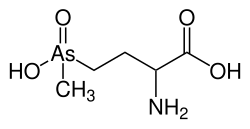
Arsinothricin
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Drug class | glutamine synthetase inhibitor |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| PDB ligand | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C5H12AsNO4 |
| Molar mass | 225.076 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Arsinothricin is a naturally occurring organoarsenical antibiotic produced by the rhizosphere bacterium Burkholderia gladioli.[1][2] Structurally, it is a non-proteinogenic amino acid analog of glutamate, in which the γ-carboxyl group is replaced by a methylarsenate moiety. Arsinothricin acts as a broad-spectrum antibiotic effective against a variety of bacterial pathogens, including multidrug-resistant species, through competitive inhibition of bacterial glutamine synthetase. Unlike many arsenic compounds that are highly toxic due to their trivalent state,[3] arsinothricin is unusual as a pentavalent arsenical, displaying antibiotic activity with a novel mechanism of action.[2][4]
References
- ^ Nadar VS, Chen J, Dheeman DS, Galván AE, Yoshinaga-Sakurai K, Kandavelu P, et al. (2019). "Arsinothricin, an arsenic-containing non-proteinogenic amino acid analog of glutamate, is a broad-spectrum antibiotic". Communications Biology. 2 131. doi:10.1038/s42003-019-0365-y. PMC 6465285. PMID 30993215.
- ^ a b Hoshino S, Onaka H, Abe I (April 2025). "Recent advances in the biosynthetic studies of bacterial organoarsenic natural products". Natural Product Reports. 42 (4): 663–671. doi:10.1039/d4np00036f. PMID 39192828.
- ^ Sattar A, Xie S, Hafeez MA, Wang X, Hussain HI, Iqbal Z, et al. (December 2016). "Metabolism and toxicity of arsenicals in mammals". Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology. 48: 214–224. Bibcode:2016EnvTP..48..214S. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2016.10.020. PMID 27829199.
- ^ Howlader AH, Suzol SH, Nadar VS, Galván AE, Nedovic A, Cudic P, et al. (October 2021). "Chemical synthesis of the organoarsenical antibiotic arsinothricin". RSC Advances. 11 (56): 35600–35606. Bibcode:2021RSCAd..1135600H. doi:10.1039/d1ra06770b. PMC 9043123. PMID 35493177.