Entomophaga (fungus)
| Entomophaga | |
|---|---|
| |
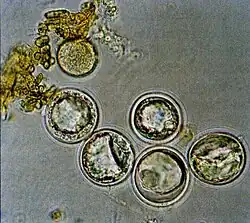
| Entomophaga maimaiga azygospores | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Division: | Entomophthoromycota |
| Class: | Entomophthoromycetes |
| Order: | Entomophthorales |
| Family: | Entomophthoraceae |
| Genus: | A. Batko, 1964 [1] |
Entomophaga is a genus of entomopathogenic fungi in the Entomophthoraceae family and also the order Entomophthorales.[2] This has been supported by molecular phylogenetic analysis (Gryganskyi et al. 2012).[3]
Well-known species are Entomophaga grylli and Entomophaga maimaiga, which can infect grasshoppers and gypsy moths respectively.
The genus name of Entomophaga was derived from combining two words in the Greek: entomon meaning insect and phaga meaning to eat. The genus was created in 1964 by the Polish mycologist Andrzej Batko (1933 - 1997). He wrote “... to commemorate the international journal Entomophaga devoted to problems of biological control of insect pests.”[1] The journal later ceased publication in 1998 and was replaced by BioControl.
Species
As accepted by Species Fungorum;[4]
- Entomophaga antochae S. Keller, 2007
- Entomophaga apiculata (Thaxt.) S. Keller, 1991
- Entomophaga aulicae (E. Reichardt) Humber, 1984
- Entomophaga batkoi (Balazy) S. Keller, 1988
- Entomophaga bukidnonensis Villac. & Wilding, 1994
- Entomophaga calopteni (Bessey) Humber, 1989
- Entomophaga caroliniana (Thaxt.) Samson, H.C. Evans & Latgé, 1988
- Entomophaga conglomerata (Sorokin) S. Keller, 1988
- Entomophaga destruens (Weiser & A. Batko) A. Batko, 1964
- Entomophaga diprionis Balazy, 1993
- Entomophaga domestica S. Keller, 1988
- Entomophaga gigantea (S. Keller) S. Keller, 1988
- Entomophaga grylli (Fresen.) A. Batko, 1964
- Entomophaga kansana (J.A. Hutchison) A. Batko, 1964
- Entomophaga lagriae Balazy, 1993
- Entomophaga limoniae S. Keller, 1988
- Entomophaga maimaiga Humber, Shimazu & R.S. Soper, 1988
- Entomophaga major (Thaxt.) S. Keller, 1991
- Entomophaga obscura (I.M. Hall & P.H. Dunn) A. Batko, 1964
- Entomophaga papillata (Thaxt.) S. Keller, 1988
- Entomophaga ptychopterae (S. Keller & Eilenberg) A.E. Hajek & Eilenberg, 2003
- Entomophaga pyriformis Balazy, 1993
- Entomophaga saccharina (Giard) A. Batko, 1964
- Entomophaga tabanivora (J.F. Anderson & Magnar.) Humber, 1984
- Entomophaga tenthredinis (Fresen.]]) A. Batko, 1964
- Entomophaga thaxteriana A. Batko, 1964
- Entomophaga thuricensis S. Keller, 2007
- Entomophaga tipulae (Fresen.) Humber, 1989
- Entomophaga transitans (S. Keller) A.E. Hajek & Eilenberg, 2003
References
- ^ a b Batko, A. 1964. Bull. Acad. Pol. Sci., Série des sciences biologiques 12, 323-326
- ^ Elya, Carolyn; De Fine Licht, Henrik H. (12 November 2021). "The genus Entomophthora: bringing the insect destroyers into the twenty-first century &". IMA Fungus. 12 (34).
- ^ Gryganskyi AP, Humber RA, Smith ME et al (2012) Molecular phylogeny of the Entomophthoromycota. Mol Phylogenet Evol 65:682–694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2012.07.026
- ^ "Entomophaga - Search Page". www.speciesfungorum.org. Species Fungorum. Retrieved 31 December 2022.