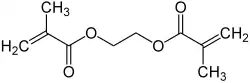
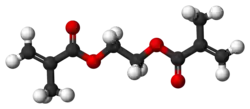
Ethylene glycol dimethacrylate
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Ethane-1,2-diyl bis(2-methylprop-2-enoate) | |
| Other names
Methacrylic acid, ethylene ester; 1,2-Bis(methacryloyloxy)ethane; 1,2-Ethanediol dimethacrylate; Diglycol dimethacrylate; Ethanediol dimethacrylate; Ethylene dimethacrylate; Ethylene glycol bis(methacrylate); Ethylene glycol dimethacrylate; Ethylene methacrylate; 2-(Methacryloyloxy)ethyl methacrylate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | EGDMA |
| 1776663 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.380 |
| EC Number |
|
| 637376 | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H14O4 | |
| Molar mass | 198.218 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.051 g/mL |
| Melting point | −40 °C (−40 °F; 233 K) |
| Boiling point | 98 to 100 °C (208 to 212 °F; 371 to 373 K) (5 mmHg) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H315, H317, H319, H335, H412 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P272, P273, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P332+P313, P333+P313, P337+P313, P362, P363, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
| Flash point | 101 °C (214 °F; 374 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
Ethylene glycol dimethylacrylate (EGDMA) is a diester formed by condensation of two equivalents of methacrylic acid with ethylene glycol. It is a colorless viscous liquid.[2] It is sometimes called ethylene dimethacrylate.[3]
Polymerization
Containing a pair of reactive alkene groups, EGDMA is a crosslinking agent. Like other acrylates, it is susceptible free radical polymerization. When used with methyl methacrylate, it leads to gel point at relatively low concentrations because of the nearly equivalent reactivities of all the double bonds involved. As a monomer, It is used to prepare hydroxyapatite/poly methyl methacrylate composites.
Preparation
EGDMA is also synthesized by esterification of methacrylic acid with ethylene glycol:
- 2 H2C=C(CH3)CO2H + HOCH2CH2OH → H2C=C(CH3)CO2CH2CH2O2C(CH3)C=CH2 + 2 H2O
It also forms inadvertently in the hydroxyethylation of methacrylic acid, which is usually intended to give (hydroxyethyl)methacrylate:
- 2 H2C=C(CH3)CO2H + CH2CH2O → H2C=C(CH3)CO2CH2CH2O2C(CH3)C=CH2 + H2O
Safety
Its toxicity profile has been fairly well studied.[4]
References
- ^ "Ethylene glycol dimethacrylate". Sigma-Aldrich.
- ^ Bielstein 2, IV, 1532
- ^ PubChem. "Ethylene glycol dimethacrylate". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2023-03-16.
- ^ Bielecka-Kowalska, Anna; Czarny, Piotr; Wigner, Paulina; Synowiec, Ewelina; Kowalski, Bartosz; Szwed, Marzena; Krupa, Renata; Toma, Monika; Drzewiecka, Malgorzata; Majsterek, Ireneusz; Szemraj, Janusz; Sliwinski, Tomasz; Kowalski, Michał (March 2018). "Ethylene glycol dimethacrylate and diethylene glycol dimethacrylate exhibits cytotoxic and genotoxic effect on human gingival fibroblasts via induction of reactive oxygen species". Toxicology in Vitro. 47: 8–17. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2017.10.028.