens, Young and Fresnel, American Book Company
- Darrigol, O. (2012), A History of Optics: From Greek Antiquity to the Nineteenth Century, Oxford, ISBN 978-0-19-964437-7
- Elton, J. (July 2009), "A Light to Lighten our Darkness: Lighthouse Optics and the Later Development of Fresnel's Revolutionary Refracting Lens 1780–1900", International Journal for the History of Engineering & Technology, 79 (2): 183–244, doi:10.1179/175812109X449612
- Frankel, E. (September 1974), The search for a corpuscular theory of double refraction: Malus, Laplace and the price [sic] competition of 1808, vol. 18, Centaurus, pp. 223–245
- Frankel, E. (May 1976), "Corpuscular optics and the wave theory of light: The science and politics of a revolution in physics", Social Studies of Science, 6 (2): 141–184, JSTOR 284930
- A. Fresnel, 1815a, Letter to Jean François "Léonor" Mérimée, 10 February 1815 (Smithsonian Dibner Library, MSS 546A), printed in G. Magalhães, "Remarks on a new autograph letter from Augustin Fresnel: Light aberration and wave theory", Science in Context, vol. 19, no. 2 (June 2006), pp. 295–307, doi:10.1017/S0269889706000895, at p. 306 (original French) and p. 307 (English translation)
- A. Fresnel, 1816, "Mémoire sur la diffraction de la lumière" ("Memoir on the diffraction of light"), Annales de Chimie et de Physique, Ser. 2, vol. 1, pp. 239–281 (March 1816); reprinted as "Deuxième Mémoire ..." ("Second Memoir ...") in Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, pp. 89–122. Not to be confused with the later "prize memoir" (Fresnel, 1818b)
- A. Fresnel, 1818a, "Mémoire sur les couleurs développées dans les fluides homogènes par la lumière polarisée", read 30 March 1818 (according to Kipnis, 1991, p. 217), published 1846; reprinted in Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, pp. 655–683; translated by E. Ronalds & H. Lloyd as "Memoir upon the colours produced in homogeneous fluids by polarized light", in Taylor, 1852, pp. 44–65 (Cited page numbers refer to the translation.)
- A. Fresnel, 1818b, "Mémoire sur la diffraction de la lumière" ("Memoir on the diffraction of light"), deposited 29 July 1818, "crowned" 15 March 1819, published (with appended notes) in Mémoires de l'Académie Royale des Sciences de l'Institut de France, vol. V (for 1821 & 1822, printed 1826), pp. 339–475; reprinted (with notes) in Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, pp. 247–383; partly translated as "Fresnel's prize memoir on the diffraction of light", in Crew 1900, pp. 81–144. Not to be confused with the earlier memoir with the same French title (Fresnel, 1816)
- A. Fresnel, 1818c, "Lettre de M. Fresnel à M. Arago sur l'influence du mouvement terrestre dans quelques phénomènes d'optique", Annales de Chimie et de Physique, Ser. 2, vol. 9, pp. 57–66 & plate after p. 111 (Sep. 1818), & pp. 286–287 (Nov. 1818); reprinted in Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 2, pp. 627–636; translated as "Letter from Augustin Fresnel to François Arago, on the influence of the movement of the earth on some phenomena of optics" in K.F. Schaffner, Nineteenth-Century Aether Theories, Pergamon, 1972 (doi:10.1016/C2013-0-02335-3), pp. 125–135; also translated (with several errors) by R.R. Traill as "Letter from Augustin Fresnel to François Arago concerning the influence of terrestrial movement on several optical phenomena", General Science Journal, 23 January 2006 (PDF, 8 pp.)
- A. Fresnel, 1821a, "Note sur le calcul des teintes que la polarisation développe dans les lames cristallisées" et seq., Annales de Chimie et de Physique, Ser. 2, vol. 17, pp. 102–111 (May 1821), 167–196 (June 1821), 312–315 ("Postscript", July 1821); reprinted (with added section nos.) in Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, pp. 609–648; translated as "On the calculation of the tints that polarization develops in crystalline plates, & postscript", Zenodo: 4058004 / doi:10.5281/zenodo.4058004, 2021
- A. Fresnel, 1821b, "Note sur les remarques de M. Biot ...", Annales de Chimie et de Physique, Ser. 2, vol. 17, pp. 393–403 (August 1821); reprinted (with added section nos.) in Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 1, pp. 601–608; translated as "Note on the remarks of Mr. Biot relating to colors of thin plates", Zenodo: 4541332 / doi:10.5281/zenodo.4541332, 2021
- A. Fresnel, 1821c, Letter to D.F.J. Arago, 21 September 1821, in Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 2, pp. 257–259; translated as "Letter to Arago on biaxial birefringence", Wikisource, April 2021
- A. Fresnel, 1822a, De la Lumière (On Light), in J. Riffault (ed.), Supplément à la traduction française de la cinquième édition du "Système de Chimie" par Th. Thomson, Paris: Chez Méquignon-Marvis, 1822, pp. 1–137, 535–539; reprinted in Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 2, pp. 3–146; translated by T. Young as "Elementary view of the undulatory theory of light", Quarterly Journal of Science, Literature, and Art, vol. 22 (Jan.– Jun. 1827), pp. 127–141, 441–454; vol. 23 (Jul.– Dec. 1827), pp. 113–35, 431–448; vol. 24 (Jan.– Jun. 1828), pp. 198–215; vol. 25 (Jul.– Dec. 1828), pp. 168–191, 389–407; vol. 26 (Jan.– Jun. 1829), pp. 159–165.
- A. Fresnel, 1822b, "Mémoire sur un nouveau système d'éclairage des phares", read 29 July 1822; reprinted in Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 3, pp. 97–126; translated by T. Tag as "Memoir upon a new system of lighthouse illumination", U.S. Lighthouse Society, accessed 26 August 2017; 19 August 2016 (Cited page numbers refer to the translation.)
- A. Fresnel, 1827, "Mémoire sur la double réfraction", Mémoires de l'Académie Royale des Sciences de l'Institut de France, vol. VII (for 1824, printed 1827), pp. 45–176; reprinted as "Second mémoire ..." in Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 2, pp. 479–596; translated by A.W. Hobson as "Memoir on double refraction", in Taylor, 1852, pp. 238–333. (Cited page numbers refer to the translation. For notable errata in the original edition, and consequently in the translation, see Fresnel, 1866–70, vol. 2, p. 596n.)
- A. Fresnel (ed. H. de Sénarmont, E. Verdet, and L. Fresnel), 1866–70, Oeuvres complètes d'Augustin Fresnel (3 volumes), Paris: Imprimerie Impériale; vol. 1 (1866), vol. 2 (1868), vol. 3 (1870)
- Grattan-Guinness, I. (1990), Convolutions in French Mathematics, 1800–1840, vol. 2, Basel: Birkhäuser, chapter 13 (pp. 852–915, "The entry of Fresnel: Physical optics, 1815–1824") and chapter 15 (pp. 968–1045, "The entry of Navier and the triumph of Cauchy: Elasticity theory, 1819–1830"), ISBN 3-7643-2238-1
- C. Huygens, 1690, Traité de la Lumière (Leiden: Van der Aa), translated by S.P. Thompson as Treatise on Light, University of Chicago Press, 1912; Project Gutenberg, 2005. (Cited page numbers match the 1912 edition and the Gutenberg HTML edition.)
- Jenkins, F.A.; White, H.E. (1976), Fundamentals of Optics (4th ed.), New York: McGraw-Hill, ISBN 0-07-032330-5
- Kipnis, N. (1991), History of the Principle of Interference of Light, Basel: Birkhäuser, chapters VII, VIII, ISBN 978-3-0348-9717-4
- Kneller, K.A. (1911), Christianity and the Leaders of Modern Science: A contribution to the history of culture in the nineteenth century, translated by Kettle, T.M., Freiburg im Breisgau: B. Herder, pp. 146–149
- Levitt, T.H. (2009), The Shadow of Enlightenment: Optical and Political Transparency in France, 1789–1848, Oxford, ISBN 978-0-19-954470-7
- Levitt, T.H. (2013), A Short Bright Flash: Augustin Fresnel and the Birth of the Modern Lighthouse, New York: W.W. Norton, ISBN 978-0-393-35089-0
- Lloyd, H. (1834), "Report on the progress and present state of physical optics", Report of the Fourth Meeting of the British Association for the Advancement of Science, no. 4, London: J. Murray, pp. 295–413
- Mach, E. (1926), The Principles of Physical Optics: An Historical and Philosophical Treatment, translated by Anderson, J.S.; Young, A.F.A., London: Methuen & Co.
- I. Newton, 1730, Opticks: or, a Treatise of the Reflections, Refractions, Inflections, and Colours of Light, 4th Ed. (London: William Innys, 1730; Project Gutenberg, 2010); republished with foreword by A. Einstein and Introduction by E.T. Whittaker (London: George Bell & Sons, 1931); reprinted with additional Preface by I.B. Cohen and Analytical Table of Contents by D.H.D. Roller, Mineola, NY: Dover, 1952, 1979 (with revised preface), 2012 (Cited page numbers match the Gutenberg HTML edition and the Dover editions.)
- Silliman, R.H. (1967), Augustin Fresnel (1788–1827) and the Establishment of the Wave Theory of Light (PhD dissertation; submitted 1967, accepted 1968), Princeton University; available from ProQuest (missing the first page of the preface)
- Silliman, R.H. (2008), "Fresnel, Augustin Jean", Complete Dictionary of Scientific Biography, vol. 5, Detroit: Charles Scribner's Sons, pp. 165–171 (The version at encyclopedia.com lacks the diagram and equations.)
- Taylor, R., ed. (1852), Scientific Memoirs, selected from the Transactions of Foreign Academies of Science and Learned Societies, and from Foreign Journals (in English), vol. V, London: Taylor & Francis
- Whewell, W. (1857), History of the Inductive Sciences: From the Earliest to the Present Time, vol. 2 (3rd ed.), London: J.W. Parker & Son, book IX, chapters V–XIII
- Whittaker, E.T. (1910), A History of the Theories of Aether and Electricity, London: Longmans, Green, & Co., chapters IV, V
- Worrall, J. (1989), Gooding, D.; Pinch, T.; Schaffer, S. (eds.), "Fresnel, Poisson and the white spot: The role of successful predictions in the acceptance of scientific theories" (PDF), The Uses of Experiment: Studies in the Natural Sciences, Cambridge University Press, pp. 135–157, ISBN 0-521-33185-4, archived from the original (PDF) on 2023-06-02
- T. Young, 1807, A Course of Lectures on Natural Philosophy and the Mechanical Arts (2 volumes), London: J. Johnson; vol. 1, vol. 2
- Young, T. (1855), Peacock, G. (ed.), Miscellaneous Works of the late Thomas Young, vol. 1, London: J. Murray