Climate finance in Brazil

Climate finance in Brazil drives the transition to a low-carbon economy, as well as climate change adaptation and mitigation.[2][3][4] The country receives resources from various sources, such as international, development institutions, and the private sector.[2]
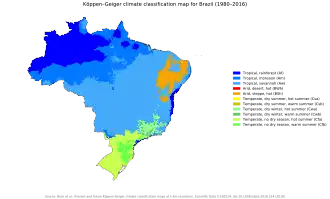
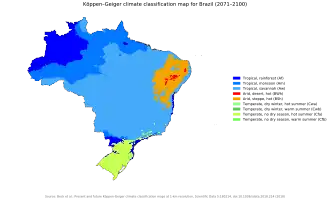
Brazil occupies a large portion of the South American continent and is considered a megadiverse country, with species spread across six terrestrial biomes and three marine ecosystems.[5] The country faces increasing climate impacts, such as severe droughts, floods, and forest fires. These changes strongly affect agribusiness and the most vulnerable population, increasing social and economic challenges. Greenhouse gas emissions in the country come primarily from land use (about 44% from forest burning) and agriculture.[6]
Recent extreme events demonstrate Brazil's exposure: for example, official studies recorded that approximately 295,000 people were displaced by climate disasters in 2019.[7] In light of this, the federal government has elevated the environmental agenda, recognizing sustainability as a national development priority and seeking to integrate climate goals into the economy.[8] Sustainable use, therefore, is critical for future generations in Brazil. The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP/UN) monitors biodiversity loss and supports initiatives that promote environmental conservation and the sustainable use of natural resources.[9]
Among the national challenges is the coordination of sectoral and financial policies across different levels of government. A recent study notes difficulties in coordinating actions under the new Climate Plan with other public investment programs, such as the Growth Acceleration Program (PAC), which follow disconnected sectoral visions. On the other hand, Brazil has the potential to attract resources because it is an emerging biodiverse economy rich in renewable energy.[10]
Definition
There is no definitive consensus on the definition of climate finance, but the term is widely used to designate financial resources mobilized by public and private actors, at the global and local levels, to support climate change mitigation and adaptation activities.[11] According to the UNFCCC, climate finance should be characterized by the nature of the activities financed—rather than by the providers, intermediaries, or financial instruments—focusing on adaptation and mitigation results.[12] The COP 15 (United Nations Climate Change Conference) in Copenhagen, in December 2009, established the political commitment to mobilize US$100 billion annually by 2020 for climate action in developing countries, enshrining the target in subsequent agreements.[13] At COP16 in Cancun in November 2010, it was decided to create the GCF as a multilateral fund to provide long-term financing for mitigation and adaptation projects, formalized in 2010 and operationalized from 2015.[14][12]
Brazilian context
Climate vulnerabilities
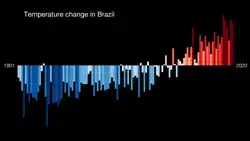
Brazil faces serious environmental challenges that justify dedicated climate financing. Torrential rains caused losses exceeding R$55.5 billion between 2017 and 2022, damaged more than 549,000 homes, and affected approximately 28.9 million people.[15] On the other hand, prolonged droughts and heat waves reduce agricultural and water productivity; it is estimated that between 2013 and 2022, Brazil lost US$19.5 billion in annual income due to excessive heat (6 billion hours of work lost per year).[16] These phenomena—which include episodes such as the April/May 2024 floods in the South and droughts in the Amazon —highlight the country's social and economic vulnerability to climate change. Studies by INPE and international agencies show that, without action, adverse weather can exacerbate inequalities and increase costs in sectors such as health and agriculture. Thus, climate finance is needed not only to cut emissions, but also to strengthen adaptation and reduce future economic impacts.[17][15]
Brazil occupies a large portion of the South American continent and is considered a megadiverse country, with species spread across six terrestrial biomes and three marine ecosystems.[5] However, the country faces increasing climate vulnerabilities, with studies indicating that up to 90% of Brazilian species could be negatively impacted by climate change, with about a quarter of them at potential risk of extinction.[18] Between 2020 and 2023, extreme weather events affected 32 million people and caused losses of 45.9 billion reais, highlighting the urgency of investments in adaptation.[19]
Brazil's energy matrix, with 83% renewable sources, represents a positive differential, but the energy sector still accounts for 18.22% of national greenhouse gas emissions. The country has set a national target of reducing emissions by 59% to 67% by 2035, compared to 2005 levels, seeking to contribute to the 1.5°C global warming limit established in the Paris Agreement.[20][21] The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP/UN) monitors biodiversity loss and supports initiatives that promote environmental conservation and the sustainable use of natural resources.[9]
Energy panorama
- Hydroelectricity (63.7%)
- Wind energy (9.20%)
- Biomass (9.00%)
- Natural gas (8.10%)
- Petroleum (5.40%)
- Coal (2.00%)
- Photovoltaics (1.30%)
- Nuclear energy (1.30%)
The Brazilian energy sector is one of the least carbon-intensive in the world, a direct result of the high share of renewable sources in the energy matrix and the historical dependence on hydropower.[22] It is estimated that approximately 45% of primary energy demand in Brazil is met by renewable sources.[23] Since 1990, electricity consumption has more than doubled, driven by economic growth and increased transportation demands.[24] Approximately 80% of the electricity generated in the country still comes from large hydroelectric plants.[25]
As a result of prolonged drought events, there was a strategic move towards diversification with investments in solar, wind, and bioenergy.[26] These investments are encouraged by a favorable regulatory environment, anchored in a national energy auction system, which drives private capital for generation and expansion of transmission infrastructure.[27] The auction policy helps to expand installed capacity and mitigate risks related to long-term energy security.[28]

Brazil is the main energy producer in Latin America and leads the region in energy exports, with a 1,579% growth in export volume between 2000 and 2023.[29] The majority of Brazil's total energy supply comes from oil (37%), followed by biofuels and waste (33%).[30] Domestic production is composed mainly of crude oil (49.7%), biofuels (29%), hydropower (10%), and natural gas (8.4%). Oil refining capacity has increased by 32% in recent decades, improving the production of derivatives.
Despite its large electricity production, the sector faces structural obstacles. Total electricity generation in Brazil reached 707,596 GWh in 2023.[31] The installed capacity of the electricity grid exceeds 150 GW, but it faces difficulties in accommodating renewable growth.[32]
To modernize the grid, approximately US$1.2 billion was allocated in 2024, with a projection of reaching US$4.2 billion by 2032. The sectors that consume the most electricity are transportation (37%), industry (34%), and residential use (12%). The average price of electricity increased from US$159.21 per MWh in 2022 to US$165.83 per MWh in 2023. On average, Brazilians spend about 4.5% of their annual income on electricity bills.[33] Among the factors driving up costs are water shortages and rising tariffs, which impact inflation.
History of climate finance
.jpg)
Climate finance in Brazil has been consolidated since the mid-2000s through various government initiatives and international partnerships. In 2008, the country proposed at COP13 and created the Amazon Fund, managed by BNDES, focused on REDD+ actions for forest protection.[34] The following year (Law 12.114/2009), the National Fund on Climate Change (Fundo Clima) was established, with resources for mitigation and adaptation projects.[35] In the agricultural sector, the Low Carbon Agriculture Program (Plano ABC), launched in 2010 by the Ministry of Agriculture, offered subsidized agricultural credit lines (2 billion reais at 5.5% per year in 2010/11) for sustainable technologies, although in the first year only 20% of these resources were used.[36]
In the 2010s, Brazil expanded the scope of climate finance with multilateral and private instruments. National companies began issuing green bonds to finance renewable energy and efficiency; for example, BRF launched the first Brazilian green bond in 2015.[37] Multilateral institutions financed key programs: in 2022, the Inter-American Development Bank (IDB) approved US$250 million (US$75 million of which came from the Green Climate Fund) for the BB Amazônia Program for a sustainable bioeconomy, implemented by Banco do Brasil.[38] In the same year, the World Bank allocated a US$500 million loan to Banco do Brasil for credit lines linked to emissions reductions.[39] At the federal level, in 2024 the Brazil Climate Investment Platform (BIP) was launched to coordinate strategic public and private projects in sectors such as bioeconomy, green industry and energy, with the support of BNDES and international partners (Bloomberg Philanthropies, GFANZ, GCF).[40]
Legal and institutional frameworks
.svg.png)
The national legal framework encompasses laws and agencies dedicated to climate change. Law No. 12,187/2009 established the National Policy on Climate Change (PNMC), and Law No. 12,114/2009 created the National Fund on Climate Change (FNMC).[41] Subsequent decrees, such as 7,343/2010, and government resolutions, such as CMN resolution 4,267/2013, regulate these instruments.[42] At the institutional level, the main climate governance body is the Interministerial Committee on Climate Change (CIM), chaired by the Civil House (with the MMA as executive secretary), reactivated in June 2023.[43] The Ministry of the Environment and Climate Change (MMA) coordinates federal policy, with support from the Ministry of Science and Technology (MCTI) in environmental monitoring and from other sectoral ministries. The FNMC, linked to the MMA, allocates accounting resources to mitigation and adaptation projects, applying reimbursable credits via BNDES and non-reimbursable credits via MMA.[42] Another relevant fund is the Amazon Fund, administered by BNDES, which raises international donations for conservation and sustainable use projects in the Legal Amazon.[44]
In 2024, the Brazilian Sustainable Taxonomy (TSB) was established by Decree 11.961/2024, creating the Interinstitutional Committee of the Brazilian Sustainable Taxonomy (CITSB), chaired by the Ministry of Finance. The TSB establishes specific criteria for classifying activities that contribute to climate, environmental, and social objectives.[45] The regulation of the TSB will be the responsibility of sectoral bodies such as the Central Bank (BCB), the Securities and Exchange Commission (CVM), and the Superintendence of Private Insurance (SUSEP). Since 2022, the Central Bank has implemented mandatory climate testing and ESG requirements for financial institutions.[46]
Financing
Public
.jpg)
The public sources of climate finance come from various national and subnational mechanisms. The National Fund on Climate Change (Fundo Clima ), created in 2009 and managed by BNDES under the coordination of the Ministry of the Environment, represents the main public climate finance instrument.[49][50] At the regional level, the constitutional funds of the North, Northeast, and Central-West (FNO, FNE, FCO) stand out, which reserved portions of their budgets for “green” or “low-emission” lines – for example, the FNO allocated approximately R$1.6 billion to low-carbon agriculture and forest restoration, and the FCO raised R$500 million through the “FCO Verde” line for sustainable projects.[10][42]
After a period of depletion during the Bolsonaro administration, when it had only 400 thousand reais in annual budget, the fund was reactivated in 2023 with 630 million reais and expanded to 10.4 billion reais in 2024.[50][51][52] Interest rates vary according to the type of project: 1% per year for forest restoration, 6.15% for general projects and 8% for solar and wind energy.[50]

The Amazon Fund, created in 2008 to receive international donations to combat deforestation, has raised 3.4 billion reais in donations in its history.[53] After four years of inactivity, the fund broke its fundraising record in 2023 with 726 million reais, diversifying its donor base to include the United Kingdom, the United States, Switzerland, the European Union and Denmark, in addition to the traditional Norway and Germany.[54]
BNDES, the main financier of renewable energy in the country, disbursed 133.8 billion reais between 2000 and 2020 for renewable projects.[55] Between 2015 and 2020, the bank supported 138 projects with an installed capacity of 10,260 MW, enough to supply 16.4 million homes and benefit 54 million people.[56]
The Alternative Energy Sources Incentive Program (PROINFA), created in 2002, offers long-term contracts for wind, solar, biomass, and small hydroelectric plants.[57] Beginning in the 1990s, the federal government began privatizing energy distribution companies in the country, with energy auctions, held since 2004, offering long-term contracts for renewable energy projects.[58][59]
Private
The private sector has a growing role in Brazilian climate finance. In recent years, companies and financial institutions have launched several green instruments. In 2024, for example, Brazil was the largest issuer of sustainable-labeled bonds in Latin America (approximately US$11 billion in total issuance), including corporate green bonds and thematic sovereign bonds (the second US$2 billion sovereign green bond was issued in 2023).[60]
.jpg)
Major Brazilian banks— Itaú, Bradesco, Banco do Brasil, and Santander —have developed green credit lines, sustainable bonds, and ESG funds.[62][63] In 2025, Itaú issued 1.4 billion reais in sustainable bonds, with 400 million reais earmarked specifically for biodiversity through the Reverte Program, which has already restored 239,000 hectares of degraded land.[64]
B3, one of the largest exchanges in Latin America, has created special designations for green bonds and green stocks.[65] Brazil leads green bond issuances in Latin America, moving US$7.2 billion in 2022.[66] The exchange has developed indices such as Ibovespa and IFIX, including companies in the renewable energy sector.
Foreign companies such as Enel, Iberdrola, Engie, and Equinor are investing significantly in solar and wind farms and green hydrogen projects.[67] Iberdrola announced investments of €47 billion between 2023 and 2025, with Brazil receiving 16% of the resources for grids (€ 4.3 billion) and 4% for renewables (€600 million).[68] Instruments such as incentivized debentures for sustainable projects, ESG investment funds, and corporate green bonds are mobilizing billions of reais in private resources. Furthermore, private development banks and multilateral agencies, in partnership with the sector, are mobilizing guarantees and financial arrangements, as is the case with the $500 million World Bank and Banco do Brasil project, which is expected to attract $1.4 billion.[39]
Channeling and monitoring mechanisms
In Brazil, public climate resources are channeled primarily through development banks and multilateral agencies. BNDES is the main intermediary, operating both non-refundable funds (Amazon Fund) and subsidized credit lines (Climate Fund, ABC Plan) for mitigation and adaptation projects.[34][36] Studies indicate that, between 2015 and 2020, BNDES approved an average of US$897 million per year in low-cost carbon credits, concentrated mainly in bioenergy and biofuels.[69] In 2019, the bank was authorized as a direct access agency to the Green Climate Fund (GCF), allowing it to access international resources (loans and grants) for national projects.[70] Banco do Brasil is also an important channel: it raised $175 million from the IDB itself and $75 million from the GCF for bioeconomy projects in the Amazon,[38] and implemented the World Bank 's large $500 million loan aimed at low-carbon credit. In parallel, regional banks (such as BNB and Caixa) and private institutions offer green lines and specific guarantees.[39]
These channels are complemented by direct multilateral support and the private market. Agencies such as the IDB, the World Bank, CAF, KfW, and the GCF itself offer co-financing lines and climate grants, while environmental foundations (e.g., Funbio) manage international resources for conservation. In the capital markets, Brazilian corporate issuers raised billions through thematic bonds: CPI estimates show that, from 2015 to 2020, an average of R$4 billion was raised annually in the land use sector through green bonds and environmental debentures.[69] This majority of the funding was obtained abroad—69% of these issuances are from Brazilian companies selling “ global notes ” abroad—according to industry reports.[37]
The monitoring and accountability mechanisms for these resources combine formal regulations and recent innovations. Funds like Amazônia have specific governance bodies: the Steering Committee involves representatives from the government, civil society, and experts, ensuring transparency in decisions. BNDES publishes public reports on all operations and conducts periodic external audits. Analysts note that the disclosure of projects financed by the Amazon Fund has become much more transparent over time.[71] At the federal level, Brazil submits biennial transparency reports to the UNFCCC that include emissions data and climate investments, but there is still no dedicated integrated national system to track all climate finance flows. Recent studies point to gaps in governance: the country's current structure is considered excessively centralized and fragmented, which hinders intersectoral coordination and visibility of climate investments.[72] To strengthen oversight, initiatives such as the BNDES-UNDP partnership to implement ClimateScanner (TCU/INTOSAI), a digital audit tool that standardizes climate policy indicators in Brazil and worldwide, are emerging.[73]
International cooperation
Brazil receives and participates in international financial cooperation at various levels. Under the Paris Agreement, the country mobilizes resources from funds such as the Green Climate Fund (GCF) and the Global Environment Facility (GEF) through national projects (e.g., the Floresta+ Amazônia program received US$96 million from the GCF to reduce forest emissions). Bilateral partnerships are also significant: Germany and Norway have historically donated to the Amazon Fund (essential for REDD+ actions ), and recently, Germany (R$88 million in 2024) and the European Union (€20 million in forest support) have increased investments in Amazon conservation.[74] Norway, the fund's largest donor, suspended R$133 million after governance disruptions in 2019 due to the environmental policies of the Jair Bolsonaro administration.[75] In addition, the World Bank has allocated carbon credits (500 million dollars in 2022) to expand sustainable financing in Brazil (via Banco do Brasil), mobilizing foreign and private investments.[39]
Brazil maintains strategic partnerships with the World Bank, the Inter-American Development Bank (IDB), and the Green Climate Fund.[76][77] In 2024, the government signed a memorandum of understanding with the World Bank for a possible allocation of US$1 billion to the Climate Fund, focusing on reforestation, green cities, and solid waste management.[77] Eco Invest Brasil, a program launched in 2024 with support from the IDB and the World Bank, aims to allocate 27 billion reais to private investments in sustainable transition projects, offering exchange rate protection to reduce risks associated with exchange rate volatility.[76]
The Brazil Climate Investment and Ecological Transformation Platform (BIP), launched in 2024, represents an innovative initiative to mobilize national and international capital. The platform, hosted by BNDES (Brazilian Development Bank) and the secretariat, seeks to connect the government's ecological transformation plans with investors, supporting three main sectors: nature-based solutions, renewable energy, and energy efficiency.[78]
Impacts and results
Climate finance efforts are already producing concrete results, although not always on a scale significant enough to meet global targets. In the Amazon, for example, there was a decline of approximately 50% in deforestation between 2022 and 2023, attributed in part to increased monitoring and projects financed by the Amazon Fund.[79] The Amazon Fund itself had approximately R$3.9 billion in international donations available in 2024 to support 114 restoration and deforestation prevention projects.[74]
In the energy sector, investments in renewable energy parks have helped increase the share of clean energy sources in the national electricity grid, making Brazil one of the countries with the least polluting grids, despite being one of the largest global energy consumers.[80] The 2022 joint project between the World Bank and Banco do Brasil expects to generate up to 90 million tons of CO₂ reductions by 2030, equivalent to approximately 4.5% of Brazil's carbon neutrality target.[39] Socially, forest management and climate infrastructure projects benefit rural and indigenous communities by generating green jobs and protecting environmental services (water, soil, biodiversity, etc.). However, the negative economic impacts of extreme events remain significant: recent floods affected 32 million people and destroyed 174,000 homes.[19]
Main sectors benefited


Several sectors are focusing on climate finance projects and investments. In renewable energy and the energy transition, solar, wind, and hybrid power plants stand out, financed both by the private sector and by Climate Fund lines that support energy efficiency and green hydrogen research. In adaptation and resilience, urban programs invest in drainage, sanitation, and urban reforestation, while BNDES resources have already been allocated to resilient infrastructure projects and critical coastal areas.[35]
In forest conservation and biodiversity (including REDD+), the Amazon Fund and similar mechanisms finance projects for managing conservation units, fighting fires, and restoring riparian forests.[74][44] The agricultural and food security sectors are also a focus: there are credit lines for low-carbon practices and efficient irrigation projects, aiming to increase productivity without expanding deforestation (it is estimated that two-thirds of the necessary climate investments should go to agriculture and energy).[81]
Sustainable mobility and green infrastructure support includes non-polluting public transportation, efficient lighting systems, and green highways, as provided for in financing lines targeted at low-emission urban mobility. Each of these sectors receives different shares of public and private resources, but they all share the goal of reducing emissions and increasing socio-environmental resilience.[35]
Challenges and perspectives
.jpg)
Several criticisms have focused on the governance and effectiveness of climate finance in Brazil. Reports have pointed out that, between 2019 and 2022, the Climate Fund financed virtually no new relevant projects—reserving only R$500,000 in 2021/22 (capable of funding one or two small initiatives)—and improperly channeling 84% of the limited resources available to a single project (the "Lixão Zero") without public bidding.[51] Internationally, there has been controversy surrounding the Amazon Fund: in 2019, Norway suspended transfers of approximately R$133 million after the Brazilian government unilaterally dissolved the fund's technical committees, alleging a breach of the governance agreement.[75]
For the near future, Brazil has proposed an ambitious resource mobilization agenda. As president of COP30, the country presented a "Baku-Belém Roadmap" in 2025, aiming to raise US$1.3 trillion by 2030 to finance the climate transition. This plan emphasizes the need to increase public financing and reform multilateral banks (World Bank, IMF) to increase lending capacity, as well as expand concessional lines focused on adaptation and compensation for climate losses and damages.[82] Also discussed are the creation of national hubs and platforms that connect Brazilian projects with international investors, and the adoption of financial regulations (carbon pricing, Central Bank climate supervision) to attract private capital. Experts highlight five priority areas: immediately eliminating illegal deforestation, formulating sectoral decarbonization strategies, creating transitional financial instruments, strengthening political support for sustainable agendas, and training the workforce for the green economy.[81]
At COP28, Brazil presented a new fund proposal, the Tropical Forests Forever Facility (TFFF). The project, which provides for US$125 billion in financing, is expected to be launched at COP30 in November 2025. Generally speaking, the TFFF would operate based on blended finance, where a smaller portion of the loan is lent by developed countries, which receive it back with interest, and the remainder, about 80%, would come from private investors.[83][84][85] Private investors could also profit by receiving a fixed rate of return, similar to Treasury bonds. Excess profits would be directed to countries based on their protected tropical forest areas, with penalties of US$400 for each hectare deforested in a one-year period.[83][84][85]
With investments in solutions that reduce the environmental impact of the transportation sector, Brazil could become one of the largest producers of biofuels by 2030. Brazil's prominence in this sector is mainly due to bioethanol, a fuel produced in the country from sugarcane or corn, in smaller quantities.[80]
See also
References
- ^ "What is the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change?". United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). Retrieved 2025-06-26.
- ^ a b "Overview of Climate Finance for Land Use in Brazil". Climate Policy Initiative (CPI). Retrieved 2025-05-08.
- ^ "World Bank and Banco do Brasil develop innovative climate finance solution". Banco do Brasil. Retrieved 2025-05-08.
- ^ "Climate finance: reality and challenges – OCBio" (PDF). Agro FGV. Retrieved 2025-05-08.
- ^ a b "Biodiversity and biomes". Ministry of the Environment and Climate Change (Brazil). Retrieved 2025-05-12.
- ^ Paulo Artaxo. "Economic and social impacts of climate change in Brazil". ClimaInfo Institute. Retrieved 2025-06-26.
- ^ Giovanna Bronze (2025-01-12). "Are heavier rains an effect of climate change? Understand". CNN Brazil. Retrieved 2025-06-26.
- ^ "Inequality and climate are crises that threaten the economy and social cohesion". United Nations Brazil. 2023-11-27. Retrieved 2025-06-26.
- ^ a b "UNEP: Brazil holds between 15% and 20% of the world's biological diversity". UN News. 2019-03-02. Retrieved 2025-05-12.
- ^ a b "The climate finance ecosystem in Brazil in 2024" (PDF). Talanoa Institute. 2024-08-28. Retrieved 2025-06-26.
- ^ "What's the role of climate finance and the finance sector for a transformation towards a sustainable future?" (PDF). Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Retrieved 2025-04-25.
- ^ a b "Top-down Climate Finance Needs". Climate Policy Initiative (CPI). Retrieved 2024-06-27.
- ^ "Climate Finance and the USD 100 billion goal". United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). Retrieved 2025-04-25.
- ^ "Cancun Agreements". United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). 2011. Retrieved 2025-04-25.
- ^ a b UOL (January 20, 2022). "Rains in Brazil caused losses of R$55.5 billion between 2017 and 2022, says CNM". Retrieved June 26, 2025.
- ^ LANCET COUNTDOWN LATIN AMERICA - CLIMATE CHANGE AND HEALTH DATA 2024 (PDF) (Report). The Lancet. 2024. Retrieved June 26, 2025.
- ^ "Brazil has 2,600 municipalities at risk of natural disasters". Deutsche Welle. June 11, 2025. Retrieved June 26, 2025.
- ^ Garcia, Rafael (April 8, 2025). "Climate crisis likely to affect more than 90% of Brazil's biodiversity, study finds". O Globo. Retrieved June 25, 2025.
- ^ a b Ramos, Marlen (January 30, 2025). "Climate events total losses of R$45.9 billion between 2020 and 2023 in Brazil". CNN Brasil. Retrieved June 25, 2025.
- ^ Fluza, Renan (November 9, 2024). "Climate Observatory criticizes target of reducing emissions by up to 67% by 2035". CNN Brasil. Retrieved June 25, 2025.
- ^ Prizibisczki, Cristiane (November 9, 2024). "New Brazilian emissions reduction target not aligned with 1.5°C". ((o))eco. Retrieved June 25, 2025.
- ^ World Energy Outlook 2023 (Report). International Energy Agency (IEA). 2023. Retrieved June 25, 2025.
- ^ Renewable Capacity Statistics 2023 (Report). International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA). 2023. Retrieved June 25, 2025.
- ^ World Energy Outlook 2023 (Report). International Energy Agency (IEA). 2023. Retrieved June 25, 2025.
- ^ Renewable Capacity Statistics 2023 (Report). International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA). 2023. Retrieved June 25, 2025.
- ^ Energy Transition Investment Trends 2023 (Report). BloombergNEF. 2023. Retrieved June 25, 2025.
- ^ "Auction System". ANEEL. 2023. Retrieved June 25, 2025.
- ^ "Auction System". ANEEL. 2023. Retrieved June 25, 2025.
- ^ Brazil (Report). International Energy Agency (IEA). 2023. Retrieved June 25, 2025.
- ^ World Energy Balances Overview (Report). International Energy Agency (IEA). 2023. Retrieved June 25, 2025.
- ^ "Generation Data". ANEEL. 2023. Retrieved June 25, 2025.
- ^ "Planning for the Expansion of the Electricity Sector". Brazilian Government Portal – Ministry of Mines and Energy. 2023. Retrieved June 25, 2025.
- ^ "Eg.Elc.Accs.Zs – Access to electricity (% of population)". World Bank – Data. 2023. Retrieved June 25, 2025.
- ^ a b Kadri, Nabil Moura; Skaf, Angela Albernaz; de Freitas, Marta Bandeira; Soeiro, Daniel Rossi; Anache, Bernardo; Budi, Janina; Hoeflinger, Tim (2020). "Fundo Amazônia: financing for conservation and sustainable development of the Amazon" (PDF). CEPAL. Retrieved June 27, 2025.
- ^ a b c "Fundo Clima (Climate Fund)". BNDES (ed.). Retrieved June 26, 2025.
- ^ a b "Low‑Carbon Agriculture: The Evolution of a New Paradigm" (PDF). Getúlio Vargas Foundation. Retrieved June 27, 2025.
- ^ a b Motoda, Érika (September 11, 2020). "Green bond moves US$8.1 billion in Brazil" (PDF). Estadão. Retrieved June 27, 2025.
- ^ a b "IDB approves financing to Banco do Brasil for bioeconomy and sustainable infrastructure in the Amazon". Inter-American Development Bank (IDB). June 18, 2025. Retrieved June 27, 2025.
- ^ a b c d e "World Bank and Banco do Brasil develop innovative climate finance solution". World Bank. December 22, 2022. Retrieved June 26, 2025.
- ^ "Federal Government presents Climate Investment and Ecological Transformation Platform". Agência Brasil. November 13, 2024. Retrieved June 27, 2025.
- ^ "National Fund on Climate Change". Government of Brazil. Retrieved June 26, 2025.
- ^ a b c "Climate Fund – Annual Report 2023". BNDES. Retrieved June 26, 2025.
- ^ "Climate Change Committee advances in the implementation of Brazilian climate policy". Agência Gov. June 29, 2024. Retrieved June 26, 2025.
- ^ a b "Amazon Fund". Amazon Fund. Retrieved June 26, 2025.
- ^ Barcellos, Thais (March 25, 2024). "What is sustainable taxonomy and why the government created a committee to discuss the issue". Planeta. Terra. Retrieved June 23, 2025.
- ^ Martins, Danylo (July 13, 2022). "Banks prepare for stricter ESG rules, including disclosure of climate risks". O Globo. Archived from the original on August 1, 2022. Retrieved June 23, 2025.
- ^ "Environment Conference: proposals benefit governments and the population, says Marina". Agência Gov. Retrieved July 6, 2025.
- ^ Ozório, Letícia (May 9, 2025). "National Environment Conference ends with 100 proposals to address the climate crisis". Exame. Retrieved July 6, 2025.
- ^ Rodrigues, Sabrina (27 June 2018). "BNDES financia projetos de restauração ecológica e economia florestal". ((o))eco. Retrieved 25 June 2025.
- ^ a b c Vilela, Pedro Rafael (1 April 2024). "Fundo Clima vai financiar projetos com juros de 1% a 8% ao ano". Agência Brasil. Retrieved 25 June 2025.
- ^ a b Pereira, José Alberto Gonçalves (26 April 2022). "Governo Bolsonaro esvazia cofres do Fundo Clima". ((o))eco. Retrieved 25 June 2025.
- ^ Mendes, Júlia (9 April 2025). "R$ 100 milhões são destinados a operação de reflorestamento na Amazônia". ((o))eco. Retrieved 25 June 2025.
- ^ Prizibisczki, Cristiane (1 February 2024). "Após quatro anos sem arrecadar, Fundo Amazônia tem recorde de doações em 2023". ((o))eco. Retrieved 25 June 2025.
- ^ Prizibisczki, Cristiane (23 July 2024). "União Europeia anuncia doação de R$ 120 milhões ao Fundo Amazônia". ((o))eco. Retrieved 25 June 2025.
- ^ Oliveira, Edenis Cesar (2017). "Investments in the Sugarcane-Energy Sector: Analysis of the Profile of Automatic Financing Operations Contracted with the BNDES System in the Period from 2000 to 2015". Journal of Administration of the Federal University of Santa Maria (in Brazilian Portuguese): 44–62. Retrieved 25 June 2025.
- ^ Kveller, Uriel Boianovsky (2023). "National Development Banks and contemporary missions: BNDES in the context of the climate emergency (2000–2022)". Retrieved 25 June 2025.
- ^ Torres Júnior, Paulo; Moreira, Carlos Américo Leire (2020). "The Renewable Energy Incentive Program in Brazil (PROINFA) and its relationship with sustainability: a study on Brazilian energy policy from a neoliberal, neo-extractivist perspective". Brazilian Journal of Development. 3: 15466–15478. doi:10.34117/bjdv6n3-427.
- ^ Rocha, Katia; Moreira, Ajax; Limp, Rodrigo (June 2013). "Determinants of high discounts in electricity transmission auctions in Brazil between 1999 and 2010". Brazilian Journal of Economics: 235–249. doi:10.1590/S0034-71402013000200005. ISSN 0034-7140.
- ^ Morais, Alexia Alves (2023). "An exploratory analysis on the application of Auction Theory in the Brazilian energy sector". doi:10.14393/ufu.di.2022.210. Retrieved 25 June 2025.
- ^ "Sustainable Bond Market Reaches New Records". Climate Bonds Initiative. 30 May 2025. Retrieved 27 May 2025.
- ^ "Converting pastures into crops has billion-dollar potential, says Itaú BBA". IstoÉ Dinheiro. 12 June 2025. Retrieved 6 July 2025.
- ^ Azevedo, Rosa Eunice Alves (30 June 2020). "Climate risks in the credit risk management of Brazilian banks". Retrieved 25 June 2025.
- ^ Friedrich, Eduardo Michael (2023). "Sustainability and corporations: an analysis of the Social, Environmental and Climate Responsibility Policies of large private banks". Retrieved 25 June 2025.
- ^ Folego, Thais (20 March 2025). "Itaú issues R$1.4 billion in sustainable bond – with an eye on biodiversity". Reset. Retrieved 25 June 2025.
- ^ Capirazi, Beatriz (16 October 2023). "'Regra frouxa' sobre ESG faz maioria das empresas listadas na B3 ter baixa transparência, diz estudo". Estadão (in Brazilian Portuguese). Retrieved 25 June 2025.
- ^ Hofmeister, Fernanda; Wenzel, Pedro; Papini, Naira (5 July 2020). "Stock market approval attracts million-dollar investments for companies at risk of deforestation". ((o))eco (in Brazilian Portuguese). Retrieved 25 June 2025.
- ^ Mauricio Junior, Roberto Donisete; Botelho, João Pedro Machado; Botelho, Matheus Machado; Pakes, Paulo Renato; Martins, Tailise Mascarenhas (11 March 2025). "O mercado de energia solar no Brasil: uma análise dos desafios e oportunidades do setor". Revista de Gestão e Secretariado (in Brazilian Portuguese). 16 (3): e4768. doi:10.7769/gesec.v16i3.4768. ISSN 2178-9010. Retrieved 25 June 2025.
- ^ Teixeira, Pedro Aurélio (18 November 2022). "Iberdrola anuncia investimento de € 47 bilhões até 2025". CanalEnergia (in Brazilian Portuguese). Retrieved 25 June 2025.
- ^ a b "Panorama de Financiamento Climático para Uso da Terra no Brasil – Mercado Financeiro" (in Brazilian Portuguese). Climate Policy Initiative. Retrieved 27 June 2025.
- ^ "Green Climate Fund accredits BNDES, enabling access to resources for climate change actions" (in Brazilian Portuguese). BNDES. 12 July 2019. Retrieved 27 June 2025.
- ^ Forstater, Maya; Nakhooda, Smita; Watson, Charlene (April 2013). "Understanding the effectiveness of climate finance: the Amazon Fund" (PDF) (in Brazilian Portuguese). Overseas Development Institute (ODI) and Department for International Development (DFID). Retrieved 27 June 2025.
- ^ "Study points to outdated and centralized climate governance in Brazil" (in Brazilian Portuguese). ClimaInfo. 22 April 2025. Retrieved 27 June 2025.
- ^ "BNDES will support tool to help oversight bodies monitor climate change actions" (in Brazilian Portuguese). BNDES. 6 May 2024. Retrieved 27 June 2025.
- ^ a b c "European Union and German government announce more resources for the Amazon Fund" (in Brazilian Portuguese). 23 July 2024. Retrieved 26 June 2025.
- ^ a b "Norway suspends transfers to the Amazon Fund" (in Brazilian Portuguese). UOL. 15 August 2019. Retrieved 26 June 2025.
- ^ a b Prizibisczki, Cristiane (26 February 2024). "With international support, Brazil intends to invest R$ 27 billion in the ecological transition" (in Brazilian Portuguese). ((o))eco. Retrieved 25 June 2025.
- ^ a b "World Bank Group and Brazil's Finance and Environment Ministries join forces to boost climate investments". World Bank. 26 February 2024. Retrieved 25 June 2025.
- ^ Schuck, Sofia (23 October 2024). "Brazil launches investment platform to accelerate green transition and seeks projects" (in Brazilian Portuguese). Exame. Retrieved 25 June 2025.
- ^ "German Minister for Economic Cooperation and Development travels to Brazil" (in Brazilian Portuguese). German Embassy in Brazil. 18 July 2024. Retrieved 26 June 2025.
- ^ a b Vega, Lina Patricia; Bautista, Karen Tatiana; Campos, Heliana; Daza, Sebastian; Vargas, Guillermo (1 June 2024). "Biofuel production in Latin America: A review for Argentina, Brazil, Mexico, Chile, Costa Rica and Colombia". Energy Reports. 30: 36. Bibcode:2024EnRep..11...28V. doi:10.1016/j.egyr.2023.10.060. ISSN 2352-4847.
- ^ a b "Brazil needs 1 trillion reais to achieve environmental goals" (in Brazilian Portuguese). BrasilAgro. 25 August 2023. Retrieved 26 June 2025.
- ^ Murad, Vinícius (19 June 2025). "In Germany, Brazil presents climate finance plan ahead of COP30" (in Brazilian Portuguese). CNN Brasil. Retrieved 26 June 2025.
- ^ a b Netto, Maria; Rizzo, Lucca; Ribeiro, João Felipe (2024). "The Brazilian G20 and the climate finance agenda: possible legacies for BRICS+ and COP30". CEBRI-Revista: Brazilian Journal of International Affairs (in Brazilian Portuguese). 12: 39–61. ISSN 2764-7897.
- ^ a b Andreoni, Manuela (3 October 2024). "An 'Elegant' Idea Could Pay Billions to Protect Trees". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 9 June 2025.
- ^ a b "In London, Brazil advances in building the Tropical Forests Forever Fund" (in Brazilian Portuguese). Ministério da Fazenda. 19 March 2025. Retrieved 9 June 2025.
Bibliography
- BHANDARY, Rishikesh Ram. The role of institutional design in mobilizing climate finance: empirical evidence from Bangladesh, Brazil, Ethiopia, and Indonesia. PLOS Climate, v.3, n.3, e0000246, 2024. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pclm.0000246. Available at: [1] (https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pclm.0000246 ). Accessed on: June 26, 2025.
- FLOSSMANN-KRAUS, Ursula. The Political Economy of Climate Finance in Brazil: how actors and their ideas shape institutions. Münster: LIT Verlag, 2023. Available at: [2] (https://ueaeprints.uea.ac.uk/id/eprint/82666/ ). Accessed on: June 26, 2025.
- LOPES, Ariane Cristina Cordeiro Gazzi; ALBUQUERQUE, Andrei Aparecido de. Climate finance: institutional effectiveness of the National Fund on Climate Change. Journal of Public Administration, Rio de Janeiro, v.57, n.3, p.1-13, 2023. DOI: 10.1590/0034-761220220318. Available at: [3] (https://doi.org/10.1590/0034-761220220318 ). Accessed on: June 26, 2025.
- MARCOVITCH, Jacques; PINSKY, Vanessa Cuzziol. Amazon Fund: financing deforestation avoidance. Journal of Administration (São Paulo), v.49, n.2, p.280-290, 2014. DOI: 10.5700/rausp1146. Available at: [4] (https://doi.org/10.5700/rausp1146 ). Accessed on: June 26, 2025.