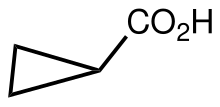
Cyclopropane carboxylic acid
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 969839 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.015.602 |
| EC Number |
|
| 2246 | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H6O2 | |
| Molar mass | 86.090 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless oil |
| Density | 1.0829 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 18.5 °C (65.3 °F; 291.6 K) |
| Boiling point | 76 °C (169 °F; 349 K) 12 Torr |
| Hazards | |
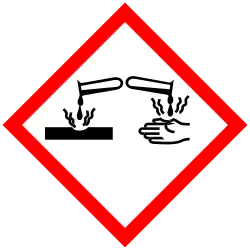
| GHS labelling:[1] | |
| |
| Danger | |
| H302, H314 | |
| P260, P264, P264+P265, P270, P280, P301+P317, P301+P330+P331, P302+P361+P354, P304+P340, P305+P354+P338, P316, P317, P321, P330, P363, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
Cyclopropane carboxylic acid is the organic compound with the formula C3H5CO2H. It is the carboxylic acid derivative of cyclopropane. It can be prepared by hydrolysis of cyanocyclopropane, which is obtained by base-induced cyclization of 4-chlorobutyronitrile.[1]
Reactions
Cyclopropane carboxylic acid has al pKa of 4.65, fairly typical for similar compounds.[2] Esterification is conveniently done with Lewis acid catalysts.[3]
The compound has been used to probe the biosynthesis of ethylene.[4]
References
- ^ Chester M. McCloskey, George H. Coleman (1944). "Cyclopropanecarboxylic Acid". Organic Syntheses. 24: 36. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.024.0036.
- ^ Wiberg, Kenneth B.; Ross, Brenda S.; Isbell, John J.; McMurdie, Neil (1993). "2-Substituted Bicyclo[1.1.1]pentanes". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 58 (6): 1372–1376. doi:10.1021/jo00058a015.
- ^ Ishihara, Kazuaki; Nakayama, Masaya; Ohara, Suguru; Yamamoto, Hisashi (2002). "Direct Ester Condensation from a 1:1 Mixture of Carboxylic Acids and Alcohols Catalyzed by Hafnium(IV) or Zirconium(IV) Salts". Tetrahedron. 58 (41): 8179–8188. doi:10.1016/s0040-4020(02)00966-3.
- ^ Tian, Qiu-Ying; Sun, Pei; Zhang, Wen-Hao (2009). "Ethylene is Involved in Nitrate-Dependent Root Growth and Branching in Arabidopsis thaliana". New Phytologist. 184 (4): 918–931. Bibcode:2009NewPh.184..918T. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.03004.x. PMID 19732351.