Achilleol A
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
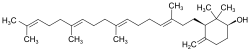
| IUPAC name
(1S,3R)-2,2-dimethyl-4-methylidene-3-[(3E,7E,11E)-3,8,12,16-tetramethylheptadeca-3,7,11,15-tetraenyl]cyclohexan-1-ol
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C30H50O | |
| Molar mass | 426.729 g·mol−1 |
| Density | g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 116 °C |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
Achilleol A is a monocyclic triterpene with the molecular formula C30H50O.[1]
Natural occurrence
The compound is found in such taxons as Achillea odorata,[2][3] Camellia oleifera, Santolina elegans, Triticum aestivum, among others.
Synthesis
There is a simple method for synthesizing the monocyclic triterpene achilleol A, employing titanium(III) chemistry as the crucial step. This synthesis validates the structure previously determined by spectroscopic analysis.[4]
References
- ^ Barrero, A.F.; Alvarez-Manzaneda, E.J.R.; Alvarez-Manzaneda r, R. (1989-01-01). "Achilleol A: A new monocyclic triterpene skeleton from Achillea odorata L.". Tetrahedron Letters. 30 (25): 3351–3352. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(00)99242-6. ISSN 0040-4039.
- ^ Daniel, M.; Mammen, Denni (1 June 2016). Analytical Methods for Medicinal Plants and Economic Botany. Scientific Publishers. p. 114. ISBN 978-93-87307-58-2. Retrieved 22 July 2025.
- ^ Keinan, Ehud (6 March 2006). Catalytic Antibodies. John Wiley & Sons. p. 201. ISBN 978-3-527-60505-7. Retrieved 22 July 2025.
- ^ Barrero, Alejandro F; Cuerva, Juan M; Alvarez-Manzaneda, E. J; Oltra, J. Enrique; Chahboun, Rachid (8 April 2002). "First synthesis of achilleol A using titanium(III) chemistry". Tetrahedron Letters. 43 (15): 2793–2796. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(02)00358-1. ISSN 0040-4039. Retrieved 22 July 2025.