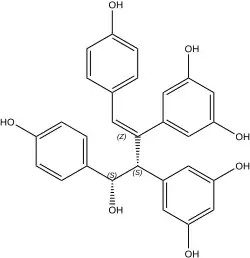
Amurensin A
Chemical structure of amurensin A
Names
IUPAC name
5,5'-((3S,4S,Z)-4-hydroxy-1,4-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)but-1-ene-2,3-diyl)bis(benzene-1,3-diol)
Identifiers
ChemSpider
UNII
InChI=1S/C28H24O7/c29-20-5-1-16(2-6-20)9-26(18-10-22(31)14-23(32)11-18)27(19-12-24(33)15-25(34)13-19)28(35)17-3-7-21(30)8-4-17/h1-15,27-35H/b26-9+/t27-,28+/m0/s1
Key: GCORPFHXPBERCR-WFRBMYQMSA-N
OC1=CC(/C([C@@H]([C@H](O)C2=CC=C(O)C=C2)C3=CC(O)=CC(O)=C3)=C\C4=CC=C(O)C=C4)=CC(O)=C1
Properties
C28 H24 O7
Molar mass
472.48 g/mol
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their
standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
Amurensin A is an oligostilbene isolated from the roots of Vitis amurensis [ 1] resveratrol dimer with a C8-C8' connection.[ 2]
References
^ Huang, K. S.; Lin, M. (1999). "Oligostilbenes from the Roots of Vitis amurensis ". Journal of Asian Natural Products Research . 2 (1): 21– 28. doi :10.1080/10286029908039886 . PMID 11261202 . ^ Natural stilbenes: an overview. Tao Shen, Xiao-Ning Wang and Hong-Xiang Lou, Nat. Prod. Rep., 2009, 26, pages 916-935, doi :10.1039/B905960A
Diptoindonesin C
Diptoindonesin F
Gnetin H
Hemsleyanol D
Isohopeaphenol
Laetevirenol A, B, C, D and E
Suffruticosol A and B
Viniferal E-ω-viniferin
Z-ω-viniferin Dimers
Diptoindonesin G
Jezonodione
B
Scirpusin A
Tibeticanol (piceatannol dimer) Trimers
Amurensin B
Gnetin E
Gneyulin A
Johorenol A
Ampelopsin E
Vaticanol G Tetramers:
Dibalanocarpol
Gnetin J (3"-hydroxygnetin E)
Gnetin K (3"-methoxygnetin E)
Gnetuhainin R (isorhapontigenin tetramer)
Laetevirenol F and G Higher polymers Oligomeric forms
Dimers Trimers Tetramers Pentamers Hexamers Higher polymers
γ-viniferin
Valeriaphenol A
Glycosides or conjugates
Diptoindonesin A (C-glucoside of ε-viniferin)Foeniculoside I (glucoside of miyabenol C), II, III and IVLaevifonol (an ε-viniferin-ascorbic acid hybrid compound)
Laevifoside (O-glucoside of ampelopsin A)