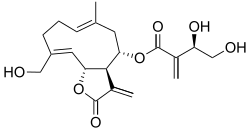
Cnicin
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(3aR,4S,6E,10Z,11aR)-10-(Hydroxymethyl)-6-methyl-3-methylidene-2-oxo-2,3,3a,4,5,8,9,11a-octahydrocyclodeca[b]furan-4-yl (3R)-3,4-dihydroxy-2-methylidenebutanoate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.042.004 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H26O7 | |
| Molar mass | 378.421 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
Cnicin is a sesquiterpene lactone, esterified with a substituted acrylic acid, and belonging to the germacranolide class of natural products. It is mainly found in Cnicus (Centaurea--formerly Cnicus--benedictus L. (Asteraceae)), and is present in spotted knapweed plants, where highest and lowest concentrations are found in the leaves (0.86-3.86% cnicin) and stems respectively.[1][2] Cnicin is used as a bitter tonic and the bitterness value is approximately 1,500.
References
- ^ Olson, B. E.; Kelsey, R. G. (1997). "Effect of Centaurea maculosa on sheep rumen microbial activity and mass in vitro". J. Chem. Ecol. 23 (4): 1131–1144. doi:10.1023/B:JOEC.0000006391.88098.12. S2CID 12499959.
- ^ Providing Supplement, with or without PEG, to reduce the effects of cnicin and enhance grazing of spotted knapweed by sheep and cattle, Masters Thesis, M Cheeseman, Montana State University
External links
 Media related to Cnicin at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Cnicin at Wikimedia Commons